Electric aircraft are quickly gaining attention as the future of sustainable aviation. With advancements in battery technology and electric propulsion systems, these innovative planes are set to revolutionize air travel. However, many fascinating details about the technology behind electric aircraft remain lesser-known. In this article, we’ll uncover 17 interesting facts about electric aircraft that you might not have heard before.
Contents
Electric Aircraft Use Zero Emissions

Electric aircraft operate with zero direct emissions, unlike traditional jet-fueled planes that release carbon dioxide and other pollutants into the atmosphere. This makes electric planes an essential technology for reducing the aviation sector’s carbon footprint, which accounts for approximately 2.5% of global emissions. As governments push for greener technologies, electric aircraft stand as a promising solution for cleaner skies.
Batteries Are the Heart of Electric Planes
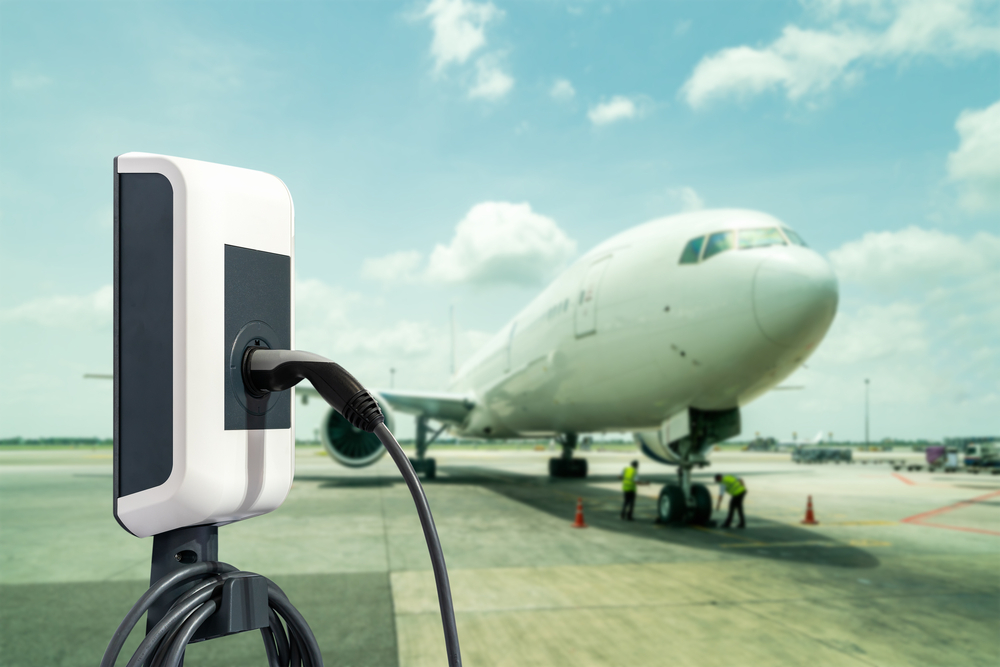

The most crucial component of an electric aircraft is its battery. Current lithium-ion battery technology is still a limitation, as it struggles to provide enough energy for long-distance flights without becoming too heavy. However, advances in solid-state batteries and energy-dense materials are paving the way for more capable electric aircraft. High energy density is essential for extending range and improving performance.
They Can Be Quieter Than Traditional Aircraft

Traditional jet engines are notoriously noisy, contributing to both noise pollution and higher stress for communities near airports. Electric planes, however, are significantly quieter, thanks to their simpler, more streamlined propulsion systems. This reduced noise opens up possibilities for airports in urban areas and for future applications like air taxis, which could operate in cities without causing major disturbances.
Electric Aircraft Are Ideal for Short-Haul Flights

Due to the current limitations of battery technology, electric planes are best suited for short-haul flights. Typically, they can cover routes under 500 miles, which is ideal for regional trips and commuter services. As battery efficiency improves, these planes will be able to fly longer distances, making electric air travel more competitive with traditional planes on a broader range of routes.
Hybrid-Electric Models Are a Transition Technology

While fully electric planes may not yet be viable for long flights, hybrid-electric models offer a practical solution during this transitional period. These aircraft use both conventional jet fuel and electric power, reducing overall emissions while extending range. Hybrid-electric planes could bridge the gap as battery technology continues to improve, allowing airlines to reduce their carbon footprint without sacrificing operational capability.
Electric Planes Are Lighter

