Space exploration has always pushed the boundaries of human knowledge and technology. Over the years, certain spacecraft have stood out for their groundbreaking contributions to our understanding of the universe. In this article, we highlight 15 pioneering spacecraft that redefined what we know about space, each playing a crucial role in expanding our horizons and paving the way for future discoveries.
Contents
Sputnik 1
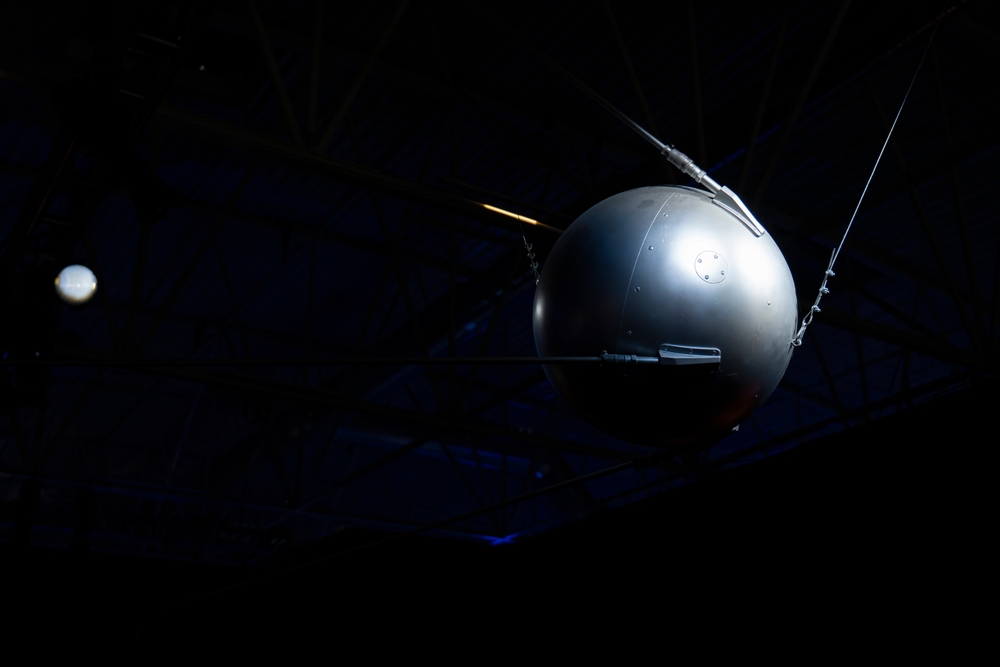

Launched by the Soviet Union in 1957, Sputnik 1 was the first artificial Earth satellite, marking the dawn of the space age. This 83.6 kg (184 lb) sphere transmitted radio pulses back to Earth, allowing scientists to study the ionosphere and proving that humans could send objects into space. Its launch prompted the Space Race and spurred advancements in satellite technology and space exploration.
Vostok 1
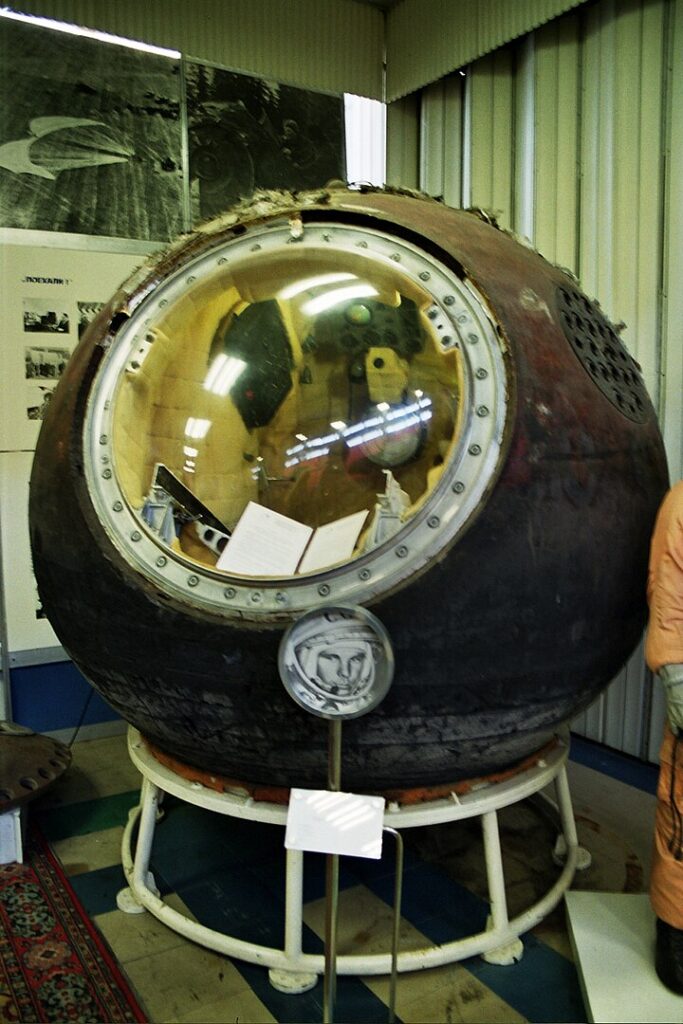

