As electric vehicles (EVs) gain popularity as a greener transportation option, it’s essential to understand the complexities behind their environmental impact. While EVs are touted for their zero tailpipe emissions, a closer look reveals various ways in which their environmental footprint may be hidden or downplayed. From production processes to end-of-life management, exploring these aspects sheds light on the broader sustainability challenges associated with EV adoption.
Contents
Production of Batteries for EVs
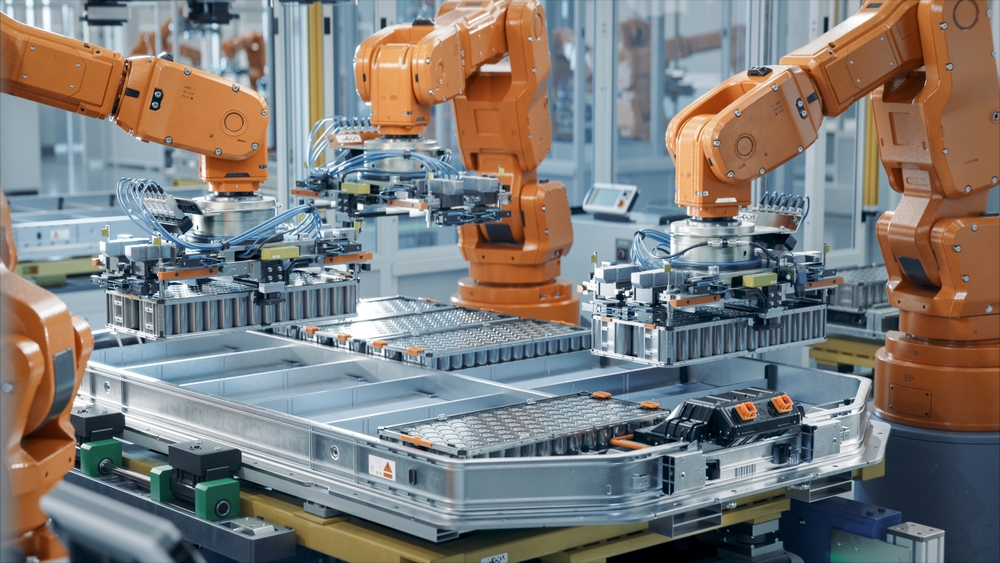
The production of batteries for electric vehicles (EVs) involves several complex and resource-intensive processes. For instance, lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly used in EVs, require the extraction of lithium, cobalt, nickel, and other materials. Mining these resources can lead to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution if not managed carefully. Additionally, the refining and processing of these raw materials often require significant energy inputs, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. Moreover, the disposal of battery production waste, such as chemicals and metals, can further impact ecosystems and human health if not handled properly.
Tire Wear and Tear
While electric vehicles (EVs) are known for their zero tailpipe emissions, they are not immune to environmental impacts related to vehicle operation. Like traditional vehicles, EVs experience tire wear and tear during use. This wear releases microplastics, rubber particles, and particulate matter into the environment. These pollutants can accumulate in soil, water bodies, and the air, posing risks to wildlife and human health. Furthermore, the disposal of worn-out tires adds to the overall waste generated by the automotive industry, highlighting the need for sustainable tire recycling practices.
Carbon Emissions in Producing Electricity for EVs
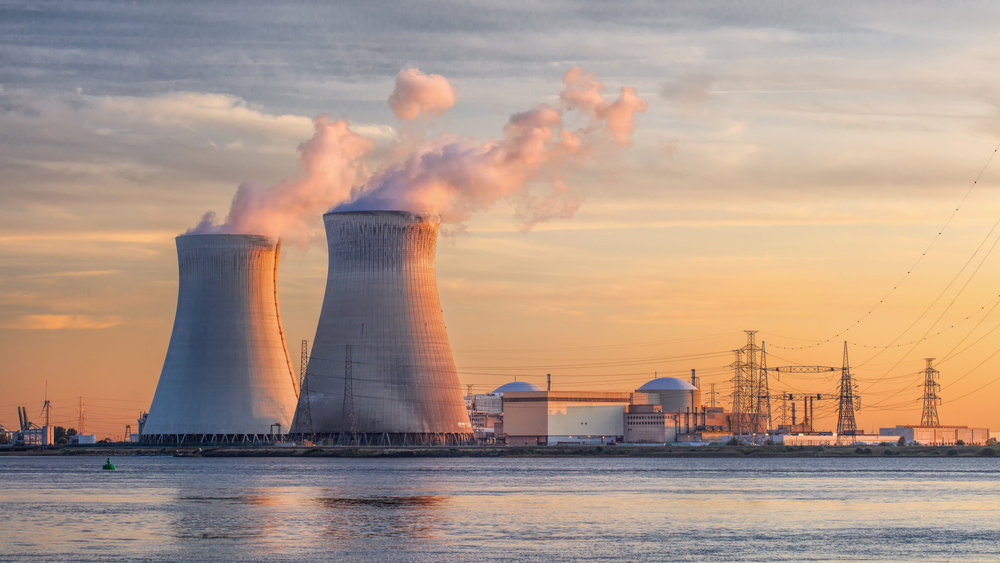

