Climate change is reshaping industries worldwide, and the fossil fuel sector is no exception. From regulatory pressures to technological advancements in renewable energy, the impact is profound. This article explores 12 ways in which climate change is influencing the fossil fuel industry, highlighting the challenges and changes companies face as they navigate this new landscape.
Contents
Regulatory Pressures and Policy Changes

Governments worldwide are enacting stringent regulations to curb carbon emissions, which directly impact the fossil fuel industry. Carbon pricing, emissions trading systems, and stricter environmental standards increase operational costs for fossil fuel companies. These regulations aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions while promoting renewable energy sources
Shift in Investor Preferences
Investors are increasingly prioritizing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, leading to divestment from fossil fuel companies. Major financial institutions and pension funds are moving their investments towards sustainable and green energy projects. This trend limits capital availability for fossil fuel enterprises, compelling them to seek alternative funding or restructure their business models.
Technological Advancements in Renewable Energy

The rapid advancement and decreasing costs of renewable energy technologies, such as solar and wind power, are rendering fossil fuels less competitive. Innovations in energy storage and grid management further enhance the reliability of renewables. As a result, fossil fuel companies are losing market share to cleaner energy alternatives.
Insurance and Risk Management Costs

Climate change-related natural disasters, such as hurricanes and wildfires, are becoming more frequent and severe. This trend raises insurance premiums for fossil fuel infrastructure and operations, adding to the industry’s financial burdens. Additionally, companies must invest in more robust risk management and resilience measures.
Market Volatility and Price Fluctuations

Climate change introduces new levels of market volatility, with fluctuating weather patterns affecting supply and demand for fossil fuels. Extreme temperatures can disrupt production and transportation while transitioning energy policies create uncertain market conditions. This volatility complicates long-term planning and investment strategies for fossil fuel companies.
Operational Disruptions and Infrastructure Damage
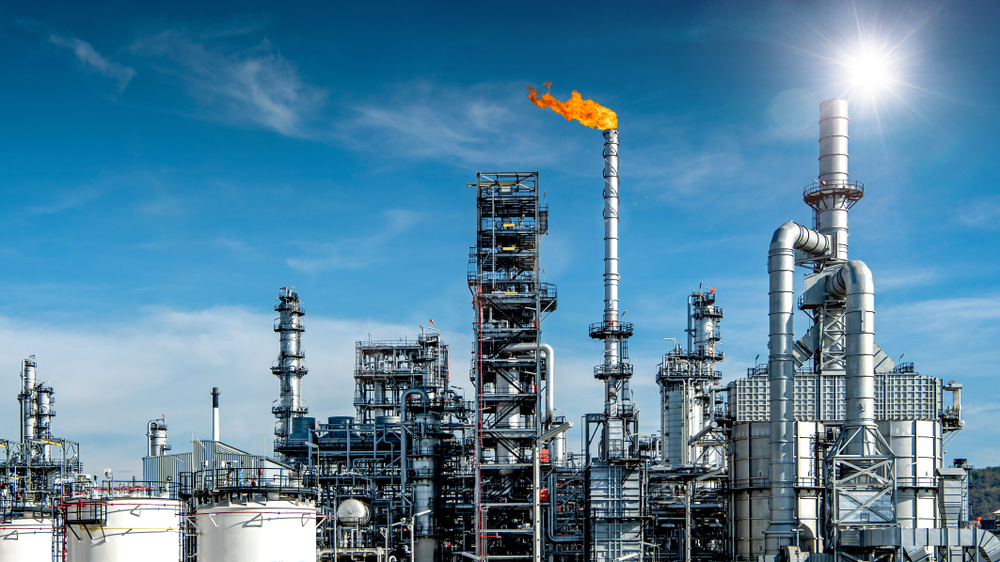

Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and floods, can cause severe damage to fossil fuel infrastructure, including refineries, pipelines, and drilling rigs. These disruptions lead to production halts, increased maintenance costs, and potential safety hazards. Companies must invest heavily in fortifying their assets against climate-related risks.
Competition from Electrification
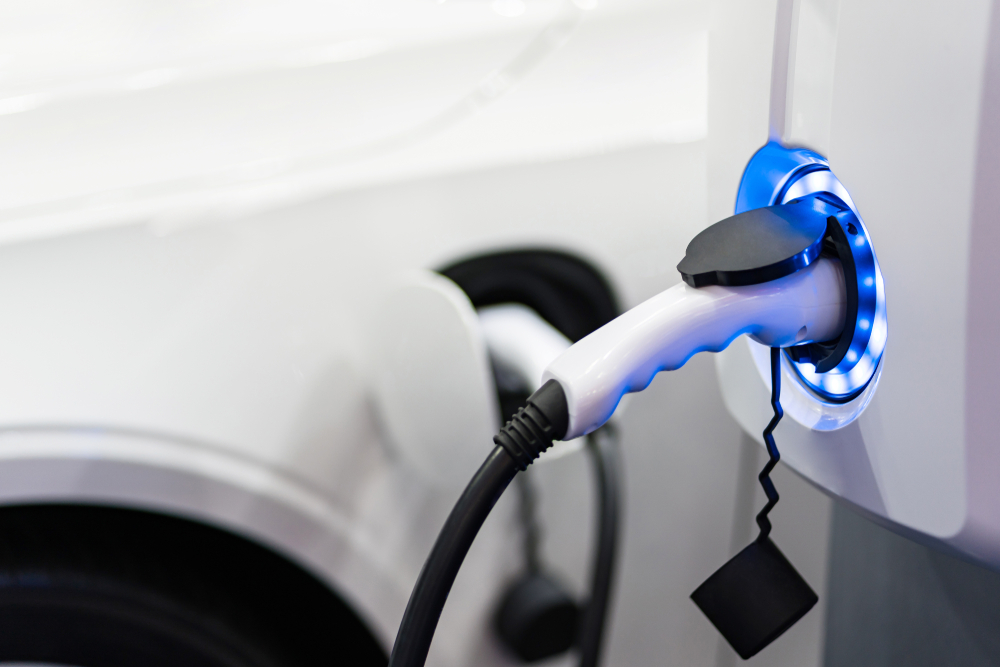

The transportation sector, a major consumer of fossil fuels, is rapidly shifting towards electrification. Electric vehicles (EVs) are gaining popularity due to technological advancements and supportive government policies. As the adoption of EVs accelerates, demand for gasoline and diesel is expected to decline.
Changes in Global Trade Dynamics

Climate policies and carbon tariffs are reshaping global trade dynamics, affecting the competitiveness of fossil fuel exports. Countries with stringent climate regulations may impose tariffs on carbon-intensive imports, disadvantaging fossil fuel exporters. This shift requires fossil fuel companies to reassess their market strategies.
Reduction in Energy Demand

Energy efficiency measures and the rise of renewable energy sources are reducing the overall demand for fossil fuels. Advances in technology and changes in consumer behavior are driving more efficient energy use across sectors. This trend challenges fossil fuel companies to diversify their energy portfolios.
Financial Risks from Carbon Pricing

The implementation of carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems, directly impacts the profitability of fossil fuel companies. These mechanisms incentivize reductions in carbon emissions, raising the cost of fossil fuel production and consumption. Companies must adapt by investing in cleaner technologies or face declining profit margins.
Impact on Workforce and Employment

The transition to a low-carbon economy affects employment within the fossil fuel industry. Job losses in traditional fossil fuel sectors may be offset by new opportunities in renewable energy and green technologies. Companies must navigate this transition, ensuring workforce retraining and supporting communities reliant on fossil fuel employment.
Rising Cost of Capital

As financial markets increasingly factor in climate risks, the cost of capital for fossil fuel projects is rising. Lenders and investors are demanding higher returns for perceived risks associated with fossil fuel investments. This trend complicates financing for new projects and may accelerate the shift towards renewable energy investments.
This article originally appeared on MyCarMakesNoise.
More from MyCarMakesNoise
13 Least Reliable Cars on the Market

When it comes to choosing a vehicle, reliability is often at the top of the list for most buyers. A car that consistently performs well without frequent visits to the repair shop is what everyone hopes for. Read More.
15 Underrated Luxury Cars That Are Worth Every Penny

In the world of luxury vehicles, certain brands and models often steal the spotlight, leaving other equally impressive options in the shadows. However, for discerning buyers looking to invest in a luxury car that stands out from the crowd, many less-known models offer exceptional value. Read More.
12 Legendary Race Cars Still Competing

In the world of motorsport, certain race cars transcend their time, leaving an indelible mark on the track and in the hearts of racing enthusiasts. These legendary machines, known for their groundbreaking performance and engineering, have not only dominated in their prime but continue to compete, proving their enduring prowess. Read More.