In 1961, Vostok 1 carried Yuri Gagarin, the first human to journey into outer space. This historic flight orbited the Earth, demonstrating that humans could survive space travel. Vostok 1’s successful mission paved the way for future manned spaceflights and cemented Gagarin’s place as a hero of space exploration.
Apollo 11
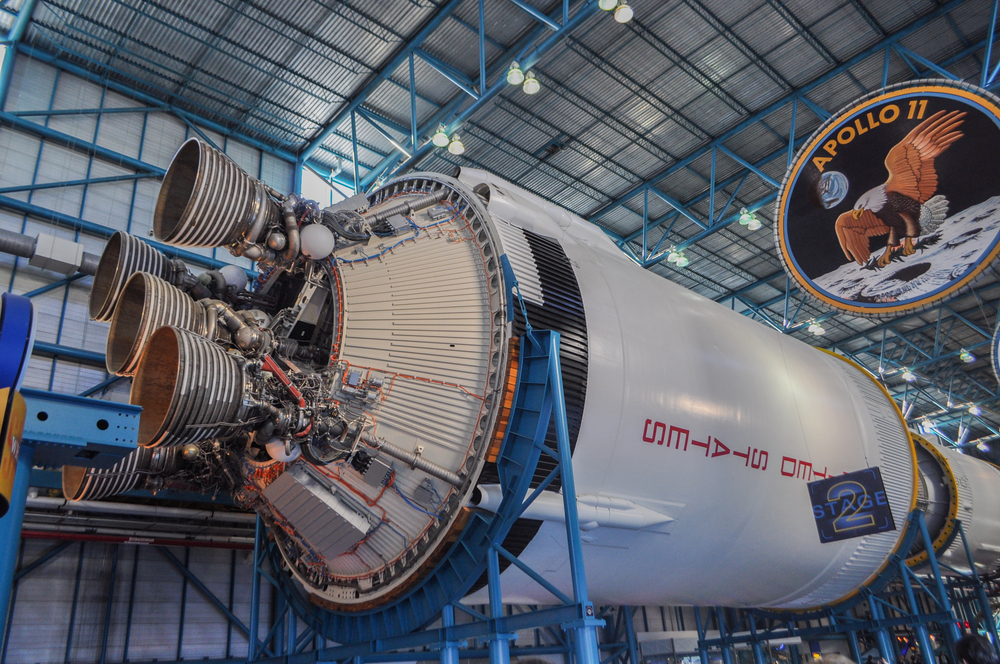

Apollo 11 landed the first humans on the Moon in 1969. Astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin made history with their lunar walk, while Michael Collins orbited above. This mission demonstrated human capability to travel to and land on another celestial body, collecting lunar samples and providing iconic imagery that continues to inspire.
Hubble Space Telescope
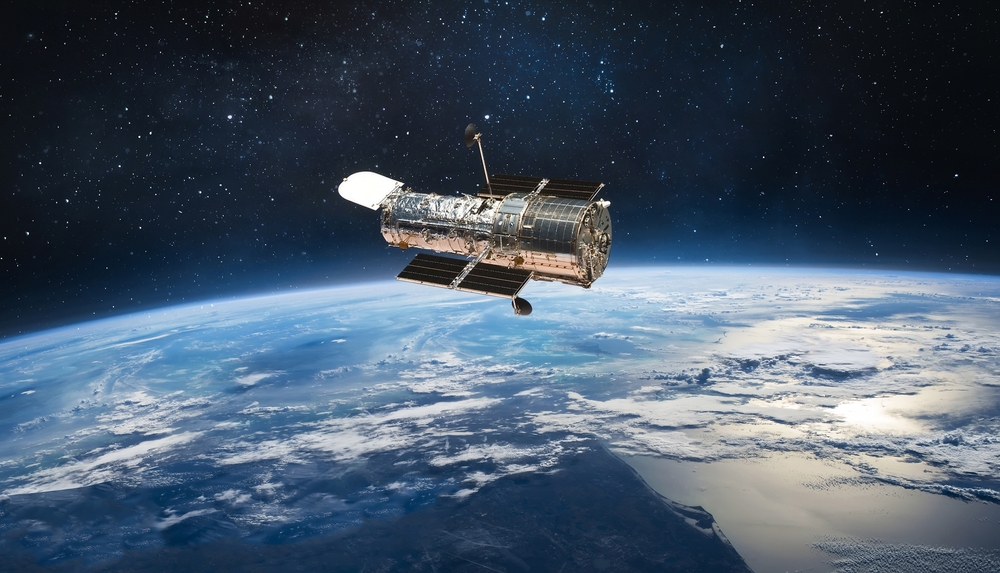