One of the key arguments for electric vehicles (EVs) is their potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to internal combustion engine vehicles. However, the environmental impact of EVs is not solely determined by their tailpipe emissions. The electricity used to charge EVs often comes from power plants, which may rely on fossil fuels like coal, natural gas, or oil. As a result, the production of electricity for EVs can still contribute to carbon emissions and air pollution. To maximize the environmental benefits of EVs, a transition to renewable energy sources for electricity generation is crucial.
Rare-Earth Components for EV Batteries

Electric vehicle (EV) batteries, particularly those using lithium-ion technology, often contain rare-earth elements such as neodymium, dysprosium, and cobalt. These elements are essential for battery performance but are challenging to extract and refine. The mining and processing of rare-earth materials can have significant environmental impacts, including habitat destruction, water contamination, and soil pollution. Furthermore, the geopolitical implications of rare-earth element supply chains highlight the need for sustainable sourcing practices and efforts to reduce dependency on these materials in battery manufacturing.
Harmful Fumes Produced by EV Batteries
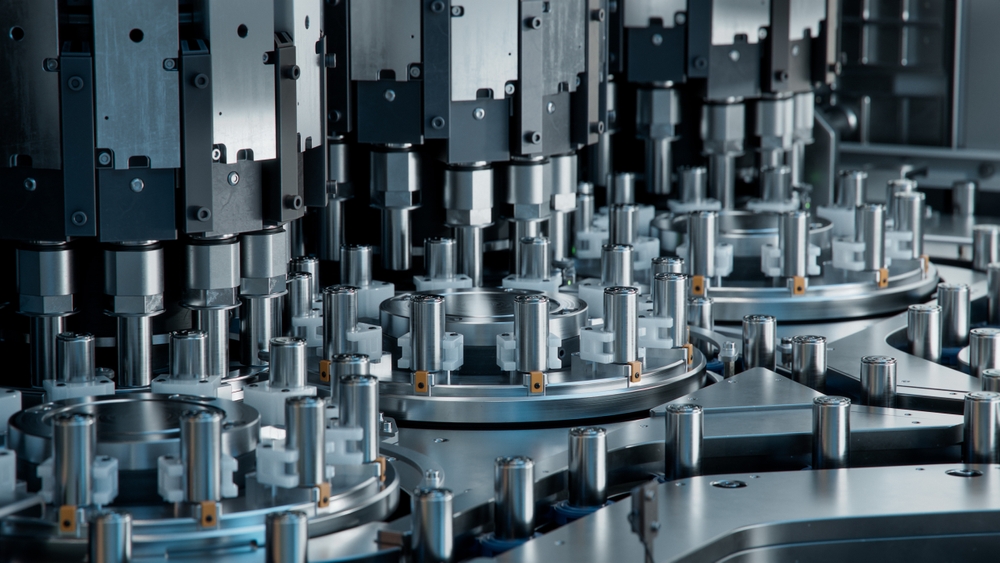

