Today’s machines contribute to progress but also emit harmful fossil fuel pollution, often called ‘The Silent Killer.’ This pollution, while not always noticeable daily, has severe long-term health effects, including respiratory and neurological issues. This article explores the hidden dangers of our atmosphere and the cost of our modern conveniences on our health.
Contents
Respiratory and Pulmonary Diseases

Exposure to fossil fuel pollution can lead to or exacerbate respiratory conditions. Pollutants such as sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) produced by burning fossil fuels can cause inflammation of the airways, leading to conditions like asthma and chronic bronchitis. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 90% of the world’s population breathes air that doesn’t meet their quality guidelines, leading to millions of deaths from diseases like COPD, lung infections, and more.
Cardiovascular Diseases

Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) from fossil fuel emissions can penetrate the cardiovascular system and increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes. The American Heart Association has linked long-term exposure to PM2.5 to cardiovascular mortality.
Cancer
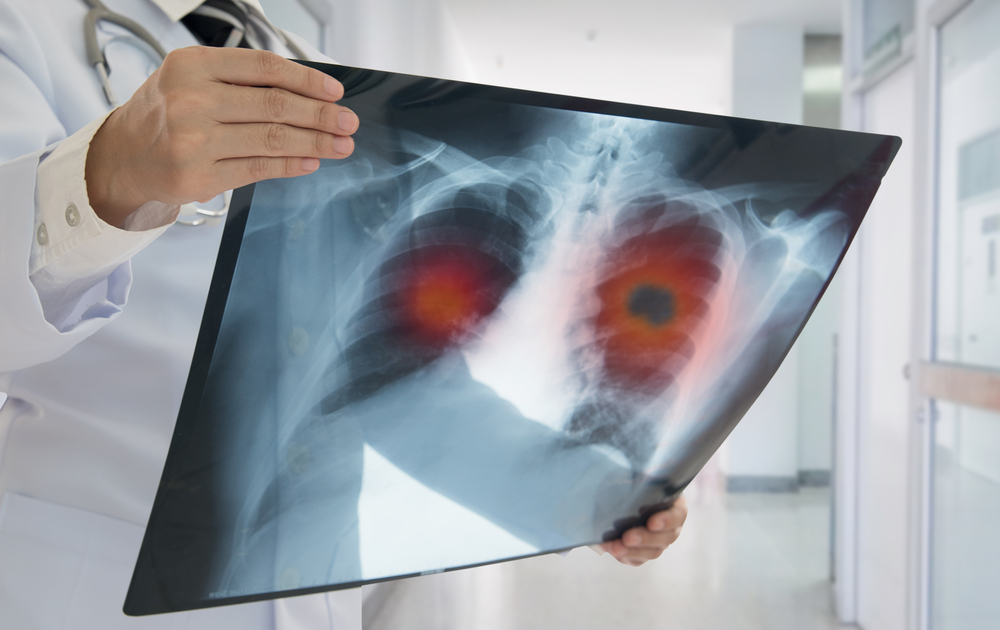
Prolonged exposure to certain components of fossil fuel pollution, notably polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), can increase the risk of developing cancers, especially lung cancer. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) classifies some PAHs as carcinogenic.
Neurological Diseases
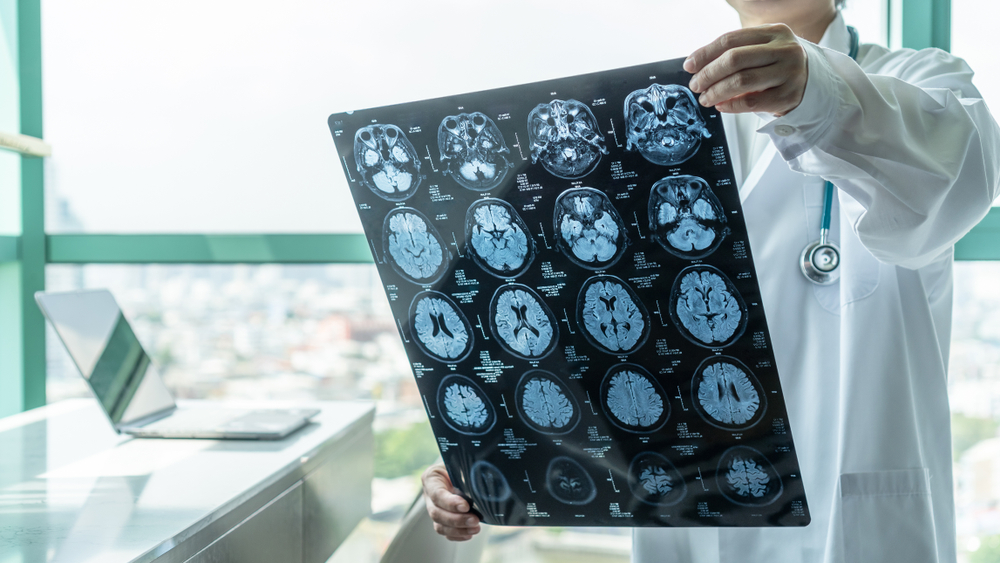
Emerging research suggests that air pollution from fossil fuels may contribute to neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and cognitive decline in children. Toxins in the air might affect the brain’s structure and neural pathways.
Premature Births

