A car’s cooling system works hard to keep everything running smoothly, but some components can overheat more easily than others. When key parts get too hot, it can lead to bigger issues under the hood and expensive repairs down the road. In this list, we’ll look at 18 common cooling system parts that are especially prone to overheating, along with a few reasons why they’re likely to run too hot. Knowing which parts to watch out for can help you keep your car in top shape and avoid unexpected breakdowns.
Contents
Radiator
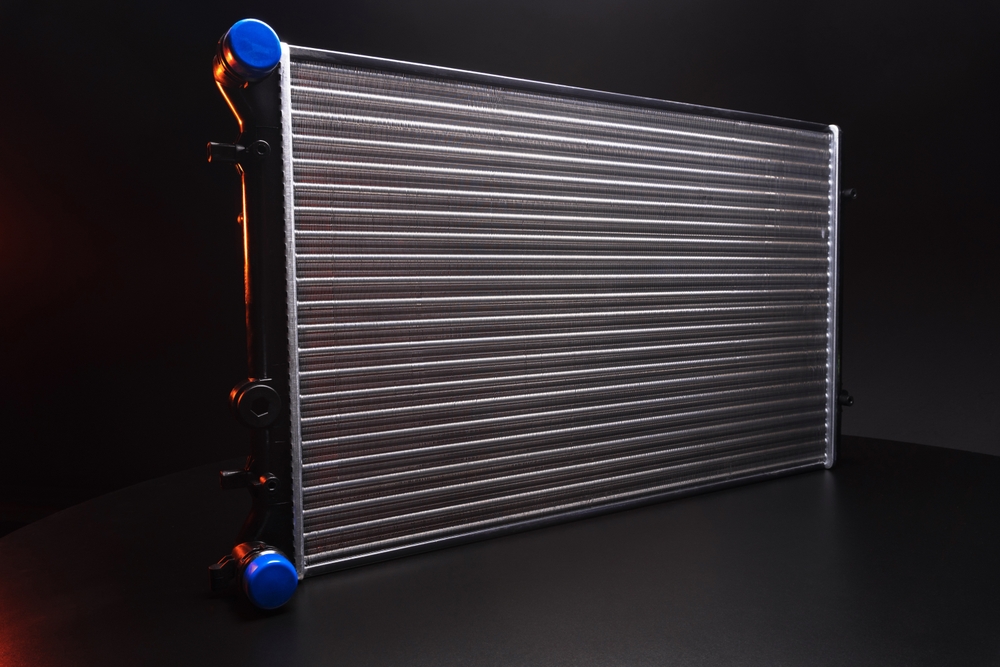
The radiator is essential for dispersing heat from the engine, as it allows coolant to flow through its metal fins and release heat into the air. A malfunctioning radiator can become clogged, restrict coolant flow, or develop leaks, causing overheating and potential engine damage.
Water Pump
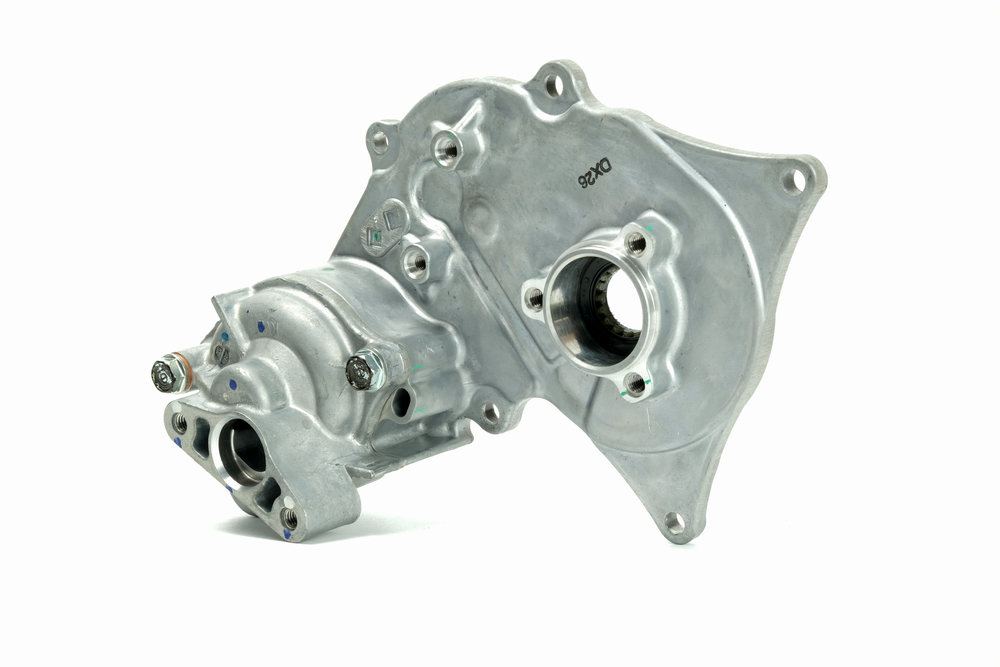