Electric propulsion systems, with fewer moving parts than traditional jet engines, contribute to a lighter overall aircraft design. Reduced weight means improved energy efficiency and lower operating costs. Electric motors are also more compact, offering aircraft designers greater flexibility in optimizing the layout and aerodynamics of future planes, further enhancing performance.
NASA Is Developing Electric Aircraft
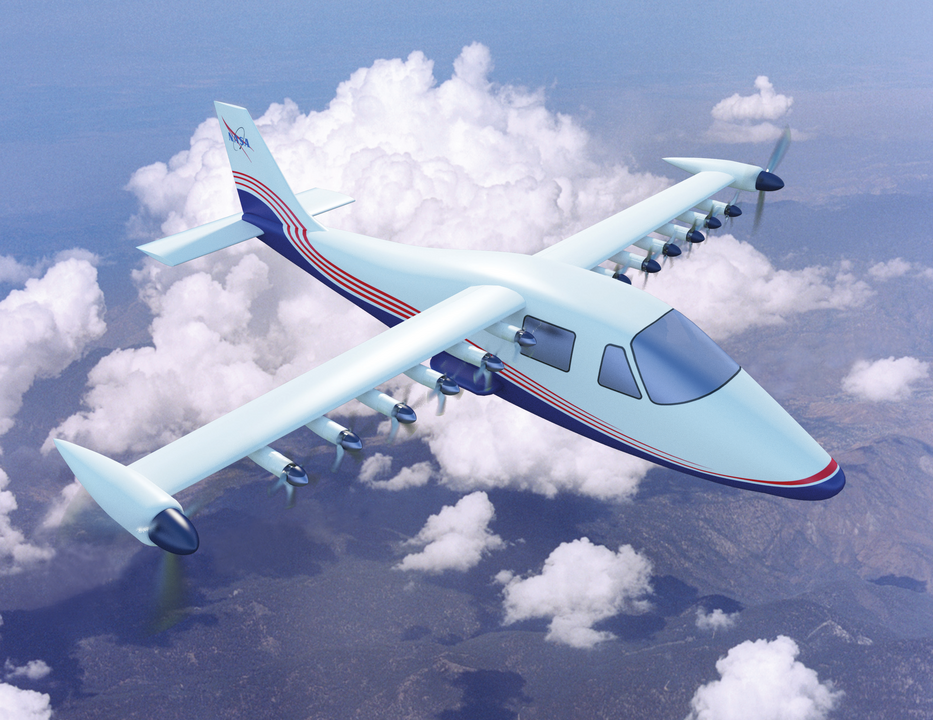

NASA’s X-57 Maxwell is a fully electric experimental aircraft designed to demonstrate how electric propulsion can make air travel cleaner, quieter, and more efficient. This aircraft has 14 electric motors integrated into its wings, and NASA hopes it will influence the development of commercial electric aircraft by proving that smaller, more efficient designs can reduce fuel use and emissions.
Electric Aircraft Can Be Cheaper to Maintain
With fewer moving parts compared to traditional jet engines, electric aircraft require less maintenance. Electric motors don’t suffer from the same wear and tear, meaning less downtime and lower costs for airlines. This efficiency could make electric planes more cost-effective over time, contributing to lower operating costs and possibly cheaper airfares for passengers.
Charging Infrastructure Is Still Developing

While electric planes are advancing, the necessary charging infrastructure at airports remains limited. Airports will need to invest in large-scale charging stations, capable of refueling planes between flights in a timely manner. This is one of the key logistical challenges that must be addressed for electric aviation to become widespread, particularly as the number of electric planes in operation increases.
Electric Aircraft Could Drastically Reduce Airline Costs