Pregnant women exposed to high levels of fossil fuel pollution can face a higher risk of premature births. A study in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives found an association between exposure to PM2.5 during pregnancy and preterm births.
Developmental Problems in Children

Children exposed to high levels of fossil fuel pollution can face developmental challenges. Evidence from the U.S. National Library of Medicine shows that early exposure to certain air pollutants can lead to reduced cognitive function and developmental delays.
Low Sperm Quality

Research, including studies published in journals such as Occupational & Environmental Medicine, has found links between exposure to fossil fuel pollutants and reduced sperm quality, which can lead to infertility in men.
Osteoporosis

Air pollution has been linked with the loss of bone mineral density. A study in The Lancet Planetary Health found that exposure to ambient air pollution, especially PM2.5, might be linked to osteoporosis-related bone fractures.
Mental Health Issues

While the relationship is complex, emerging evidence suggests that long-term exposure to polluted air can negatively impact mental health. Depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders can be exacerbated by prolonged exposure to poor air quality, as suggested in studies like those from Environmental Health Perspectives.
Eye Problems

Air pollution has been associated with various eye problems, including dry eye and cataracts. Fine particulate matter can irritate the eyes and lead to inflammatory reactions, as found in research presented in journals such as JAMA Ophthalmology.
Chronic Headaches

Exposure to high levels of air pollutants, particularly nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and sulfur dioxide (SO2), can trigger chronic headaches. Symptoms often include persistent, recurring headaches that do not easily respond to typical pain relievers. Prevention could involve minimizing exposure by using air purifiers and avoiding outdoor activities when pollution levels are high. Treatment often focuses on symptom management with pain relievers and lifestyle adjustments.
Skin Aging and Dermatological Issues