The water pump circulates coolant throughout the engine and radiator, maintaining the engine’s temperature. If it fails due to worn bearings or leaks, coolant circulation slows or stops, causing rapid overheating. This is a critical part that directly impacts engine temperature control.
Thermostat
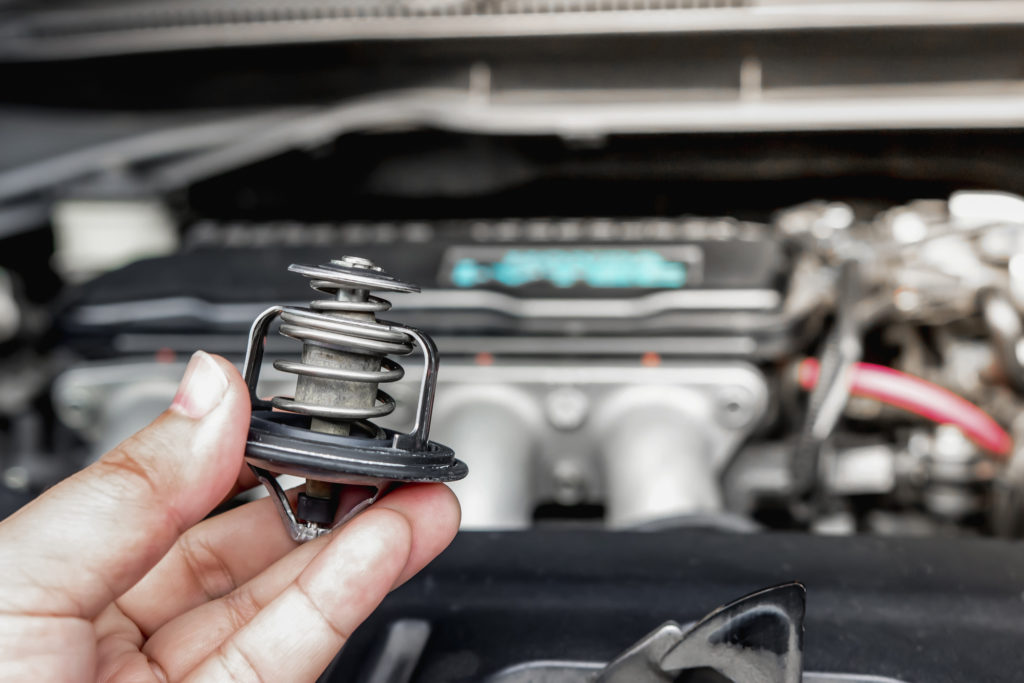

The thermostat regulates the coolant flow based on engine temperature, opening and closing as needed. When stuck closed, it restricts coolant flow, leading to overheating, especially during high engine loads or warm weather.
Radiator Fan
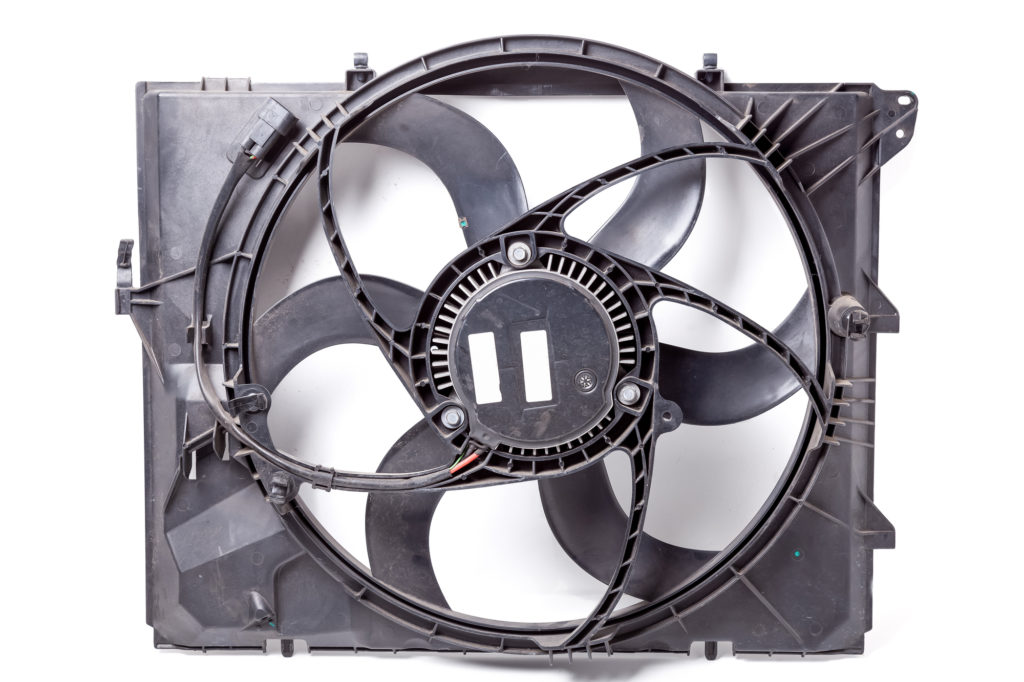

