Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming more popular, but there are still plenty of misconceptions about them. From concerns about range to confusion over charging times, these myths can make it hard to understand the true potential of EVs. In this article, we’ll clear up 15 of the most common misunderstandings and reveal what electric cars are really capable of.
Contents
EVs have a very limited range.
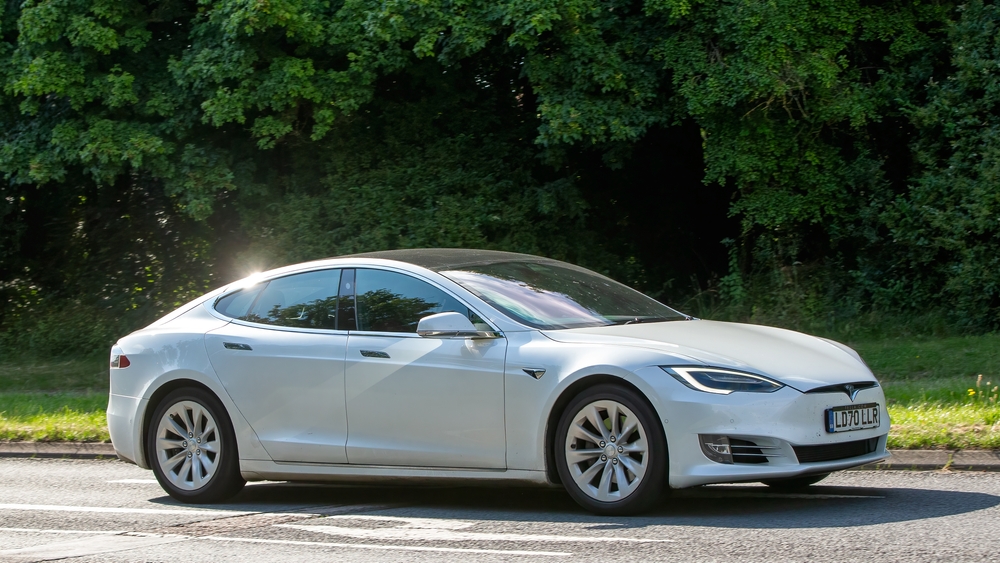

Many people think electric vehicles can only travel short distances before needing a charge, but modern EVs have improved range. Models like the Tesla Model S can cover over 370 miles on a single charge, and many EVs offer ranges above 200 miles, making them suitable for long trips.
Electric vehicles are slower than gas-powered cars.

Electric motors provide instant torque, allowing EVs to accelerate quickly. Cars like the Tesla Model 3 Performance can go from 0 to 60 mph in just 3.1 seconds, rivaling and even surpassing many traditional sports cars.
EVs take too long to charge.
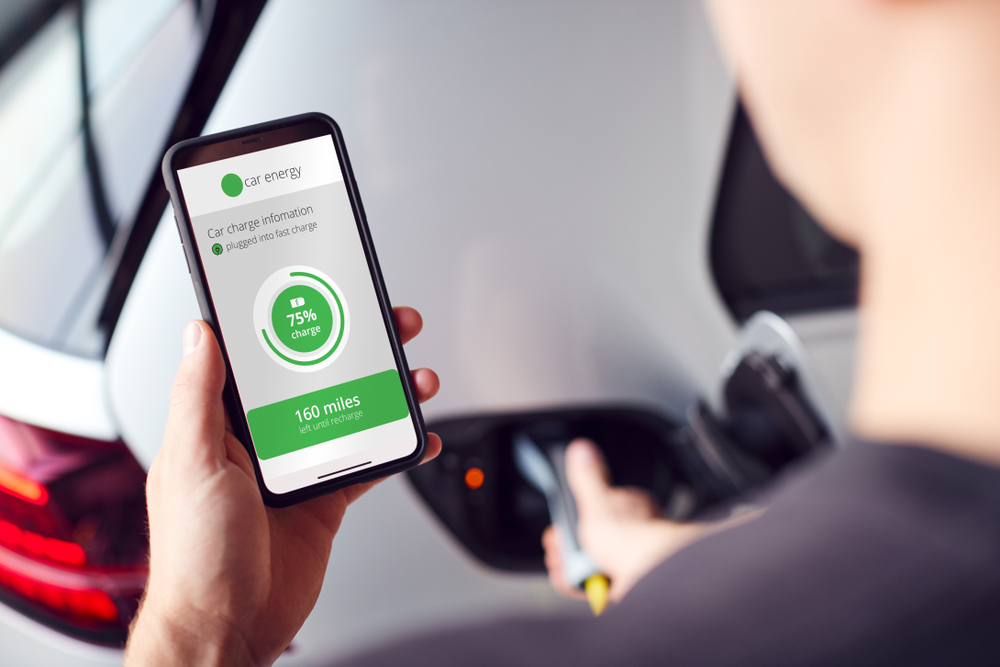

