Turbochargers are a popular feature in modern vehicles, but there are still plenty of misconceptions surrounding them. While they boost engine power and efficiency, many drivers have the wrong idea about how they work and their effects on a vehicle. Lets clear up 17 of the most common false claims about turbochargers and explains how they actually operate.
Contents
Turbochargers Are Only for Sports Cars

It’s often assumed that turbochargers are exclusive to high-performance sports cars. However, they’re now found in a wide range of vehicles, including everyday sedans and trucks. Turbochargers boost engine efficiency by increasing power without requiring a larger engine. This allows manufacturers to meet fuel efficiency and emissions standards, making turbochargers a versatile component. So, they’re just as common in commuter cars as they are in sports models.
Turbochargers Cause Engine Wear

Some believe turbochargers lead to faster engine wear due to the added power they produce. This misconception stems from older designs that lacked the durability of modern systems. Today’s engines are specifically engineered to accommodate turbochargers, ensuring long-term reliability. With regular maintenance, turbocharged engines can last just as long as their naturally aspirated counterparts.
All Turbochargers Cause Turbo Lag
The idea that turbochargers always create lag in acceleration persists, though it’s outdated. Early turbochargers did suffer from delayed power delivery, but modern designs have significantly improved. Advanced technologies like twin-scroll and variable-geometry turbos nearly eliminate lag. They allow for quicker spooling and smoother power transitions.
Turbocharged Engines Always Overheat

It’s commonly thought that turbochargers overheat engines because of the increased power they generate. In reality, manufacturers have implemented effective cooling systems to counteract this. Intercoolers and advanced cooling technologies help manage the extra heat produced by turbochargers. As long as proper maintenance is followed, overheating is not an issue for modern turbocharged engines. These systems are designed to keep everything running at safe operating temperatures.
Turbocharged Cars Require Premium Fuel

Another misconception is that all turbocharged engines must run on premium gasoline. While some high-performance models may benefit from premium fuel, many turbocharged vehicles are designed to use regular gasoline. This depends on the specific engine and its tuning. Using the recommended fuel type in the owner’s manual ensures optimal performance. Not all turbocharged engines need higher-octane fuel for everyday driving.
Turbochargers Make Engines Less Reliable
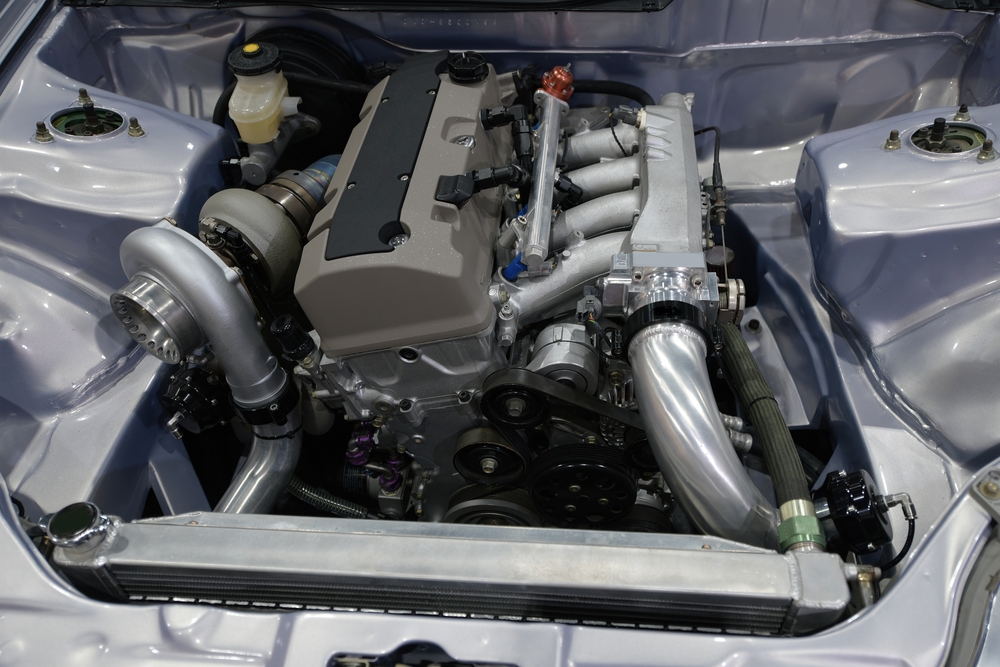