Radiator fans provide essential airflow to cool the radiator, particularly in slow-moving traffic. If a fan motor or relay fails, the radiator receives less airflow, causing the coolant to overheat, especially in warmer climates or at low speeds.
Coolant Reservoir
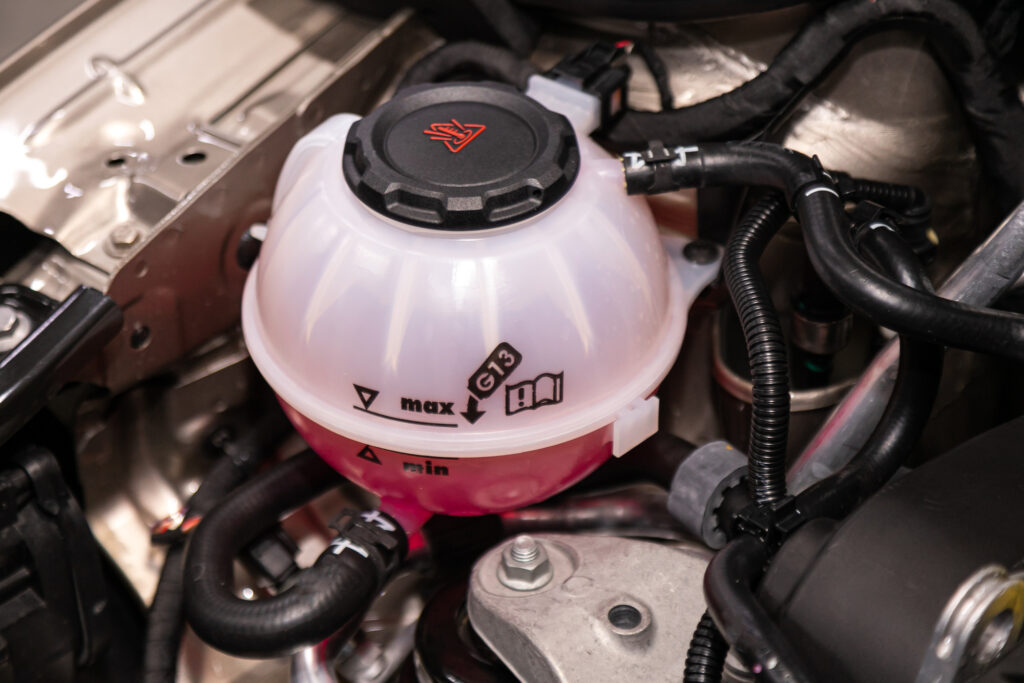

The coolant reservoir holds excess coolant expelled from the radiator during high temperatures. A damaged or leaking reservoir can lead to low coolant levels, reducing the cooling system’s efficiency and causing overheating.
Heater Core
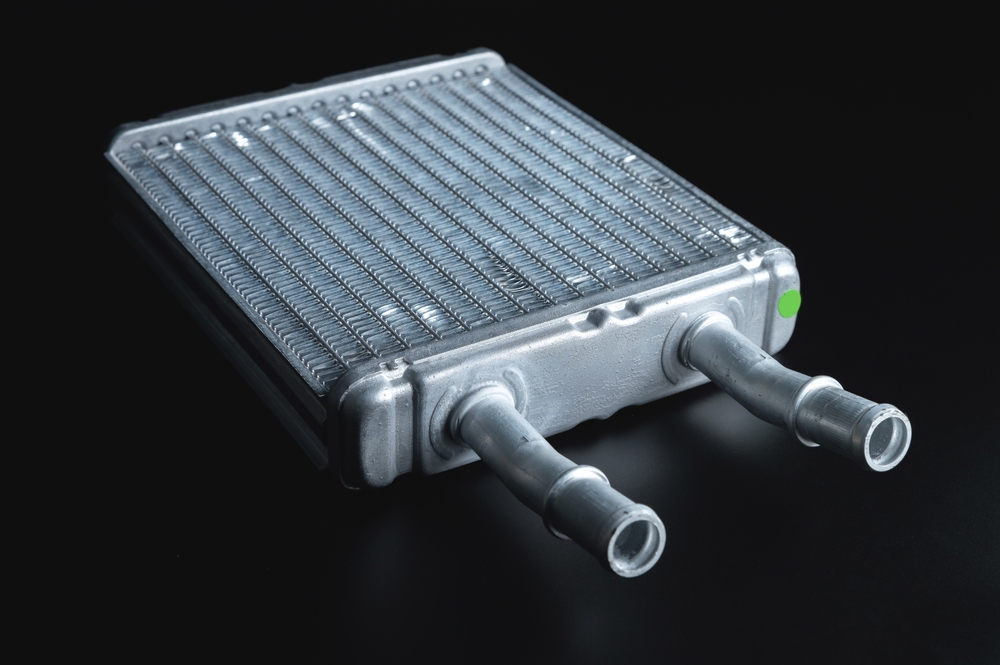