During the production of electric vehicle (EV) batteries, various chemical processes are involved, which can lead to the emission of harmful fumes and pollutants if not properly controlled. For example, the manufacturing of lithium-ion batteries may release sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particulate matter into the air. Exposure to these pollutants can have adverse effects on air quality and human health, particularly for workers in battery production facilities and surrounding communities. Implementing stringent emissions controls and sustainable manufacturing practices is essential to mitigate these environmental risks.
EV Battery Disposal
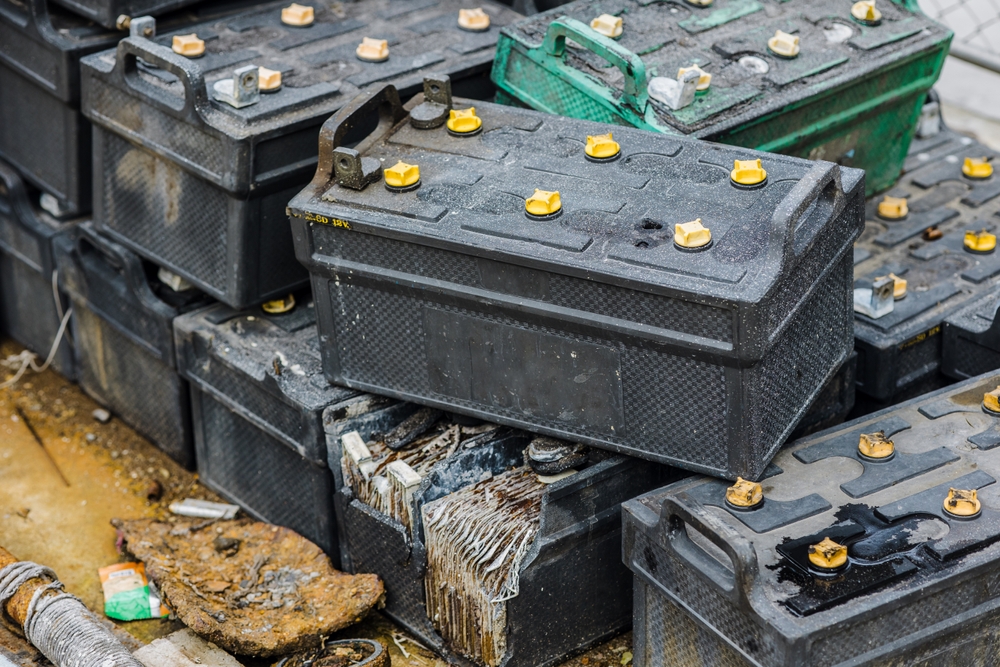

The disposal of electric vehicle (EV) batteries presents unique environmental challenges due to their composition and potential for toxic elements. While EV batteries are designed to last for many years, they eventually reach the end of their usable life and require proper disposal or recycling. Improper disposal methods can lead to soil and water contamination, as well as risks of exposure to heavy metals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel. Developing efficient and environmentally sound battery recycling technologies and infrastructure is crucial to minimize the environmental impact of EV battery disposal.
Infrastructure Development
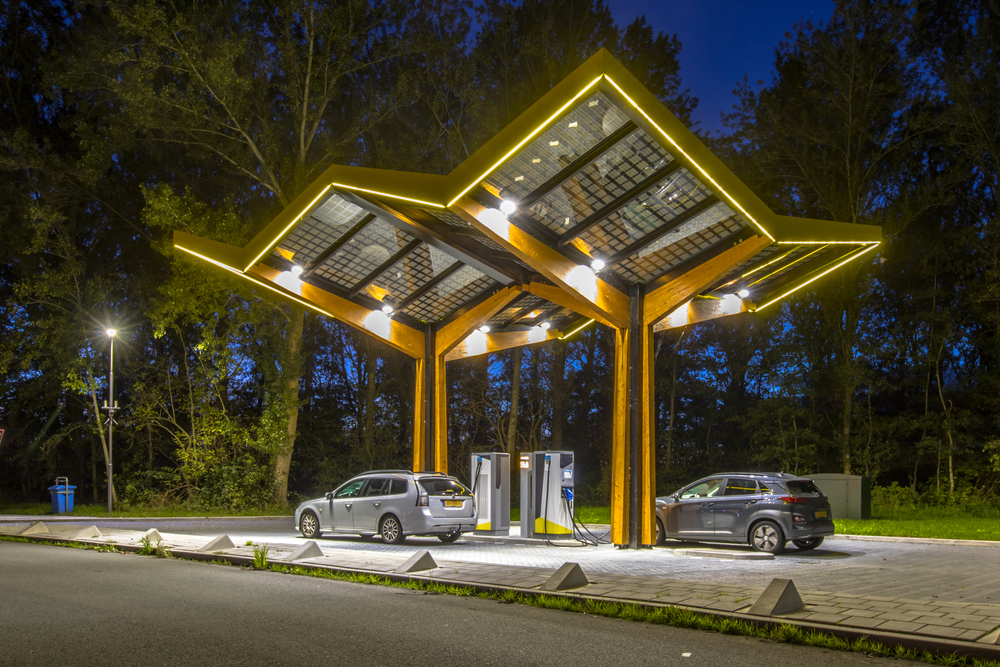