There’s a widespread belief that turbochargers reduce engine reliability. However, modern engines are built to integrate turbochargers efficiently, with durability in mind. Turbochargers today undergo rigorous testing to ensure they can withstand the added stress. When properly maintained, turbocharged engines can be as dependable as naturally aspirated ones. Their reliability depends largely on regular upkeep rather than the turbo itself.
Turbocharged Engines Are Louder
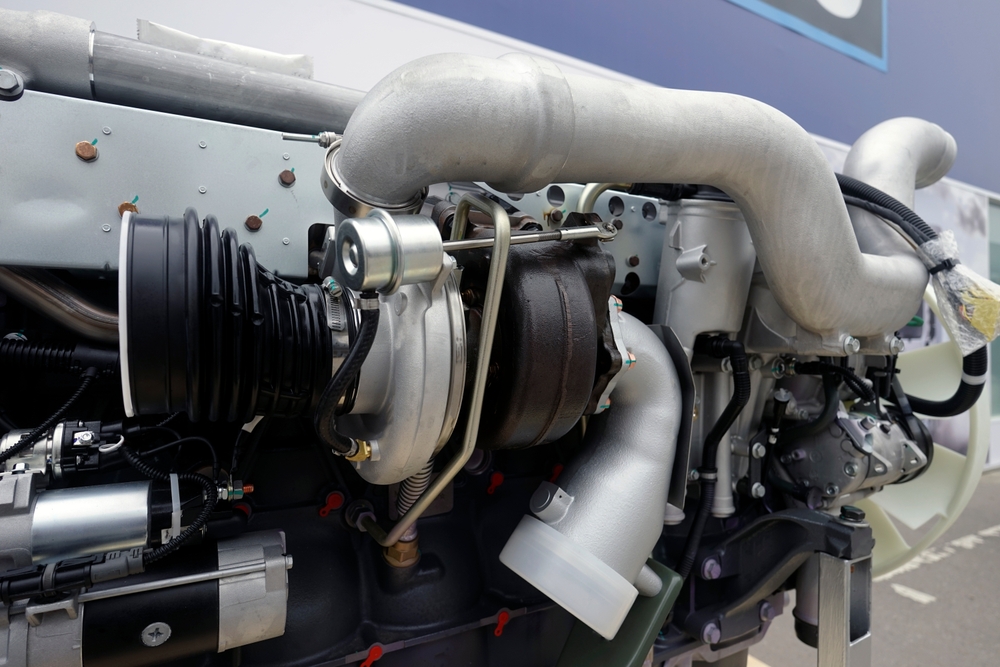

Many assume that turbochargers make engines noticeably louder. While older models did produce a distinct whine, modern turbochargers are much quieter. Enhanced design and soundproofing technology have minimized engine noise in newer vehicles. In most cases, drivers can’t tell the difference between a turbocharged and non-turbocharged engine based on sound alone.
Turbochargers Are Maintenance-Free
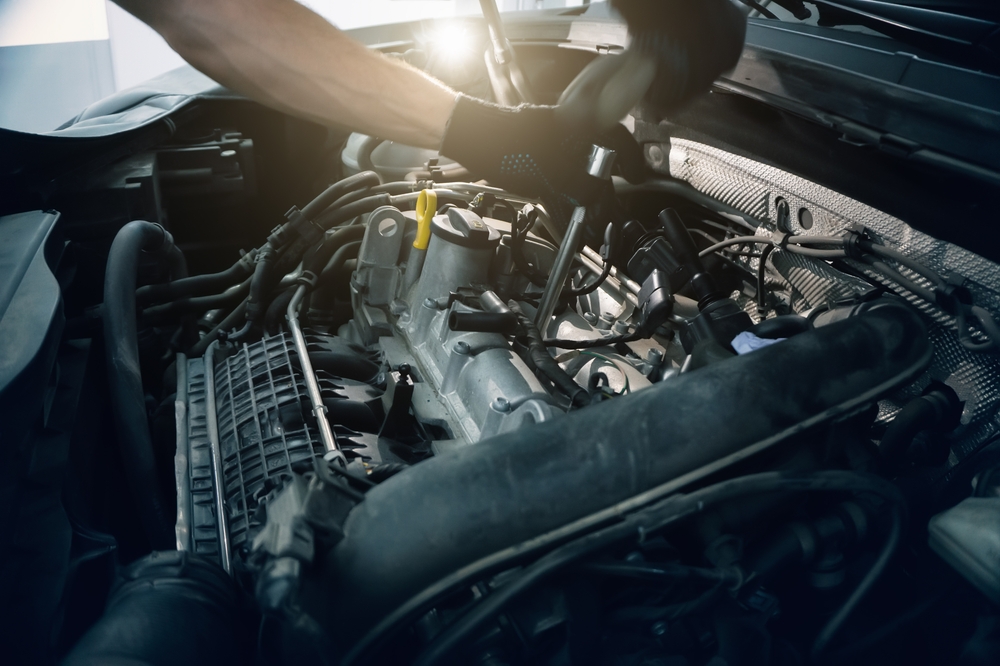

