Electric cars are often praised for their environmental benefits, but they also have a hidden environmental impact. From battery production to electricity generation, there are several ways electric cars contribute to air pollution. Here are some ways electric cars pollute the air, shedding light on the dark side of clean energy.
Contents
Battery Production Emissions
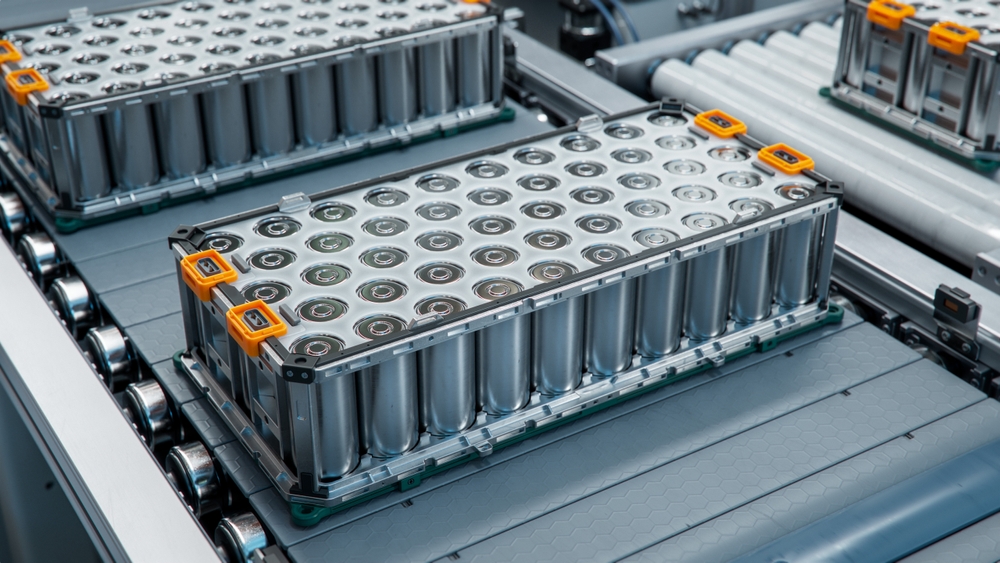
The production of lithium-ion batteries, which power electric cars, is energy-intensive and generates significant emissions. Mining and processing lithium, cobalt, and nickel require large amounts of energy, often sourced from fossil fuels. A study by the Swedish Environmental Research Institute found that producing a lithium-ion battery for an electric car can emit up to 17.5 tons of CO2, depending on the battery size.
Electricity Generation Emissions

Electric cars rely on electricity, which is often generated from fossil fuels like coal and natural gas. In many regions, a significant portion of electricity comes from these sources. According to the International Energy Agency, in 2020, 61.3% of global electricity was generated from fossil fuels. As a result, electric cars indirectly contribute to air pollution through the emissions produced during electricity generation.
Rare Earth Element Extraction
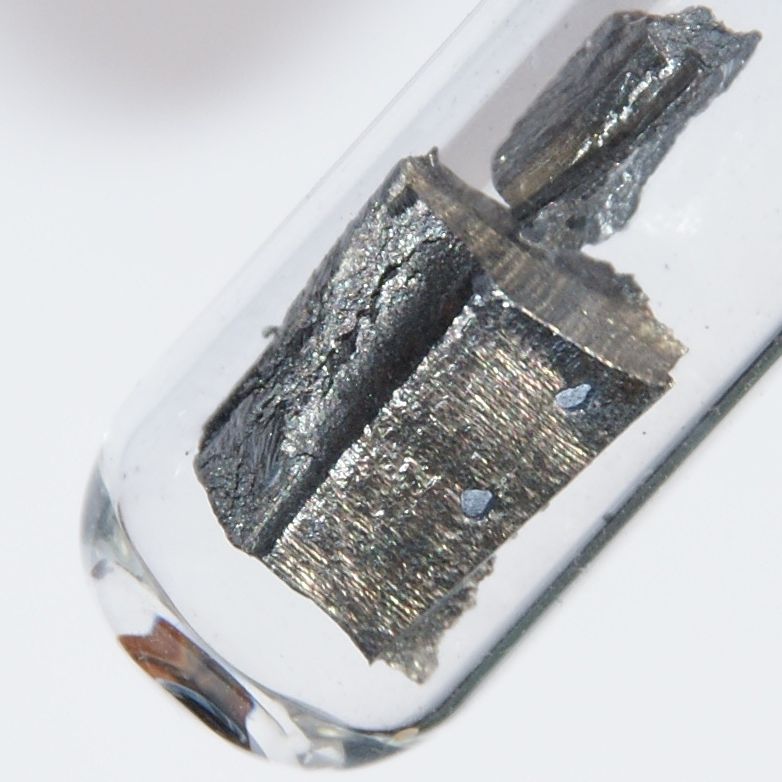
Electric cars use rare earth elements in their motors and batteries, including neodymium, dysprosium, and lithium. Extracting and processing these elements can release toxic chemicals and particulate matter into the air. For example, lithium extraction involves large quantities of water and chemicals, leading to emissions of sulfur dioxide and other pollutants.
Manufacturing Emissions