The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) necessitates the development of infrastructure, including charging stations and grid upgrades. While these initiatives support the transition to cleaner transportation, they also have environmental implications. The construction and maintenance of charging infrastructure can lead to land use changes, habitat disruption, and energy consumption. Moreover, the extraction of materials for infrastructure development, such as metals for charging stations and transmission lines, can contribute to environmental degradation if not managed sustainably.
Water Usage
The production and operation of electric vehicles (EVs) involve significant water usage throughout their lifecycle. For instance, battery manufacturing requires water for cooling and chemical processes. Additionally, charging EVs at home or public charging stations indirectly consumes water through electricity generation and distribution. In regions already facing water scarcity or pollution issues, the water footprint of EVs must be carefully considered and managed to minimize environmental impacts on freshwater ecosystems and communities.
Supply Chain Emissions

The global supply chain for electric vehicles (EVs) encompasses various stages, from raw material extraction to vehicle assembly and distribution. Each stage involves transportation, manufacturing, and energy consumption, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and environmental impacts. The sourcing of materials from distant locations, along with the logistics of component delivery and vehicle distribution, adds to the carbon footprint of EVs. Promoting sustainable supply chain practices, including local sourcing, efficient logistics, and emissions reduction strategies, is essential for mitigating these environmental challenges.
End-of-Life Vehicle Management
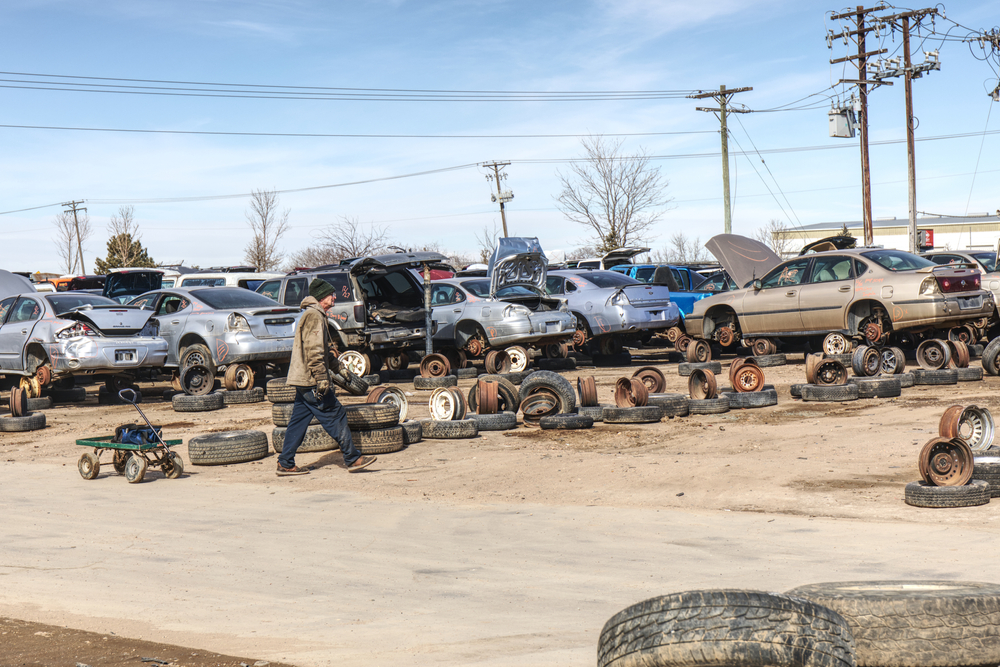

Managing electric vehicles (EVs) at the end of their life cycle involves challenges related to dismantling, recycling, and disposal. EV batteries, in particular, require proper handling due to their chemical composition and potential for hazardous waste. Without effective end-of-life vehicle management practices, the environmental impact of EVs can increase, including risks of soil contamination, water pollution, and resource depletion. Developing comprehensive policies, regulations, and recycling initiatives for EVs and their components is essential for sustainable vehicle lifecycle management.
This article originally appeared on MyCarMakesNoise.
More from MyCarMakesNoise
10 Benefits of Driving Hybrids Over Conventional Cars

As the tides turn against conventional gasoline engines, the allure of hybrids goes beyond just being eco-friendly. Read More.
10 Must-Have Motorcycle Accessories for Comfort and Protection

This article delves into those often overlooked essentials that not only elevate the riding experience but also ensure safety and convenience at every twist and turn. Read More.
The 14 Most Fuel-Saving Motorcycles

As urban landscapes continue to expand and roads become increasingly congested, the need for practical and sustainable transportation solutions is more pressing than ever. Enter the realm of fuel-efficient motorcycles, a blend of innovation, performance, and economy that answers the daily commute dilemma. Read More.