Since its launch in 1990, the Hubble Space Telescope has provided stunning images and invaluable data about the universe. Orbiting above Earth’s atmosphere, it has captured detailed views of distant galaxies, nebulae, and stars, contributing to major discoveries such as the accelerating expansion of the universe.
International Space Station (ISS)
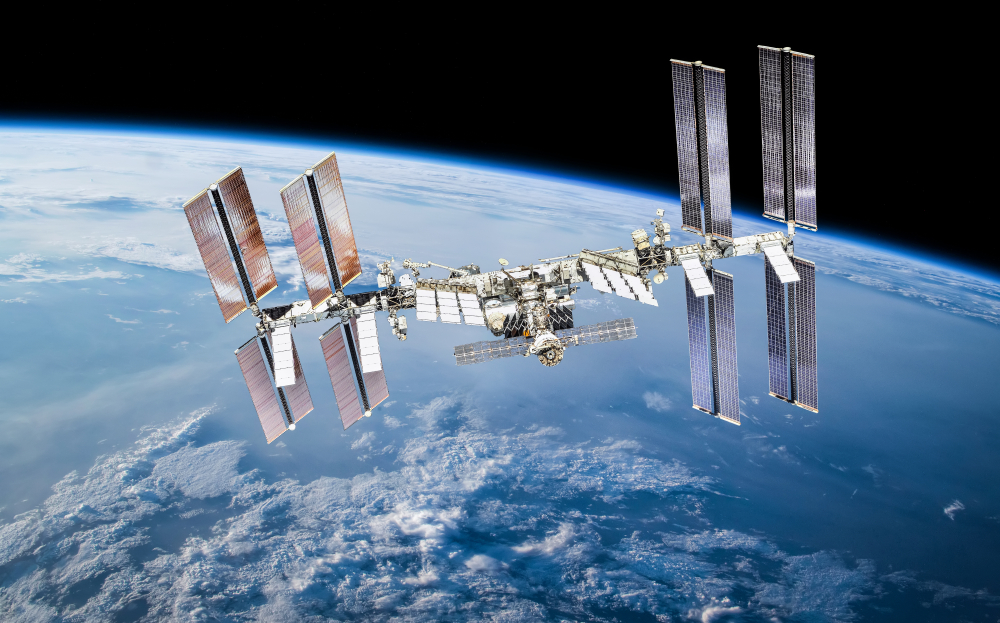

Continuously inhabited since 2000, the ISS serves as a unique laboratory for scientific research and international cooperation. Orbiting Earth, it facilitates studies in microgravity, biology, physics, and astronomy, and is a testbed for the technologies needed for future deep space exploration.
Cassini-Huygens
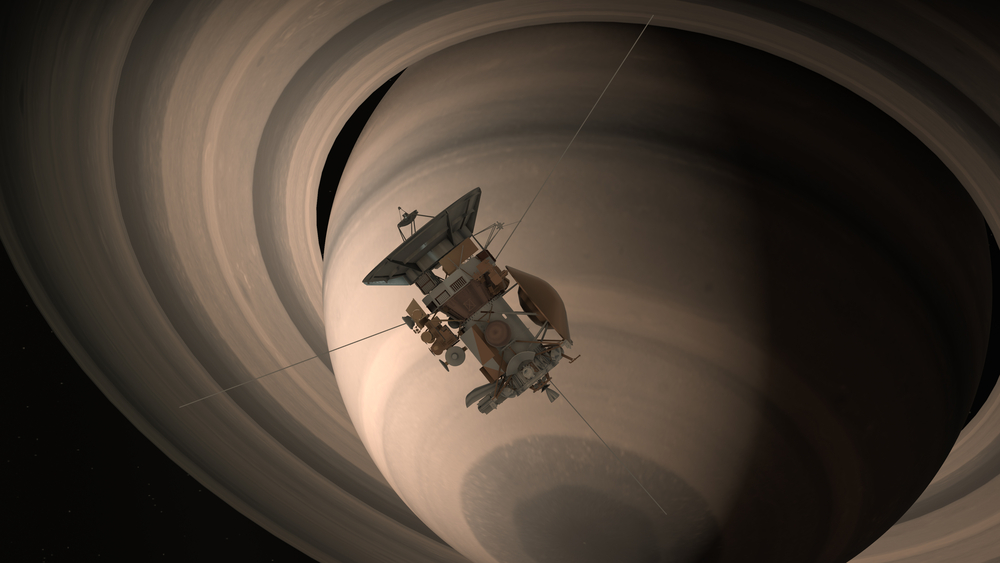