The overall manufacturing process of electric cars generates emissions. Producing the steel, aluminum, and plastics used in electric vehicles requires significant energy, often sourced from fossil fuels. A report by the Union of Concerned Scientists indicates that the production emissions of an electric car can be 15-68% higher than those of a conventional car due to the battery production.
Tire and Brake Wear
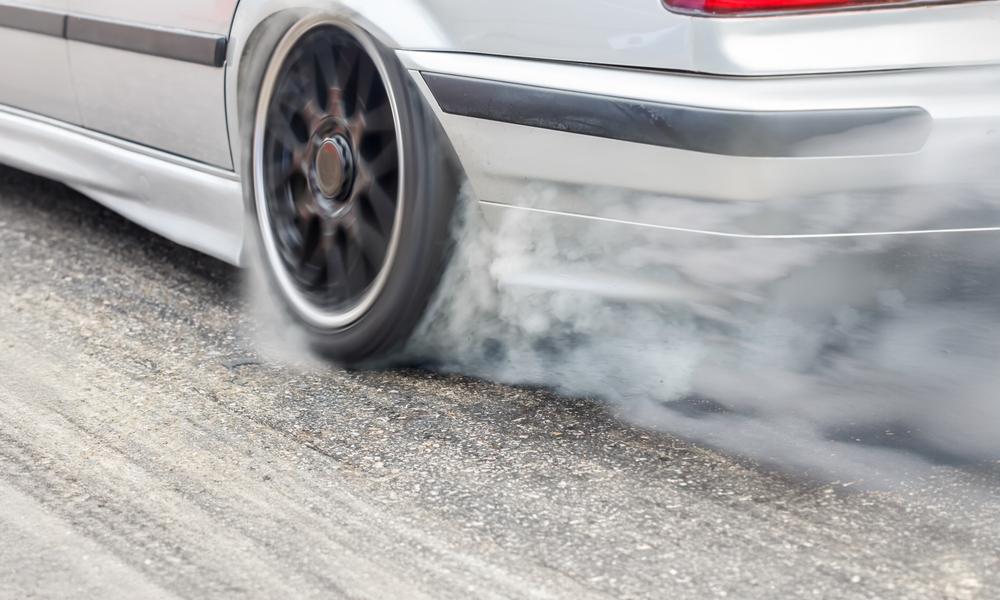