The heater core functions as a mini-radiator within the car’s heating system. When blocked or leaking, it affects overall coolant flow, leading to increased temperatures within the engine and a decline in heating efficiency.
Radiator Hoses
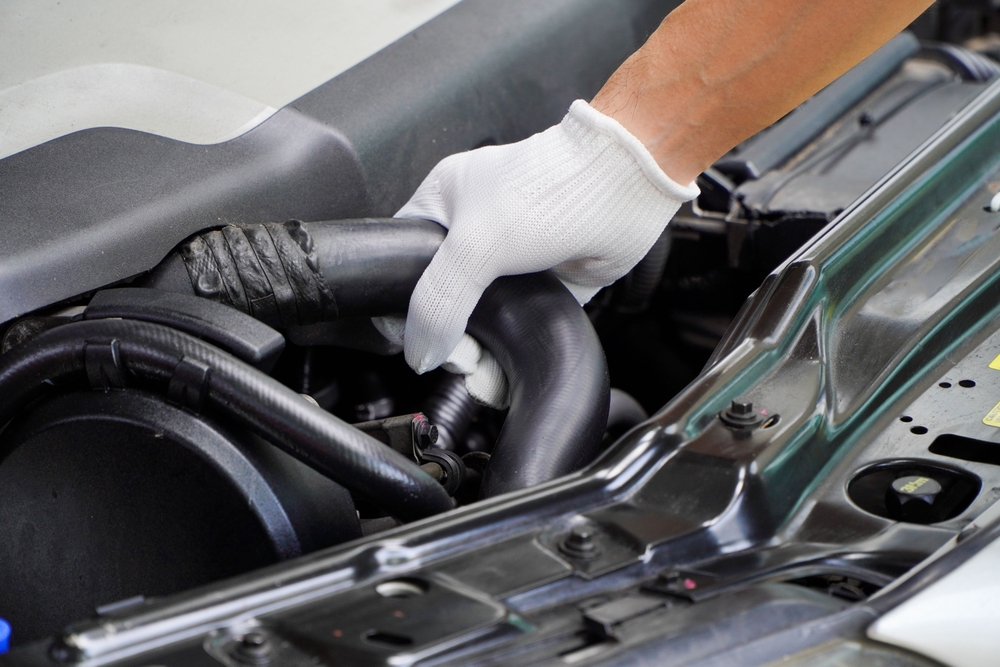

Radiator hoses transfer coolant between the engine, radiator, and other components. Hoses can become brittle, crack, or develop leaks over time, reducing coolant levels and causing potential overheating due to inadequate coolant flow.
Fan Clutch

The fan clutch controls the radiator fan’s speed based on engine temperature. A malfunctioning clutch can cause the fan to operate inadequately, leading to overheating during idle or slow driving conditions.
Thermostat Housing
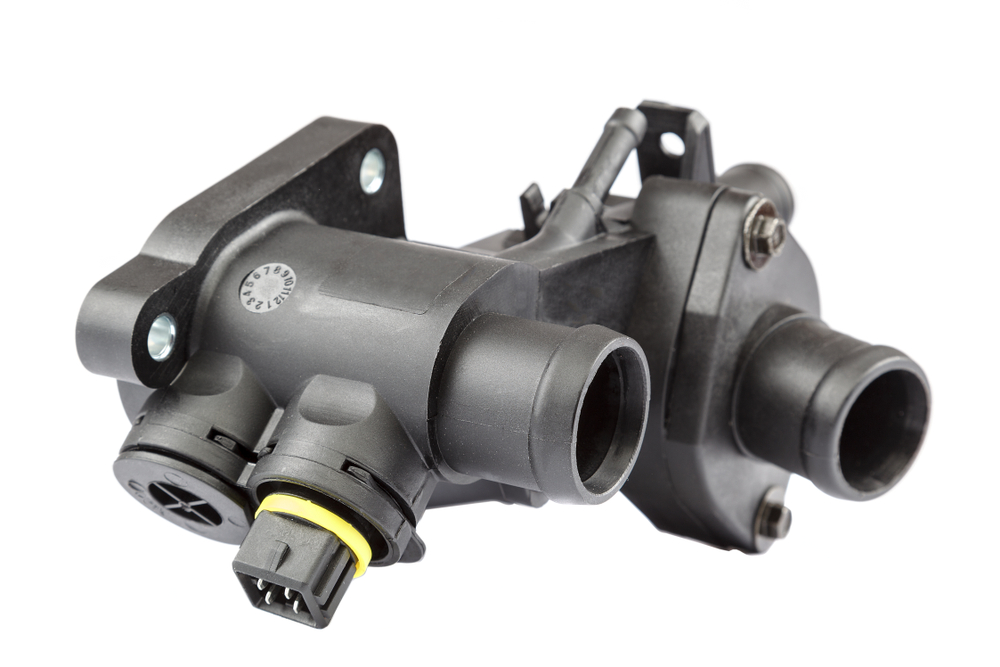