Pollutants like polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) can accelerate skin aging and contribute to dermatological conditions such as eczema and hives. Symptoms include premature wrinkles, dryness, and inflammatory skin conditions. Reducing exposure through protective skincare and indoor air purification can help, while treatments might include moisturizers and prescription topical creams.
Increased Risk of Diabetes
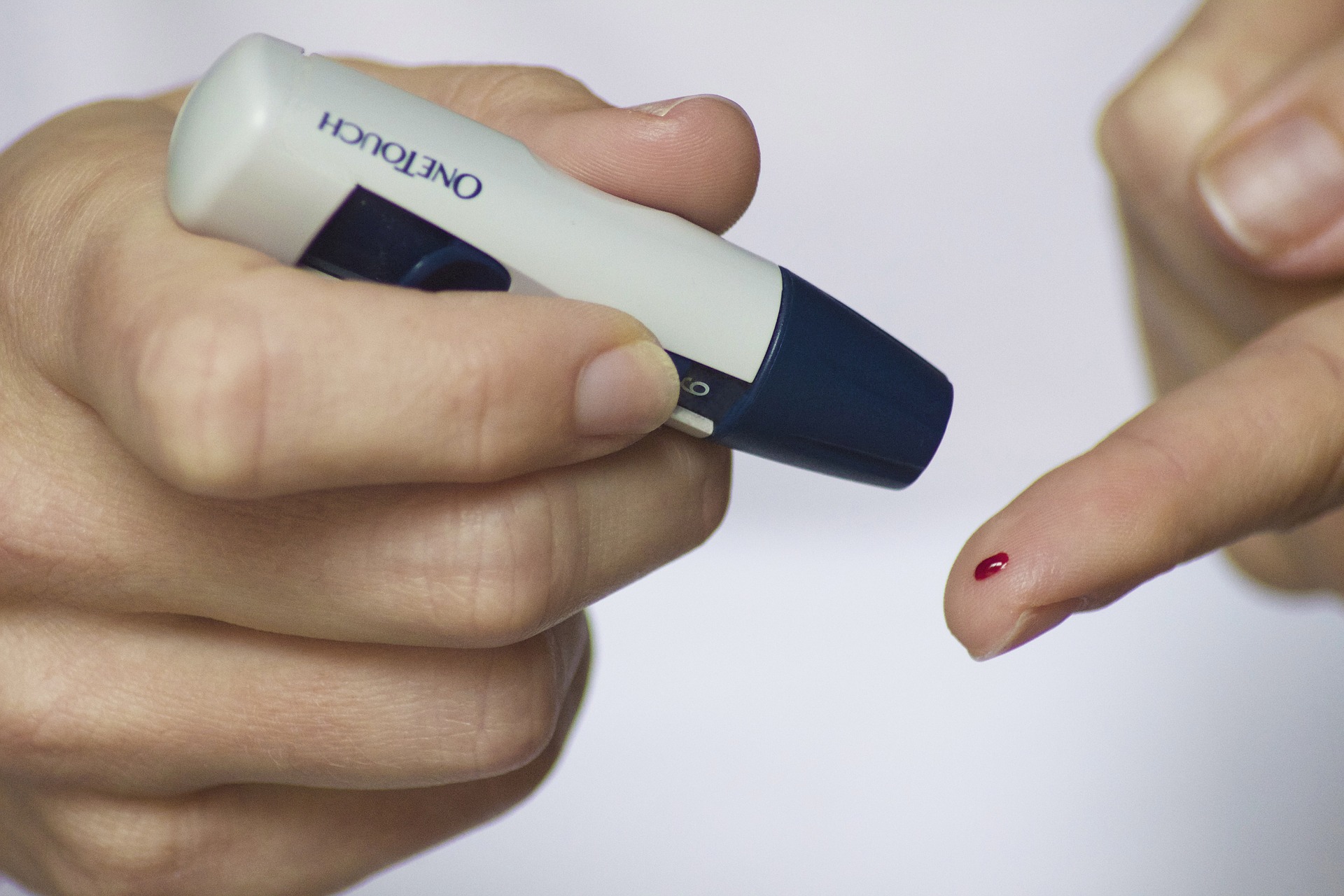
Emerging research suggests that chronic exposure to particulate matter (PM2.5) may increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes by inducing insulin resistance. Symptoms of diabetes include excessive thirst, frequent urination, and unexplained weight loss. Prevention focuses on maintaining a healthy lifestyle, whereas treatment involves managing blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and possibly medication.
Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
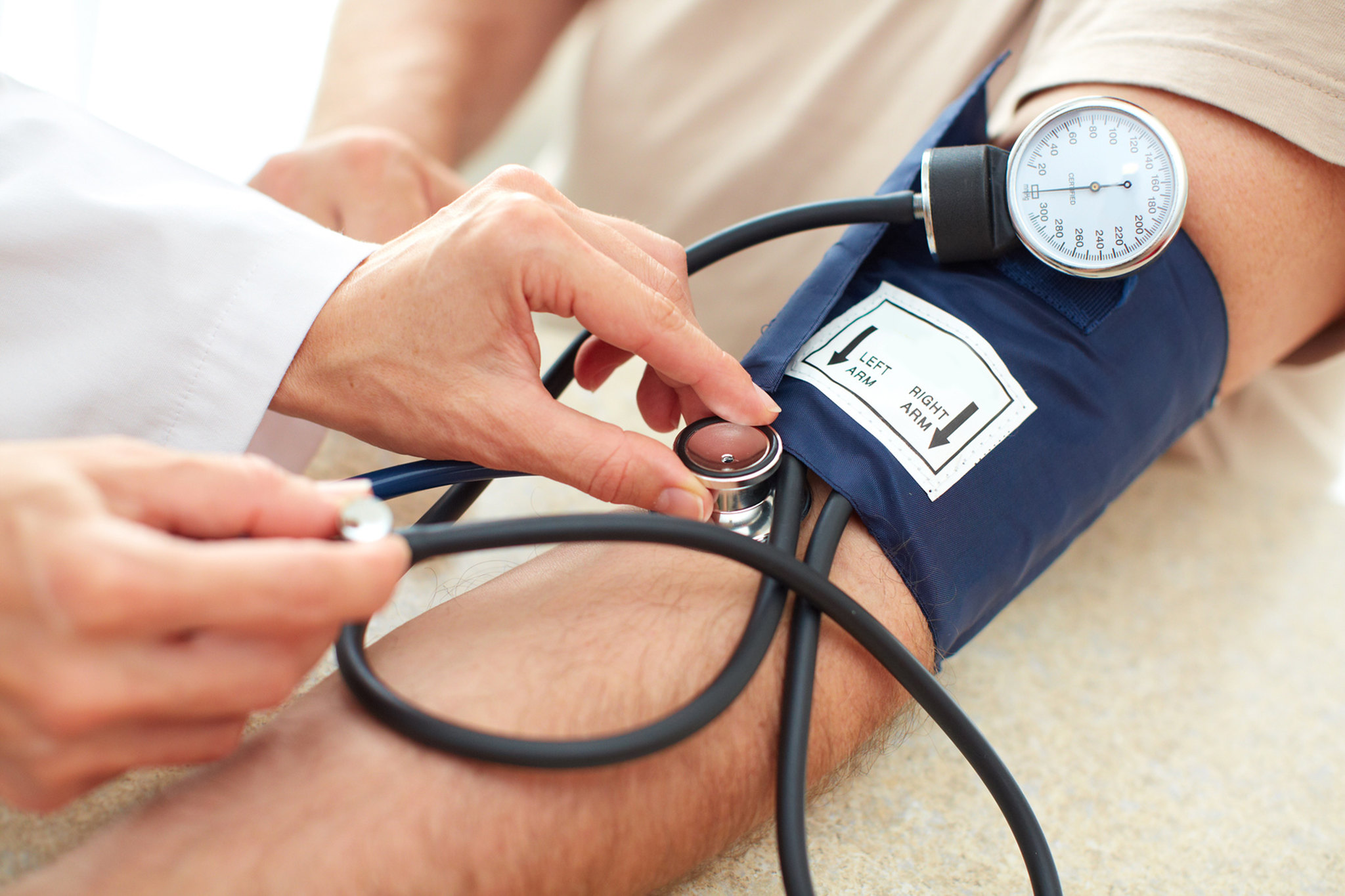
Long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution has been linked with elevated blood pressure levels, a risk factor for heart disease. Symptoms may be nonexistent initially but can escalate to headaches, shortness of breath, and nosebleeds. Monitoring air quality, regular exercise, and a healthy diet can help prevent hypertension, while treatment might include blood pressure medications.
Anxiety and Stress Disorders