The Cassini-Huygens mission explored Saturn and its moons from 2004 to 2017. Cassini provided detailed images and data on Saturn’s rings, atmosphere, and magnetosphere, while the Huygens probe landed on Titan, revealing its surface and atmospheric composition. This mission revolutionized our understanding of the Saturnian system.
Mars Pathfinder
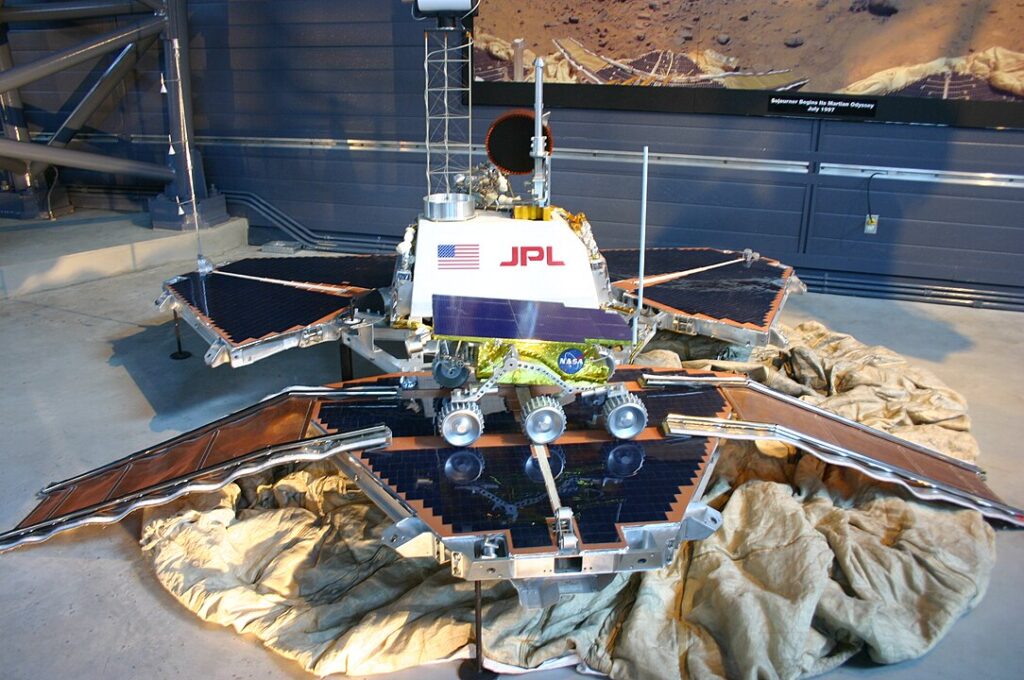

Mars Pathfinder, which landed on Mars in 1997, delivered the Sojourner rover. This mission demonstrated innovative landing techniques and rover technology. Sojourner conducted experiments and provided detailed images, proving the feasibility of future Mars rovers and missions.
Curiosity Rover
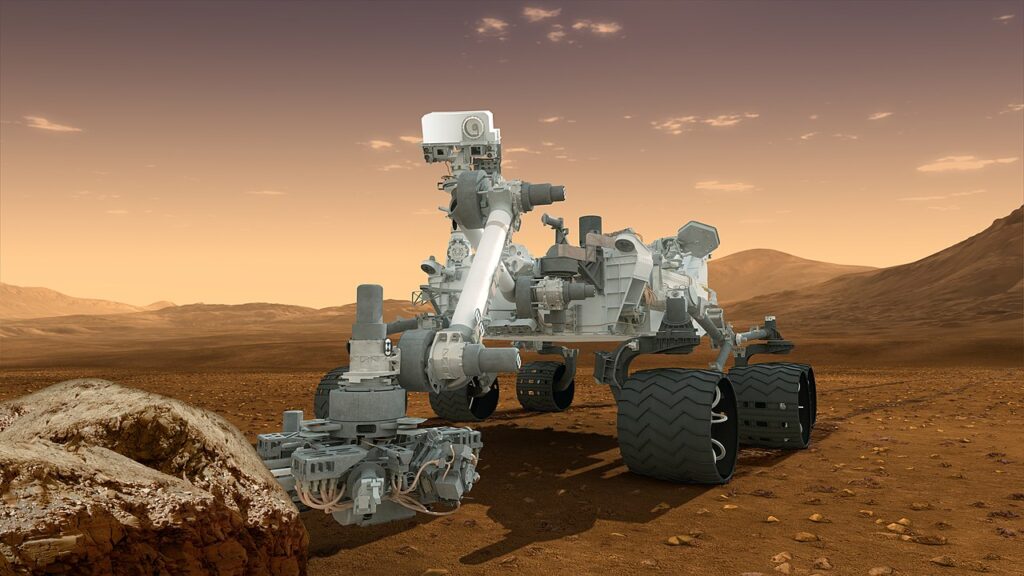
Curiosity landed on Mars in 2012 and has since conducted detailed geological and atmospheric studies. Equipped with a suite of scientific instruments, it analyzes soil and rock samples, seeking signs of past life and studying the planet’s climate and geology, paving the way for human exploration of Mars.
New Horizons
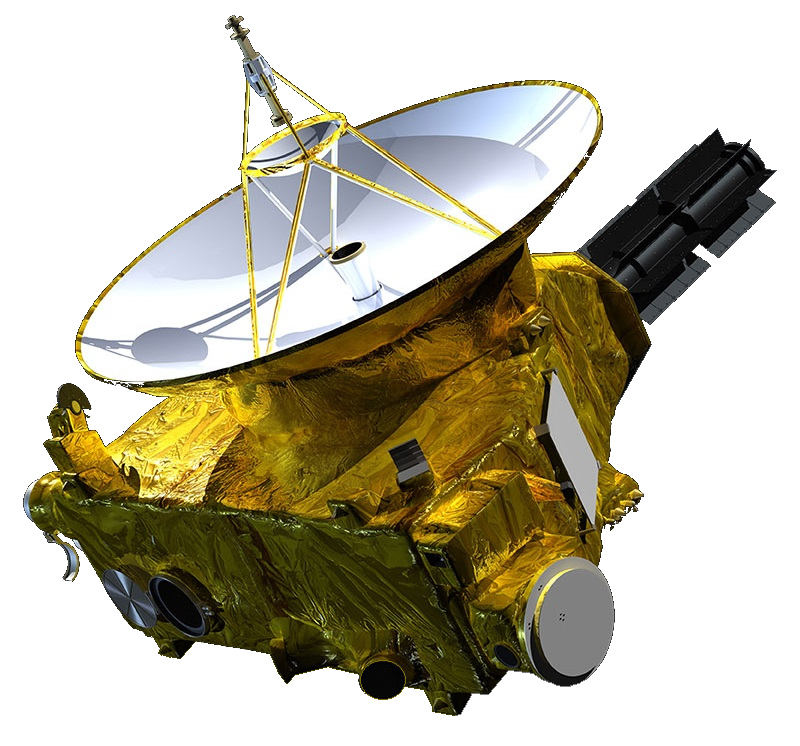