The thermostat housing encases the thermostat and provides a pathway for coolant flow. If the housing leaks or cracks, it can lead to coolant loss, which reduces the cooling system’s ability to regulate temperature.
Cooling System Pressure Cap
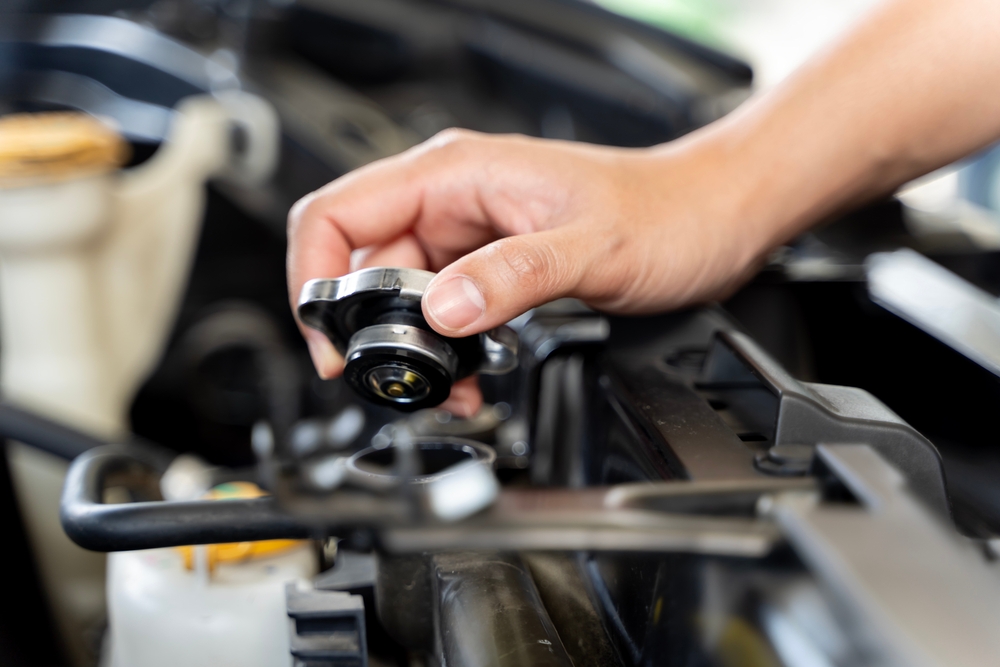