There’s a misconception that turbochargers don’t need any special care. In fact, turbocharged engines require regular maintenance to function efficiently. Oil changes are especially important, as clean oil helps lubricate the turbo’s moving parts. Dirty or old oil can damage the turbo over time. Keeping up with maintenance tasks ensures the turbocharger remains in good condition, prolonging its lifespan.
Turbochargers Are Expensive to Repair
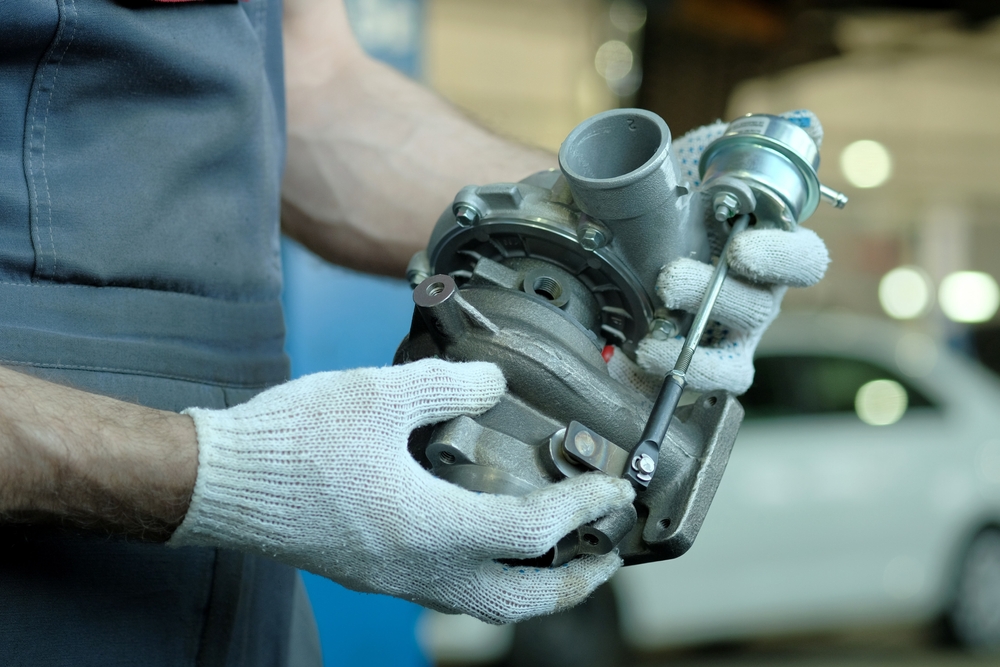

People often assume that fixing or replacing a turbocharger is prohibitively expensive. While repairs can be costly if severe damage occurs, turbochargers are generally durable and built to last. Many turbocharged engines can run their entire lifespan without needing a turbo replacement. If properly cared for, the cost of maintaining a turbocharged engine is no higher than that of a naturally aspirated one. Proactive maintenance can prevent expensive repairs down the line.
Turbochargers Always Improve Fuel Efficiency