Launched in 2006, New Horizons provided the first close-up images of Pluto in 2015. This mission revealed Pluto’s complex surface features and atmosphere, transforming our understanding of this distant world. It continues to explore the Kuiper Belt, offering insights into the outer solar system’s formation.
Pioneer 10
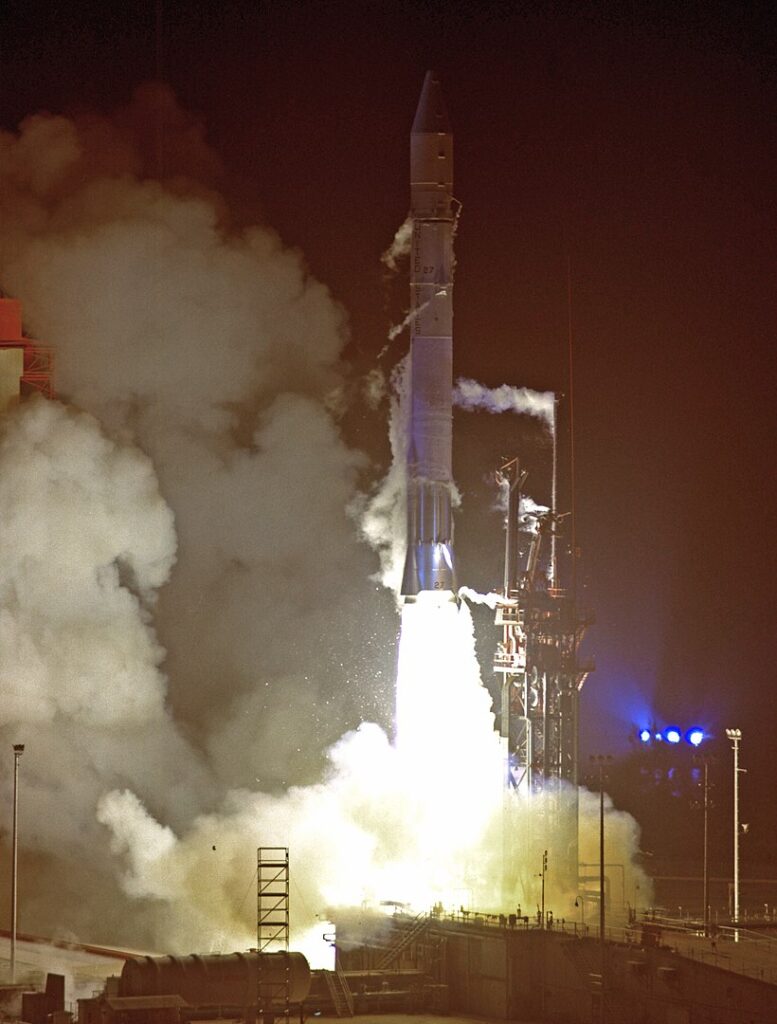