The pressure cap maintains system pressure to raise the boiling point of the coolant, preventing it from boiling over. A faulty cap can lower system pressure, allowing coolant to boil at lower temperatures and increasing the risk of overheating.
Cylinder Head Gasket
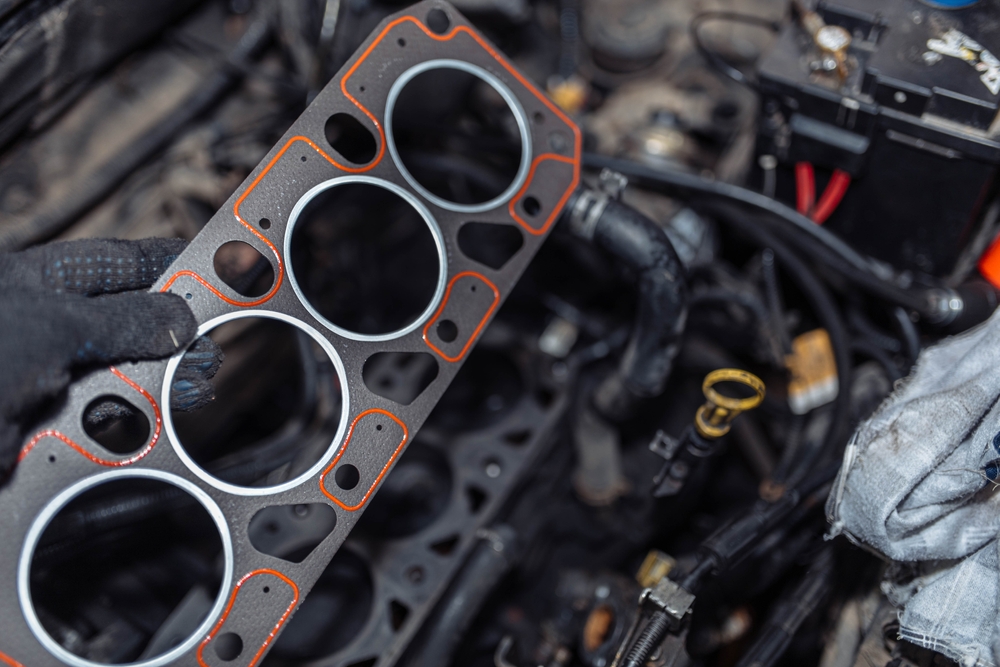
The head gasket seals the engine block and cylinder head, preventing coolant and oil from mixing. A blown gasket can allow coolant to enter the combustion chamber, reducing coolant levels and causing overheating.
Engine Block
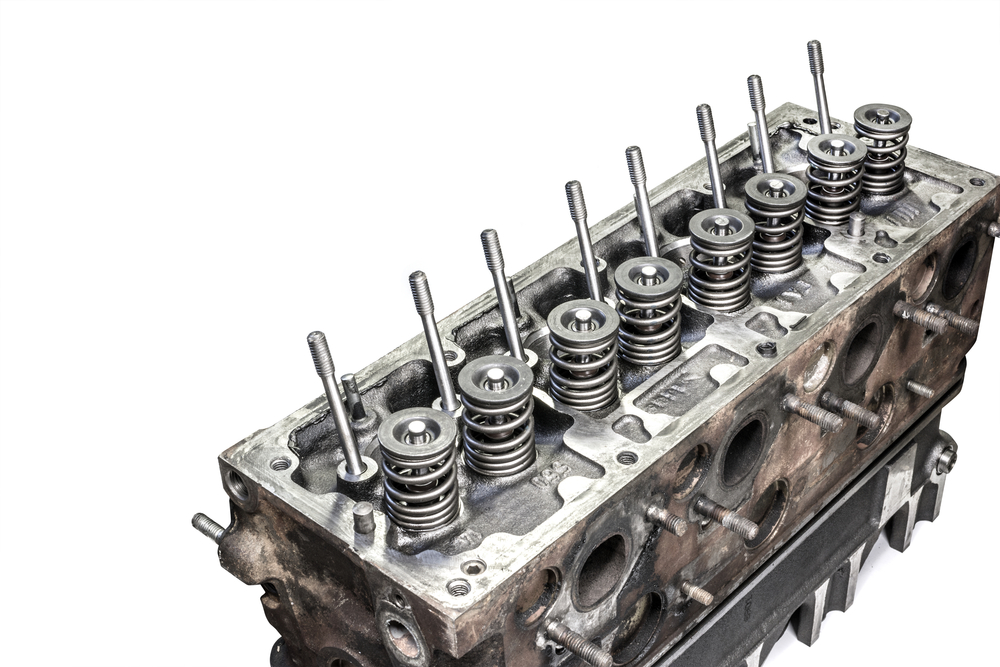
The engine block houses many components that rely on proper coolant flow. If there’s a blockage or crack within the engine block, it can obstruct coolant flow, causing localized hotspots and eventual overheating.
Radiator Cap
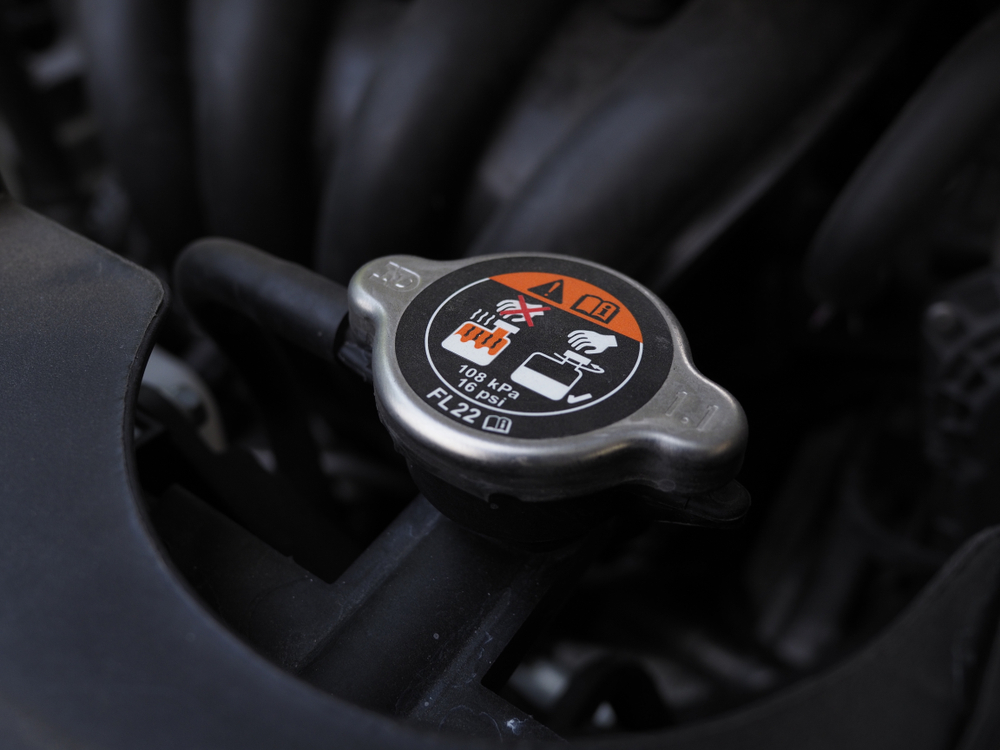