While it’s true that charging can take time, rapid chargers are becoming more common. A fast charger can add up to 80% charge in 30 minutes for many EV models, and advancements in charging technology continue to reduce charging times.
You can’t drive an EV in cold weather.
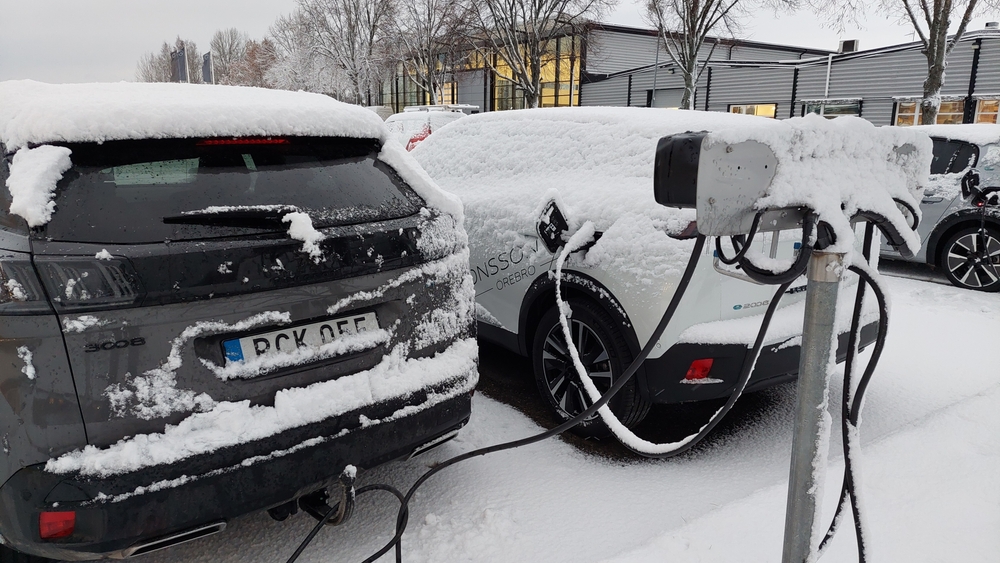

EVs do experience reduced efficiency in cold weather, but they are still functional. Preconditioning systems allow drivers to heat the battery and cabin while still plugged in, minimizing energy loss and ensuring smooth operation even in colder climates.
EV batteries don’t last long.

EV battery technology has advanced significantly. Most batteries are designed to last well over 100,000 miles, with manufacturers like Tesla offering warranties that extend up to 8 years or 120,000 miles. Degradation over time is minimal.
Electric cars are too expensive for most people.
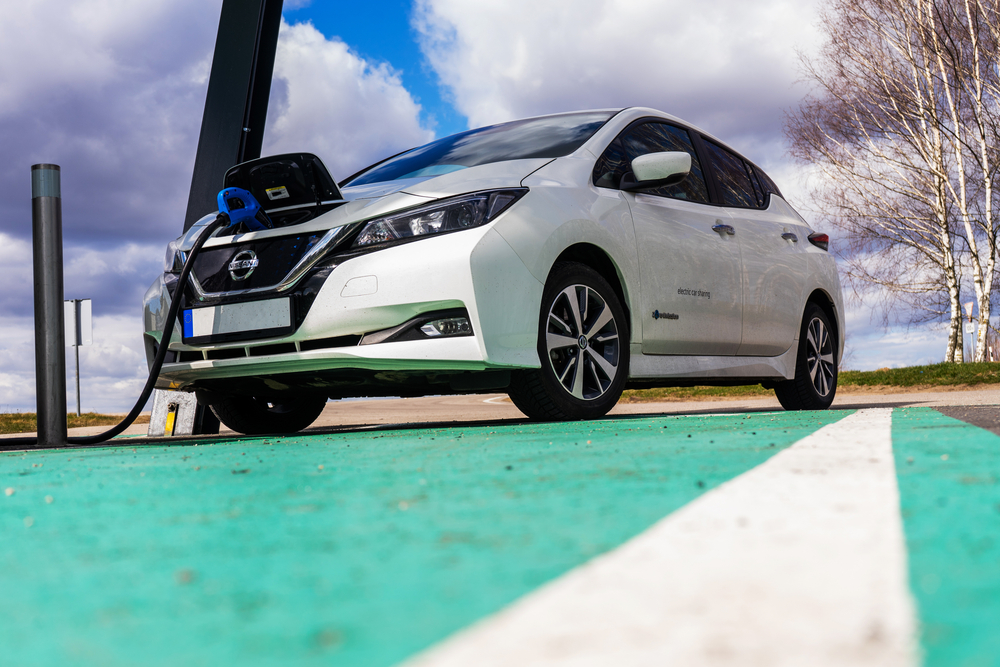