Pioneer 10 was the first spacecraft to travel through the asteroid belt and make a flyby of Jupiter in 1973. It provided the first close-up images of Jupiter and studied its magnetosphere, radiation belts, and moons, setting the stage for future outer planet exploration.
Galileo
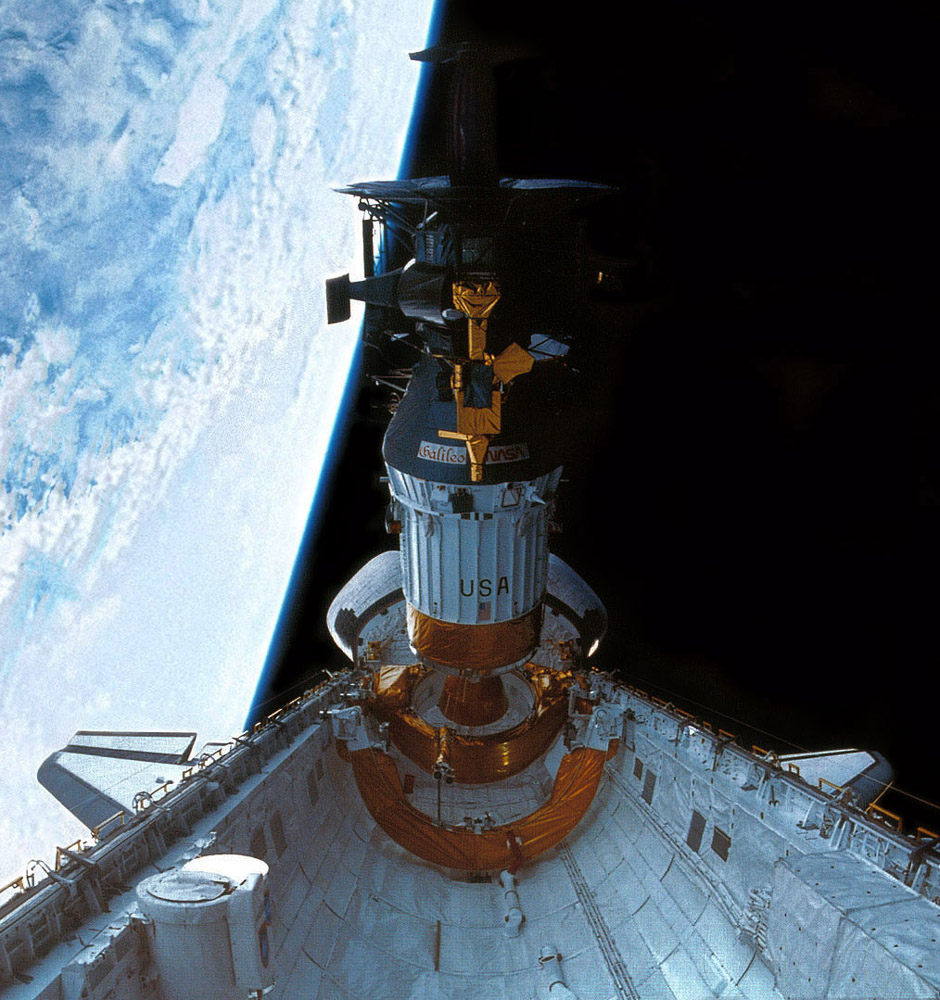

Galileo orbited and studied Jupiter and its moons from 1995 to 2003. It provided detailed data on Jupiter’s atmosphere, magnetic field, and its major moons, including evidence of subsurface oceans on Europa, contributing significantly to our understanding of the Jovian system.
Kepler Space Telescope
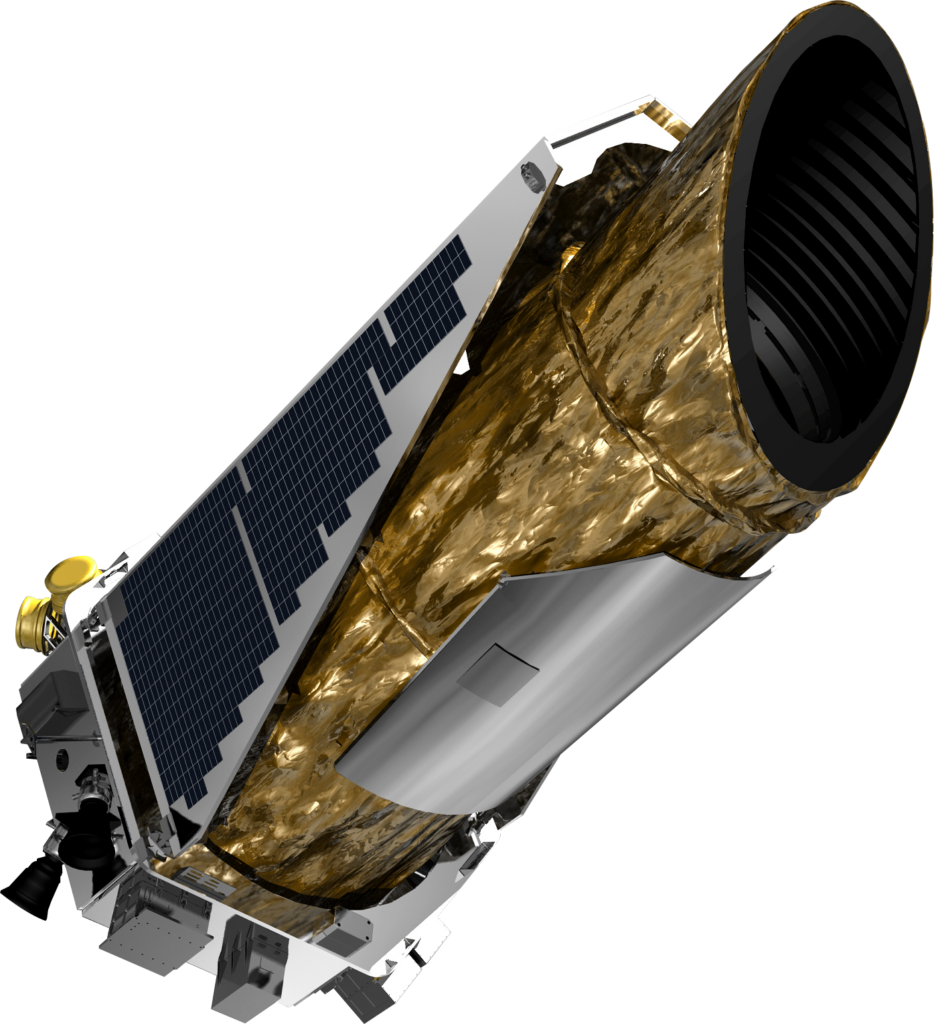
Launched in 2009, the Kepler Space Telescope has discovered thousands of exoplanets, many of which are potentially habitable. By monitoring the brightness of stars, it identified planets transiting them, revolutionizing our knowledge of planetary systems beyond our own.
Chandrayaan-1
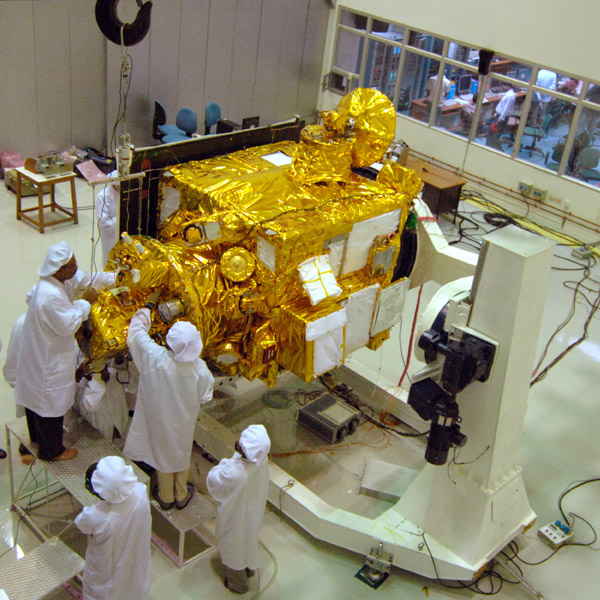