The radiator cap keeps the cooling system sealed under pressure. When compromised, it reduces pressure, which can lead to coolant boiling and escaping, ultimately causing a drop in coolant levels and an increased likelihood of overheating.
Oil Cooler
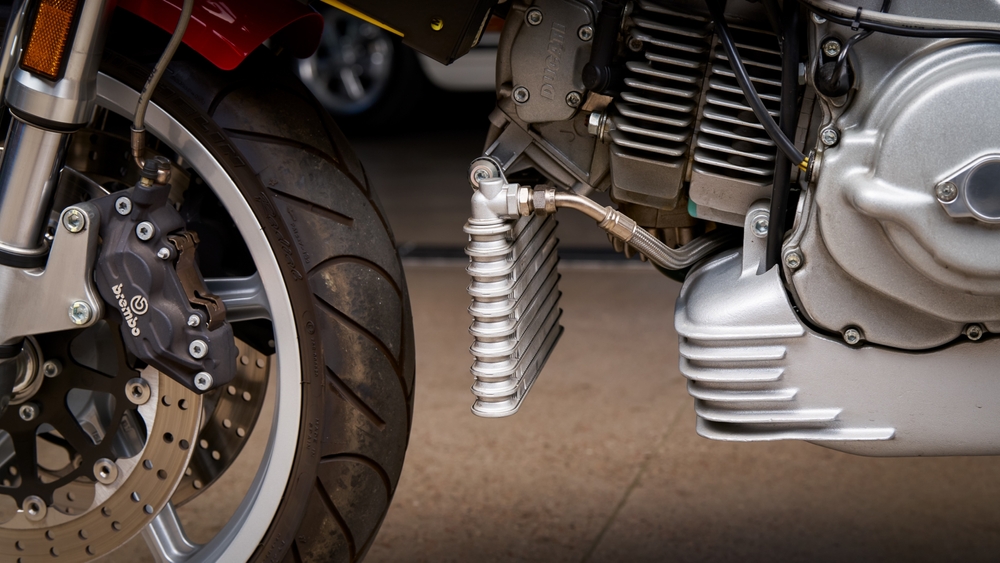

The oil cooler removes excess heat from engine oil, keeping both oil and engine temperatures stable. If the oil cooler fails, it can lead to elevated engine temperatures, stressing the cooling system further and potentially causing overheating.
Coolant Temperature Sensor
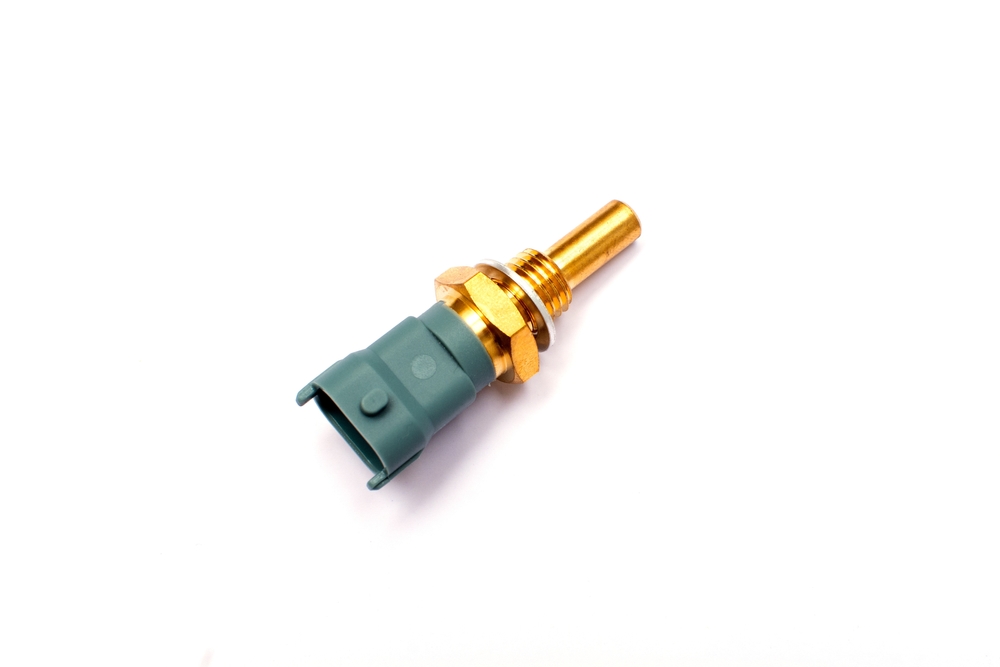