Studies indicate that high levels of air pollution can also exacerbate anxiety and stress disorders. Symptoms include persistent feelings of worry, tension, and physical manifestations such as increased heart rate. Treatment involves psychological therapies and, in some cases, medications, while prevention might include stress management techniques and ensuring indoor environments have clean air.
Hearing Loss

Some studies have suggested a correlation between air pollution and increased risk of hearing loss, potentially due to toxins affecting nerve cells in the ears. Symptoms include difficulty hearing or constant ringing in the ears. Preventive measures include regular hearing check-ups and using personal protective equipment in high-noise environments. Treatment may involve hearing aids or other auditory devices.
Gastrointestinal Disorders

Exposure to certain air pollutants may lead to or worsen conditions such as gastritis or peptic ulcers. Symptoms often include stomach pain, nausea, and indigestion. Preventive strategies could include a diet high in antioxidants and low in processed foods, while treatments may involve medications to reduce stomach acid and soothe the gastrointestinal lining.
Fatigue

Chronic exposure to polluted air can lead to unexplained fatigue, as the body expends energy fighting off the effects of pollutants. Symptoms include constant tiredness, decreased energy levels, and a feeling of lethargy. Prevention involves maintaining a clean indoor environment and a healthy diet rich in vitamins. Treatment focuses on lifestyle changes such as improved sleep hygiene and increased physical activity.
Immune System Suppression
Long-term exposure to pollutants can weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections. Symptoms might include frequent sickness or prolonged recovery times. Preventative measures include enhancing indoor air quality and maintaining a balanced diet. Treatment generally focuses on boosting the immune system through supplements and healthy lifestyle choices.
Kidney Damage

Recent studies have linked air pollution, particularly fine particulate matter, to an increased risk of chronic kidney disease. Symptoms may include reduced kidney function without obvious signs until the condition is advanced. Prevention could involve regular screening for kidney function, especially in polluted areas, while treatment might include medications and dietary adjustments to manage kidney health.
This article originally appeared on MyCarMakesNoise.
More from MyCarMakesNoise
10 Unusual Road Rules You`ll Encounter Internationally

The world’s highways are littered with peculiar and often surprising regulations, from banned car colors to unusual restrictions on eating and drinking while driving. In this article, we’ll take you on a journey through the world’s weirdest car laws, revealing ten astonishing things you can’t do on the road. Read More.
13 Classic Sports Cars with Unbelievable Speed

From the roaring engines of American muscle cars to the sophisticated allure of European racers, these vehicles represented a Golden Age of Speed, setting benchmarks for performance that would influence generations of engineers and enthusiasts alike. Read More.
The Best Motorcycles for Long-Distance Travel

These road-ready warriors, equipped with the latest technologies and luxuries, are designed to devour mile after mile easily. Read More.