Fuel is one of the largest expenses for airlines, but electric planes, which rely on cheaper electricity rather than jet fuel, could significantly cut operating costs. Reduced fuel expenses, combined with lower maintenance costs, could make flying more affordable in the long run. Airlines investing in electric aircraft might also be able to offer cheaper flights, making air travel more accessible.
The First Commercial Electric Flight Took Off in 2019
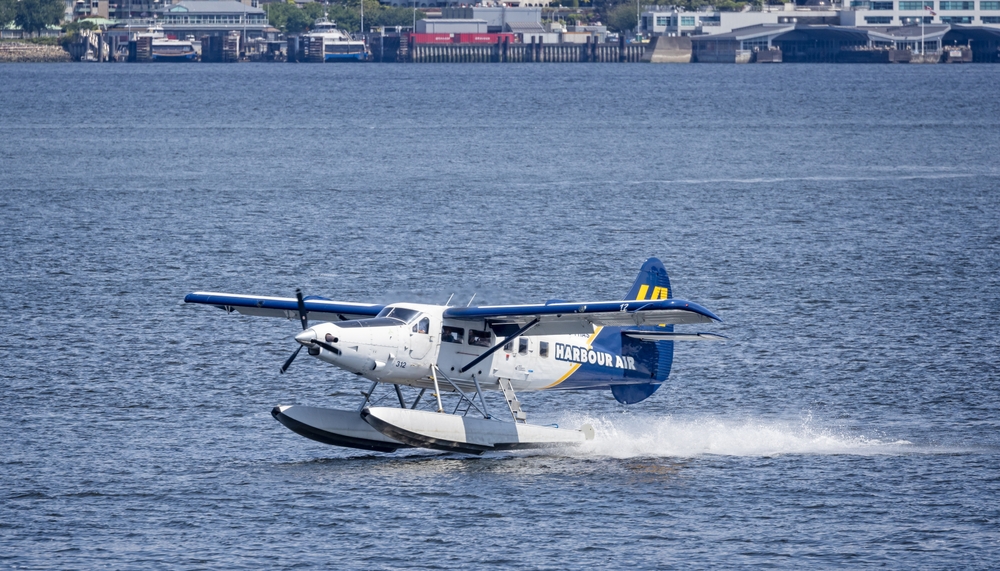

In December 2019, Harbour Air, a Canadian airline, successfully tested the world’s first fully electric commercial aircraft—a seaplane retrofitted with an electric motor. This milestone marked a significant step toward commercializing electric aviation. Harbour Air’s goal is to eventually convert its entire fleet to electric planes, which would make it the world’s first all-electric airline.
Electric Planes Have Multiple Motors

Many electric aircraft designs incorporate multiple small electric motors instead of a single large engine. This distributed propulsion system improves efficiency, redundancy, and safety, as the failure of one motor doesn’t necessarily compromise the entire aircraft. Having multiple motors also allows for more innovative aircraft designs, which can enhance aerodynamics and performance.
Urban Air Mobility Is Tied to Electric Aircraft

The development of electric aircraft is closely linked to the rise of urban air mobility (UAM), where small, electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) aircraft could be used for short flights within cities. These air taxis would reduce traffic congestion, cut down travel times, and offer a new way to navigate dense urban environments. Electric propulsion is essential for the success of UAM, as it allows for quieter, more sustainable flight.
Electric Drones Are Leading the Charge

While electric passenger planes are still in development, electric drones are already widely used in industries like agriculture, surveillance, and logistics. These smaller, more agile aircraft serve as test beds for the technologies that will eventually power larger electric aircraft. Advances made in drone technology—such as battery efficiency and autonomous flight—are helping shape the future of electric aviation.
Electric Planes Could Fly at Higher Altitudes

With lighter designs and fewer emissions, electric aircraft could potentially fly at higher altitudes than traditional planes. This could make air travel more efficient by reducing drag and taking advantage of thinner air, which requires less energy to move through. Flying at higher altitudes could also open up new air routes and reduce congestion in lower airspace.
Hydrogen Fuel Cells Are Another Option
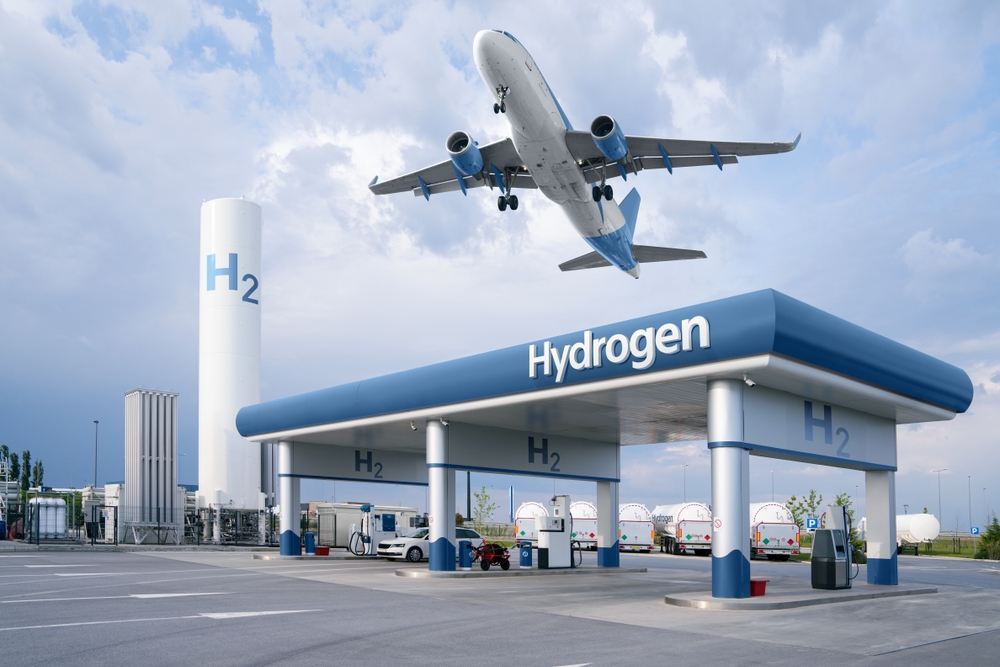