This sensor monitors coolant temperature, sending data to the engine control unit (ECU) to adjust cooling system components accordingly. A malfunctioning sensor may not trigger fans or alerts, leading to undetected overheating.
Head Gasket

Apart from sealing engine components, the head gasket prevents coolant from mixing with fuel or oil. A failure leads to reduced coolant levels, potentially causing overheating and more extensive engine damage.
Timing Belt
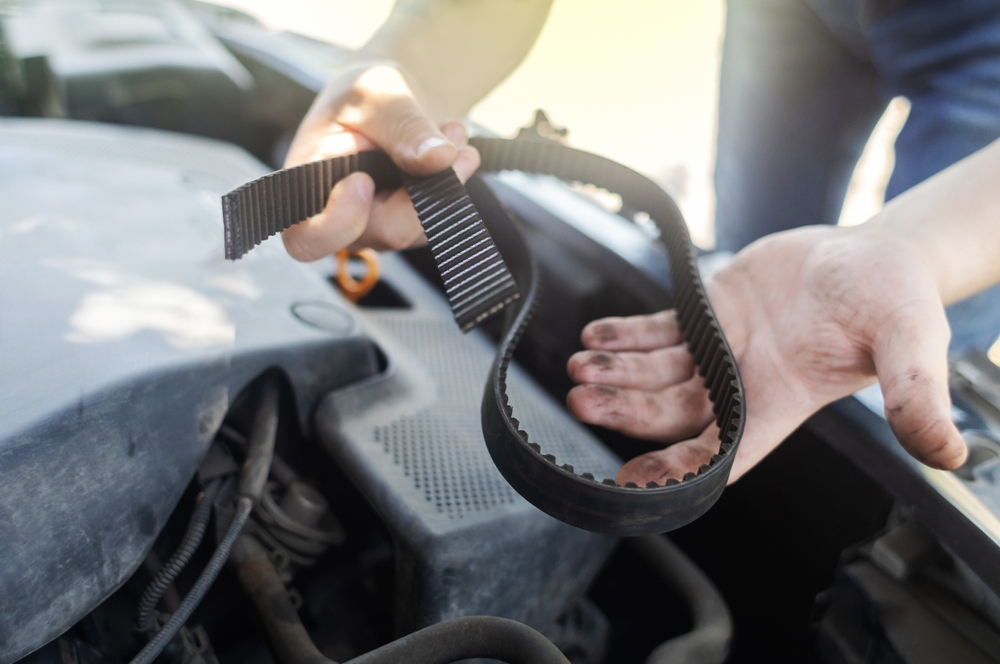

While not directly part of the cooling system, the timing belt drives the water pump on some engines. If the belt fails, the water pump stops circulating coolant, leading to a quick and severe overheating situation.
Intercooler (for Turbocharged Engines)

An intercooler cools compressed air in turbocharged engines. If it overheats or fails, it can increase the engine’s intake air temperature, putting extra strain on the cooling system and causing engine overheating.
This article originally appeared in MyCarMakesNoise.
More from MyCarMakesNoise
25 Iconic Race Cars That Redefined Speed and Style

Race cars are not just about speed and performance; they’re also about making a visual statement. From bold colors to sleek lines, some race cars stand out not only for their engineering but also for their striking looks. In this article, we’ll take a look at the 25 most eye-catching race cars in history that have turned heads both on and off the track. Read More
17 Legendary Railroad Museums Featuring Classic Locomotives

Railroad museums offer a fascinating glimpse into the history of trains, preserving the classic locomotives that once shaped travel and industry. From steam-powered giants to early electric engines, these museums bring rail history to life. Read More
17 Myths Surrounding the Longevity of Hybrid Vehicles

Hybrid vehicles have grown in popularity, yet there are still plenty of misconceptions about their longevity. These myths often cause unnecessary doubt for potential buyers. Here, we’ll address 17 common myths about hybrid vehicle durability and uncover the facts behind their reliable performance. Read More