It’s commonly thought that turbochargers automatically improve fuel efficiency, but this isn’t always the case. Turbochargers allow smaller engines to produce more power, which can reduce fuel consumption. However, if driven aggressively, a turbocharged engine can use more fuel than a non-turbocharged one. The benefit to fuel economy depends heavily on driving habits and how the turbo is utilized. It’s not a guaranteed solution for better gas mileage.
Turbocharged Cars Can’t Be Tuned for More Power

Some enthusiasts believe that once a turbocharger is installed, it can’t be modified for additional power. In fact, turbocharged engines are some of the most tunable, offering more power potential through modifications. Changes in software tuning or upgrading turbo components can significantly increase performance. The key is finding the right balance to avoid overstressing the engine. Proper tuning can unlock more horsepower without sacrificing reliability.
All Turbochargers Are the Same
A common belief is that all turbochargers work in the same way. However, there are several types of turbos, each with different designs and purposes. Twin-scroll, single, and variable-geometry turbos all offer distinct benefits, depending on the engine’s needs. Whether it’s enhancing low-end torque or providing top-end power, each turbocharger is designed for specific performance goals. This variety makes turbocharging versatile for a wide range of applications.
Turbochargers Can Be Installed on Any Engine

There’s a misconception that turbochargers can be easily fitted to any engine. In reality, not all engines are designed to handle the extra pressure and heat generated by a turbo. Retrofitting a turbo onto an engine requires careful consideration of factors like cooling and fueling systems. Engines that aren’t built for turbocharging could suffer serious damage if a turbo is added without proper modifications. It’s not as simple as just bolting on a turbocharger.
Turbochargers Are Only for High-Speed Driving

Many think that turbochargers are only beneficial at high speeds. In fact, turbochargers enhance engine performance across all driving conditions. Whether accelerating from a standstill or cruising at highway speeds, the turbocharger provides additional power. This makes them useful for daily driving as well as high-performance situations. Their versatility is one of the reasons turbochargers are so widely used today.
Turbocharged Cars Have Shorter Lifespans

It’s often assumed that turbocharged engines don’t last as long as naturally aspirated ones. However, modern engineering ensures that turbocharged engines are built for longevity. With proper care, a turbocharged engine can last as long as a non-turbo one. Components like oil and coolant systems are specifically designed to handle the additional stresses of turbocharging. The key to longevity is routine maintenance, not the presence of a turbocharger.
Turbochargers Only Provide Power at High RPM
Some believe that turbochargers only deliver power when the engine is revved to high RPMs. While this was true for early turbos, modern designs like twin-scroll and variable-geometry turbos provide power throughout the entire RPM range. These technologies allow turbochargers to spool up quickly, delivering torque at low RPMs. This results in better responsiveness during normal driving conditions, making turbos suitable for all types of driving.
Turbocharged Engines Are Too Complex for DIY Maintenance

There’s a misconception that turbocharged engines are too complex for regular maintenance by the average car owner. While they do have additional components, maintaining a turbocharged engine is not much more difficult than a non-turbo one. Basic tasks like oil changes, air filter replacements, and spark plug checks remain the same. Understanding the key areas that require attention will allow DIY enthusiasts to handle routine maintenance with ease.
This article originally appeared in MyCarMakesNoise.
More from MyCarMakesNoise
19 Military Transport Vehicles Known for Their Durability

When it comes to military operations, durability is key for transport vehicles that need to withstand harsh environments and tough terrains. From rugged off-road trucks to armored personnel carriers, these vehicles are designed to handle the demands of combat and logistical missions. Read More.
10 Classic Trucks That Fell Short of Expectations

Classic trucks often evoke a sense of nostalgia and rugged charm, but not all of them hit the mark with consumers. Some models, despite their unique features and innovative designs, struggled to find their place in the market. Read More.
13 Fun Facts About Harley-Davidson Motorcycles

Harley-Davidson motorcycles have been a symbol of freedom and adventure for over a century. From their humble beginnings in a small wooden shed in Milwaukee to becoming a global icon, these bikes have captured the hearts of riders worldwide. Read More.