While the upfront cost of an EV may be higher, federal and state tax credits, along with reduced maintenance and fuel costs, make them more affordable in the long run. Entry-level models like the Nissan Leaf offer a budget-friendly option for many drivers.
There aren’t enough charging stations.
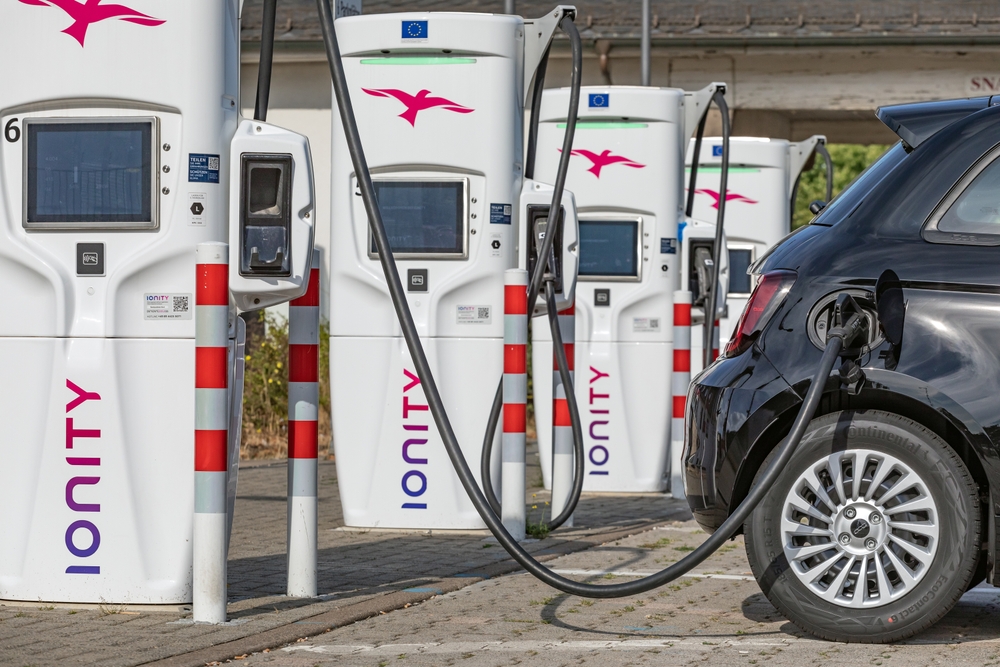

The charging network is expanding rapidly, with over 50,000 public charging stations available in the U.S. alone. Many EV manufacturers, such as Tesla, also have proprietary networks like Superchargers that are constantly growing.
EVs are not powerful enough for long road trips.

Electric vehicles are capable of long-distance travel, especially with their improved ranges and the availability of fast-charging stations. Many EVs now offer navigation systems that plan routes based on charging locations, making road trips easier.
EVs aren’t environmentally friendly because of battery production.
While battery production does have an environmental impact, studies show that over their lifetime, EVs still have a lower carbon footprint compared to gas-powered cars. The electricity to charge them can also come from renewable sources, further reducing emissions.
Electric cars are only good for city driving.

Although EVs excel in city conditions due to regenerative braking, they are equally capable on highways. Their smooth acceleration and quiet ride make them ideal for long-distance driving as well.
EVs are not safe in accidents.

EVs undergo the same rigorous safety testing as gas-powered vehicles. In fact, many EVs, like the Tesla Model 3 and Audi e-tron, have received top safety ratings due to their low center of gravity, which reduces rollover risk, and advanced safety features.
Electric vehicles can’t tow heavy loads.

Contrary to popular belief, many EVs are designed to handle towing. The Tesla Cybertruck, for instance, is expected to tow up to 14,000 pounds, demonstrating that electric powertrains can offer substantial towing capabilities.
You need a special outlet to charge an EV at home.

While a 240V outlet (Level 2 charger) can speed up charging, many EVs can be charged using a standard 120V outlet, known as Level 1 charging. This slower method is still sufficient for overnight charging in many cases.
EV batteries are prone to catching fire.

While battery fires can occur, they are exceedingly rare and are less frequent than fires in gasoline-powered vehicles. EV manufacturers use advanced safety systems to monitor battery conditions and prevent overheating.
It’s difficult to find mechanics to repair EVs.

Although EVs require specialized knowledge for repairs, many dealerships and independent shops are now trained to handle them. Additionally, EVs have fewer moving parts, which means they typically require less maintenance than gas-powered cars.
This article originally appeared in MyCarMakesNoise.
More from MyCarMakesNoise
20 Best Value Sports Cars You Can Buy Right Now

Sports cars are often seen as high-performance machines with hefty price tags, but there are several models that offer great value without compromising on speed, handling, or style. In this article, we’ll explore some of the best value sports cars you can buy right now, highlighting models that deliver impressive performance at an affordable price. Read More
20 Key Developments in RV Comfort and Technology

RVs have evolved dramatically over the years, with key developments in comfort and technology making road travel more luxurious and convenient. Modern advancements such as smart home integration, solar power systems, and enhanced climate control allow travelers to enjoy the same amenities they would at home. Read More
20 Best-Looking Concept Cars That Never Made It to Production

Concept cars often showcase the cutting-edge designs and futuristic ideas of automakers, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. However, not all of these stunning vehicles make it to production. In this article, we’ll take a look at some of the best-looking concept cars that, despite their incredible designs, never reached the showroom floor. Read More