India’s first lunar probe, Chandrayaan-1, launched in 2008, discovered water on the Moon. Its instruments mapped the Moon’s surface in detail and confirmed the presence of hydroxyl and water molecules, significantly impacting lunar science and future exploration missions.
Rosetta
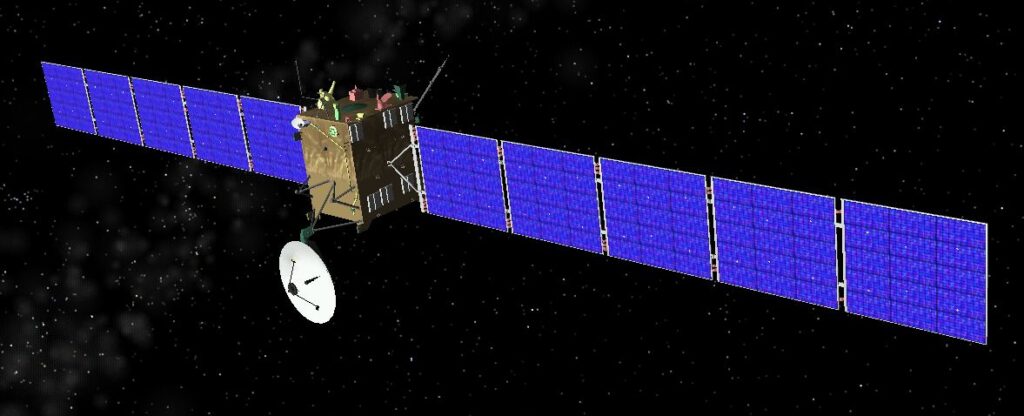