Hydrogen fuel cells offer another alternative to traditional batteries for electric aircraft. By converting hydrogen into electricity, fuel cells can provide a longer range than current batteries, making them a promising technology for long-haul electric flights. Hydrogen fuel cells produce only water as a byproduct, further reducing the environmental impact of aviation.
Several Major Airlines Are Already Investing in Electric Fleets
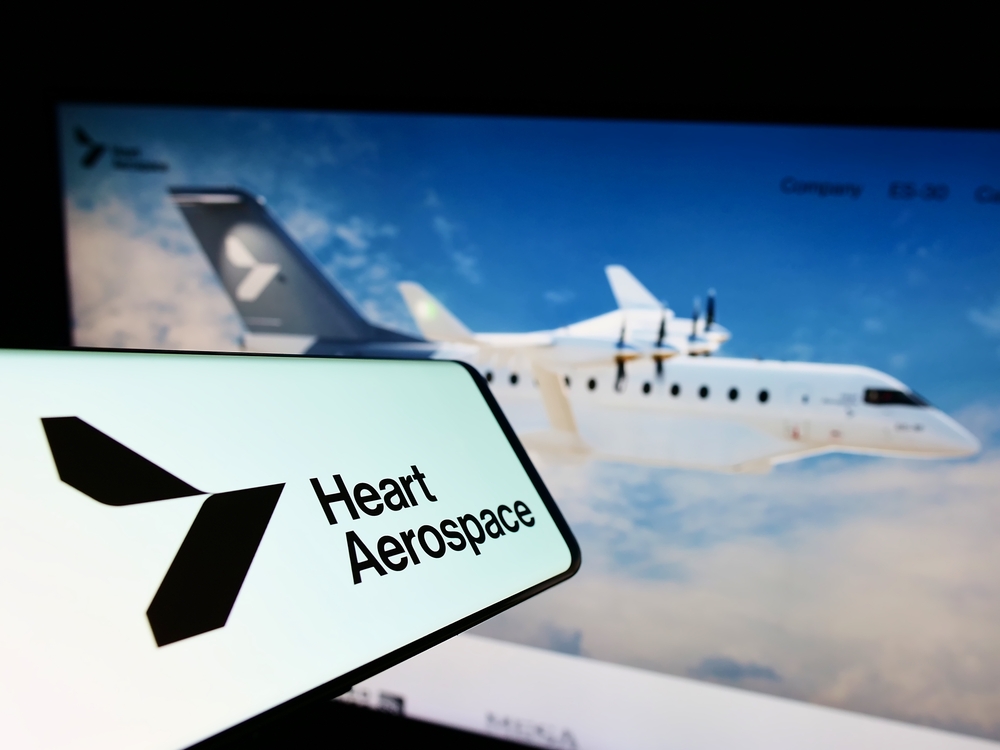

Airlines like United, EasyJet, and Air New Zealand have recognized the potential of electric aircraft and are investing in the technology. These airlines are working with companies like ZeroAvia and Heart Aerospace to develop electric planes for commercial use. Their investments demonstrate a growing commitment to sustainability and mark the beginning of a major shift in the aviation industry.
This article originally appeared in MyCarMakesNoise.
More from MyCarMakesNoise
25 Iconic Race Cars That Redefined Speed and Style

Race cars are not just about speed and performance; they’re also about making a visual statement. From bold colors to sleek lines, some race cars stand out not only for their engineering but also for their striking looks. In this article, we’ll take a look at the 25 most eye-catching race cars in history that have turned heads both on and off the track. Read More
20 Functional Utility Vehicles That Put Practicality Over Style

Utility vehicles are designed for practicality and performance, but not all hit the mark when it comes to style. Some models, despite their functionality, have failed to impress with their design. Read More
20 Cars That Struggled with Aerodynamics and Performance

Aerodynamics play a crucial role in a vehicle’s efficiency and performance. However, some automobiles have designs that hinder their aerodynamic capabilities, resulting in poor fuel economy and handling. Here are some automobiles with the worst aerodynamic designs, highlighting the challenges they face on the road. Read More