Electric cars, like all vehicles, contribute to air pollution through tire and brake wear. As tires and brakes wear down, they release particulate matter into the air. A study by the University of Birmingham found that non-exhaust emissions, including tire and brake wear, can account for up to 55% of total particulate emissions from vehicles.
Road Dust Resuspension
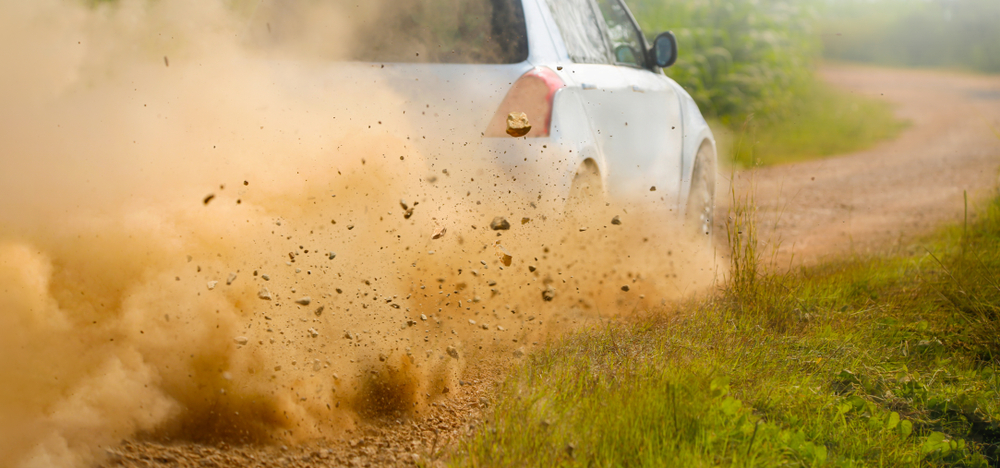

Electric cars, due to their weight and frequent use of regenerative braking, can contribute to road dust resuspension. Heavier vehicles stir up more dust from the road surface, which can contain harmful particulates like heavy metals. This resuspended dust contributes to air pollution and can negatively impact respiratory health.
Battery Recycling Emissions
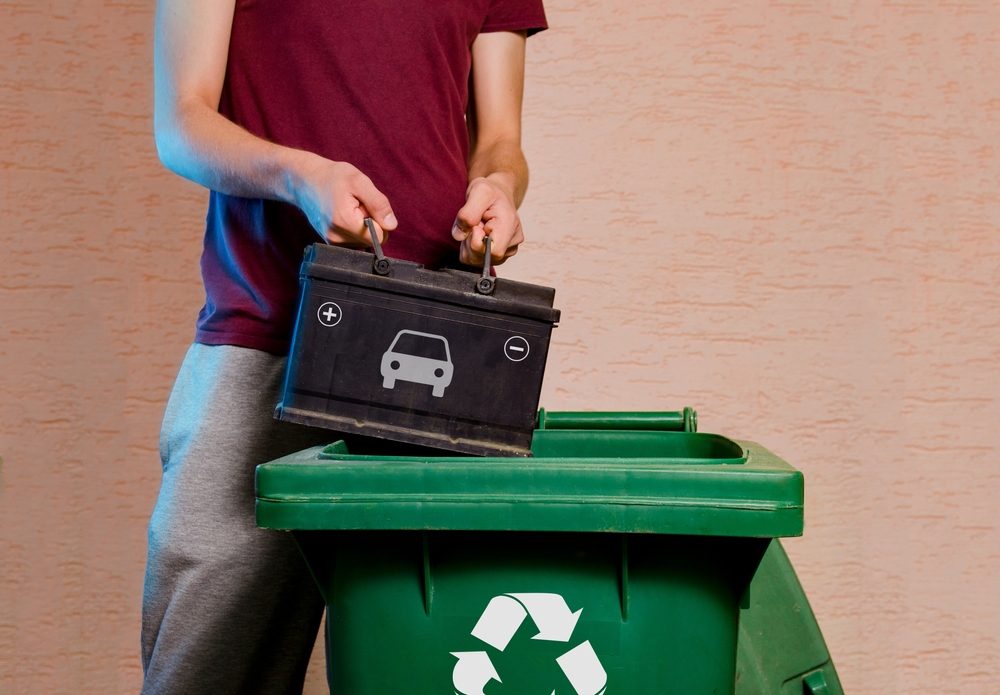