Launched in 2004, Rosetta orbited and landed a probe on comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko in 2014. This mission provided unprecedented data on the comet’s composition, structure, and activity, enhancing our understanding of the early solar system’s formation and evolution.
Juno
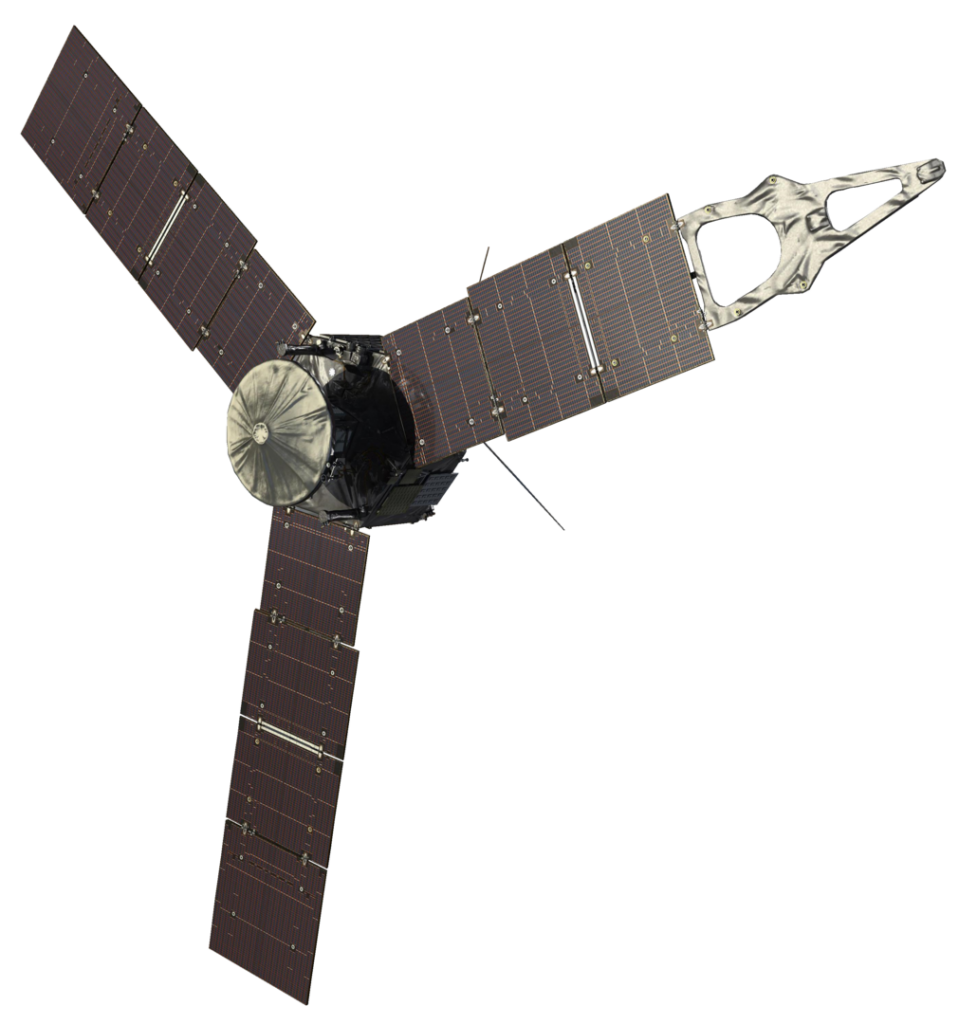

Juno, launched in 2011, is studying Jupiter’s atmosphere, magnetic field, and interior structure. Its close-up observations have revealed details about Jupiter’s polar regions, deep atmosphere, and core, providing insights into the planet’s formation and evolution.
This article originally appeared in MyCarMakesNoise.
More from MyCarMakesNoise
20 Misconceptions About Race Cars You Probably Believe

Race cars have long been the subject of fascination and intrigue, but with that comes a host of misconceptions. From the belief that they are simply souped-up street cars to the idea that they are only about speed, many myths surround these high-performance machines. Read More.
12 Unmanned Space Probes Exploring Our Solar System
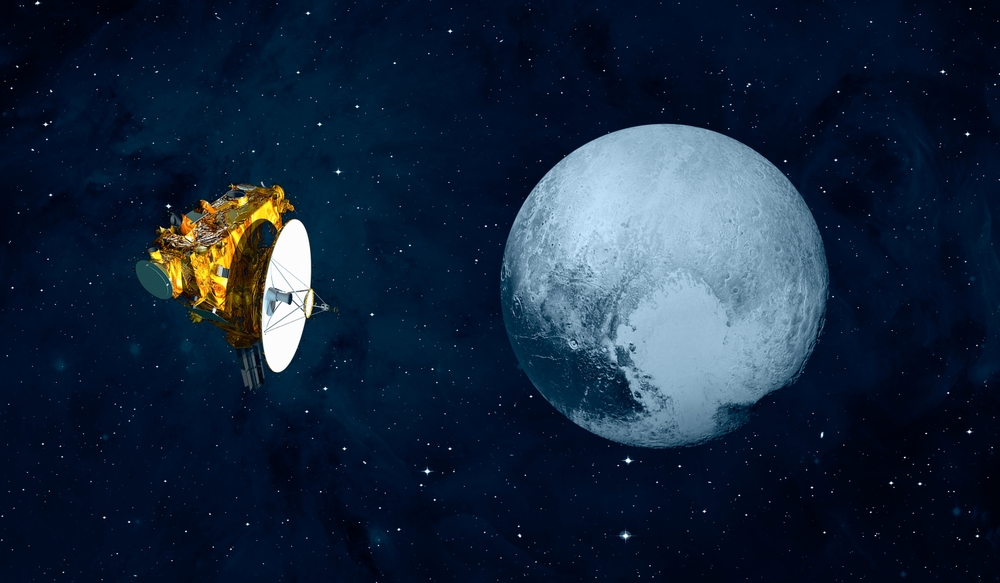

The exploration of our solar system has been significantly advanced by unmanned space probes. These remarkable spacecraft have journeyed to distant planets, moons, and even beyond the solar system, providing invaluable data and breathtaking images. Read More.
15 Iconic Airplanes from Classic Aviation Movies

Aviation has always captivated audiences, and classic movies have brought some of the most iconic airplanes to the big screen. From World War II fighters to modern jets, these films showcase the beauty and power of aviation history. Read More.