The recycling process of lithium-ion batteries generates emissions and hazardous waste. While recycling is essential to mitigate resource depletion, it involves energy-intensive processes that release CO2 and other pollutants. The process can also emit toxic chemicals if not properly managed, contributing to air pollution.
Energy Loss During Transmission
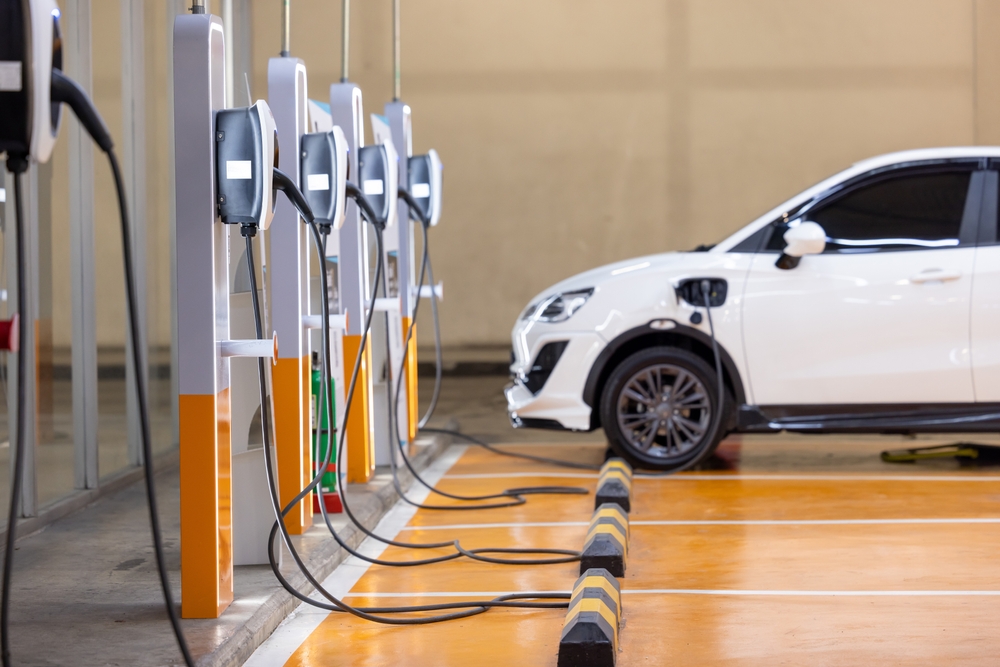

The transmission of electricity from power plants to charging stations involves energy loss, typically around 5-10%. This inefficiency means that more electricity must be generated to compensate for losses, leading to additional emissions from power plants. This indirect contribution to air pollution is often overlooked in the overall assessment of electric car emissions.
Construction of Charging Infrastructure
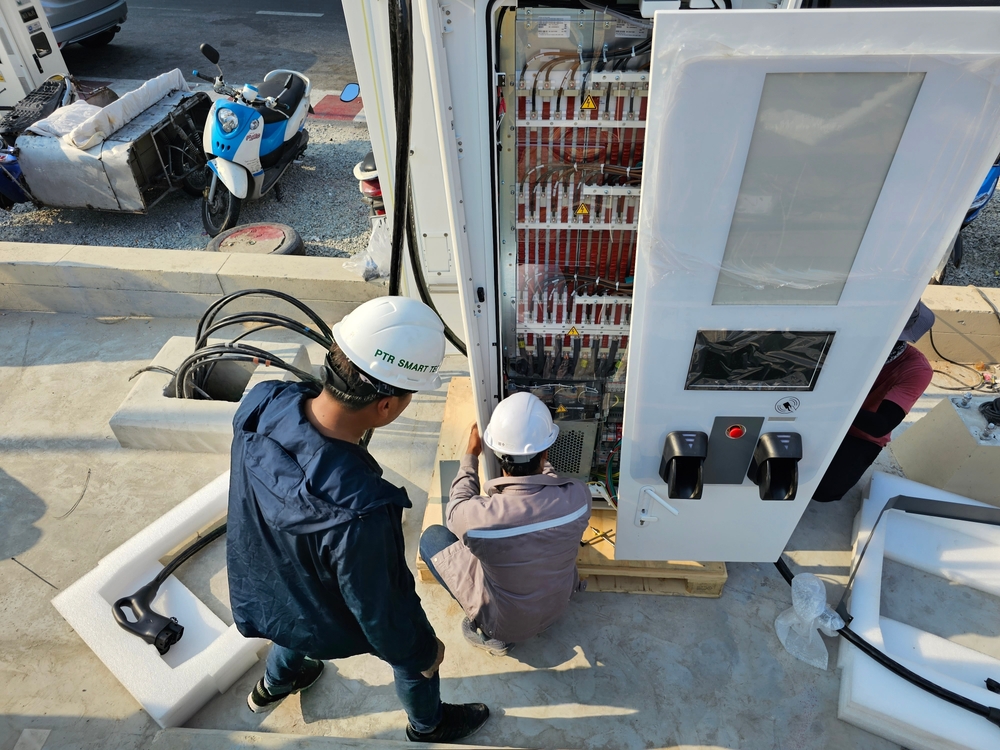

Building the necessary charging infrastructure for electric cars, including charging stations and power lines, generates emissions. The production and transportation of materials, as well as the construction activities, contribute to air pollution. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) notes that construction activities can release particulate matter, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and nitrogen oxides (NOx).
Lifecycle Emissions

The entire lifecycle of an electric car, from production to disposal, involves emissions. A comprehensive analysis by the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT) found that while electric cars have lower lifetime emissions compared to conventional cars, they still contribute to air pollution throughout their lifecycle, including manufacturing, operation, and end-of-life disposal.
Mining Operations for Battery Materials
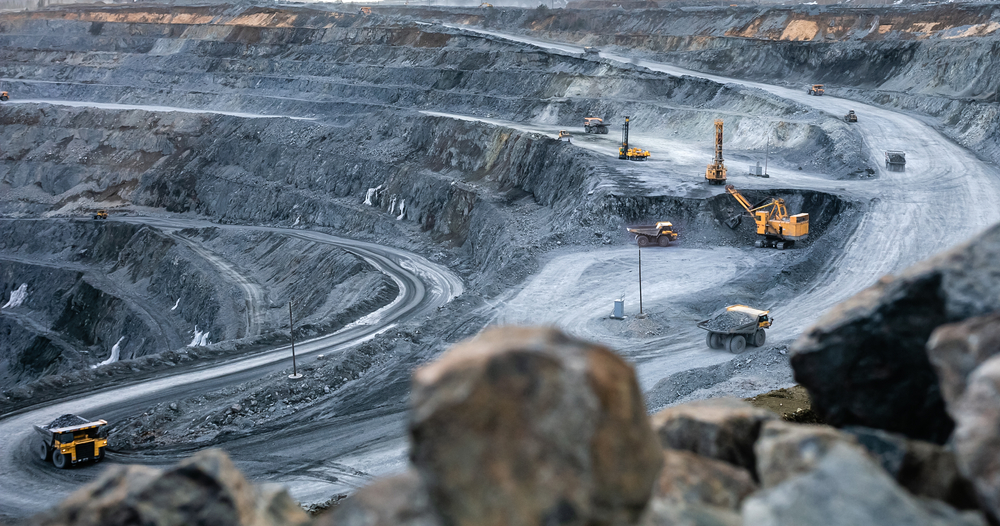

Mining operations for lithium, cobalt, and nickel can release significant amounts of dust and pollutants into the air. For example, cobalt mining in the Democratic Republic of Congo has been associated with the release of sulfur dioxide and particulate matter, which can cause respiratory problems and environmental degradation.
Power Plant Emissions
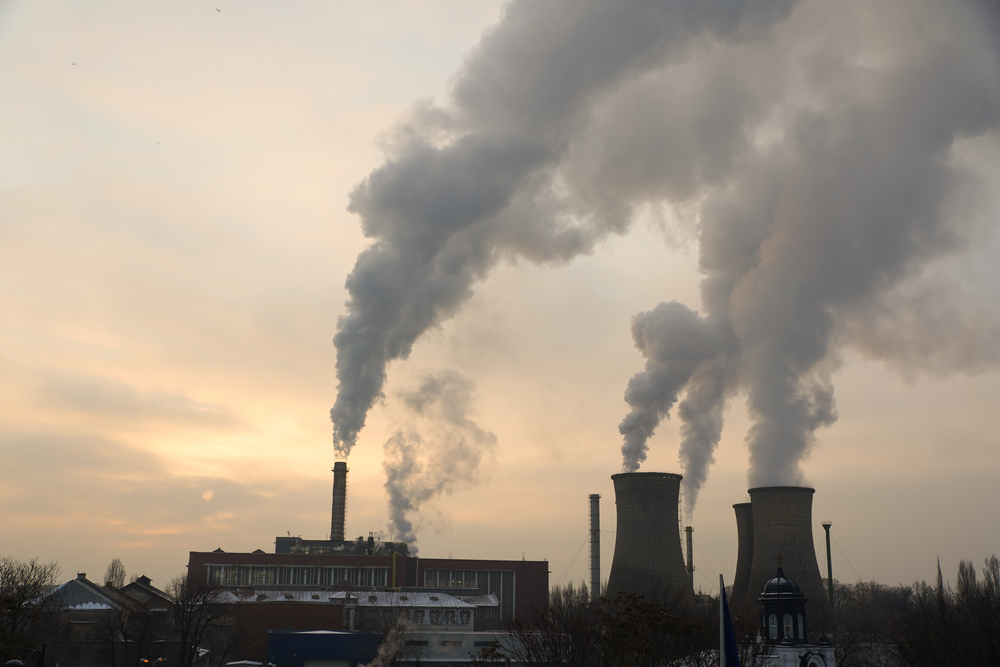

Electric cars depend on electricity, which is often generated by power plants that burn fossil fuels. These power plants emit large amounts of CO2, NOx, and sulfur dioxide (SO2). According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), fossil fuel-based power plants were responsible for about 62% of electricity generation in the United States in 2020, contributing to air pollution.
Use of Lubricants and Fluids

Electric vehicles still require lubricants and coolants to function effectively. The production and disposal of these fluids can contribute to environmental pollution. While EVs generally require fewer fluids than conventional cars, the chemicals involved can still pose risks to air quality if not managed properly.
High Energy Consumption in Cold Climates

Electric cars can be less efficient in cold climates, leading to increased energy consumption. The need for battery heating and cabin heating can significantly reduce the range of electric vehicles and require more frequent charging. This increased demand for electricity, especially in regions where fossil fuels are the primary energy source, can lead to higher emissions from power plants, indirectly contributing to air pollution.
Depletion of Natural Resources

The demand for lithium, cobalt, and nickel for electric car batteries puts significant pressure on natural resources. Extracting these materials can lead to habitat destruction and loss of biodiversity, indirectly affecting air quality. For example, lithium mining in South America’s “lithium triangle” has led to the depletion of water resources, which affects local ecosystems and can release dust and other particulates into the air.
Transportation of Raw Materials

Transporting raw materials for battery production, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, generates emissions. These materials are often transported over long distances using ships, trucks, and trains, which burn fossil fuels and release CO2, NOx, and particulate matter into the air.
Emissions from Battery Disposal

Improper disposal of lithium-ion batteries can lead to the release of toxic chemicals and heavy metals into the environment. If batteries are not properly recycled, they can leach harmful substances into the air and soil, contributing to air pollution and environmental contamination.
Secondary Pollution from Electric Car Components
The production of various components used in electric cars, such as electronics, wiring, and cooling systems, generates emissions. These components often require energy-intensive manufacturing processes and the use of chemicals that can release pollutants into the air.
Environmental Impact of Renewable Energy Sources

While renewable energy sources are cleaner than fossil fuels, their production and installation can still contribute to air pollution. For example, manufacturing solar panels and wind turbines involves energy-intensive processes that can emit CO2 and other pollutants. The transition to renewable energy to power electric cars must be carefully managed to minimize environmental impact.
Increased Electricity Demand

The increased demand for electricity to charge electric cars can strain existing power grids, leading to higher emissions from power plants. If the additional electricity demand is met by fossil fuel-based power plants, it can result in increased emissions of CO2, NOx, and SO2, contributing to air pollution.
This article originally appeared in MyCarMakesNoise.
More from MyCarMakesNoise
10 Car Modifications That Will Transform Your Vehicle

In the realm of automotive enthusiasts, personalizing an import car is more than just a hobby; it’s an expression of individuality and passion. This article is a guide tailored for those looking to elevate their vehicles beyond the ordinary. Read More
10 Companies Revolutionizing Self-Driving Vehicles

The automotive landscape is undergoing a transformative shift as the autonomous era unfolds, with technology paving the way for self-driving vehicles. In this dynamic and groundbreaking industry, several companies are at the forefront, driving innovation and shaping the future of transportation. Read More
10 Impressive Car Brands You Might Not Know About

In the vast world of automobiles, beyond the well-trodden path of renowned brands, lies a trove of lesser-known car manufacturers that offer exceptional value without compromising on quality and performance. Read More














