The rise of green technologies, especially electric vehicles (EVs), offers hope for fighting climate change. However, there are hidden costs that are often ignored, including environmental damage and social effects. This article explores the complex issues related to mining the critical minerals needed for these technologies, providing a comprehensive view of the challenges.
Contents
Environmental Degradation
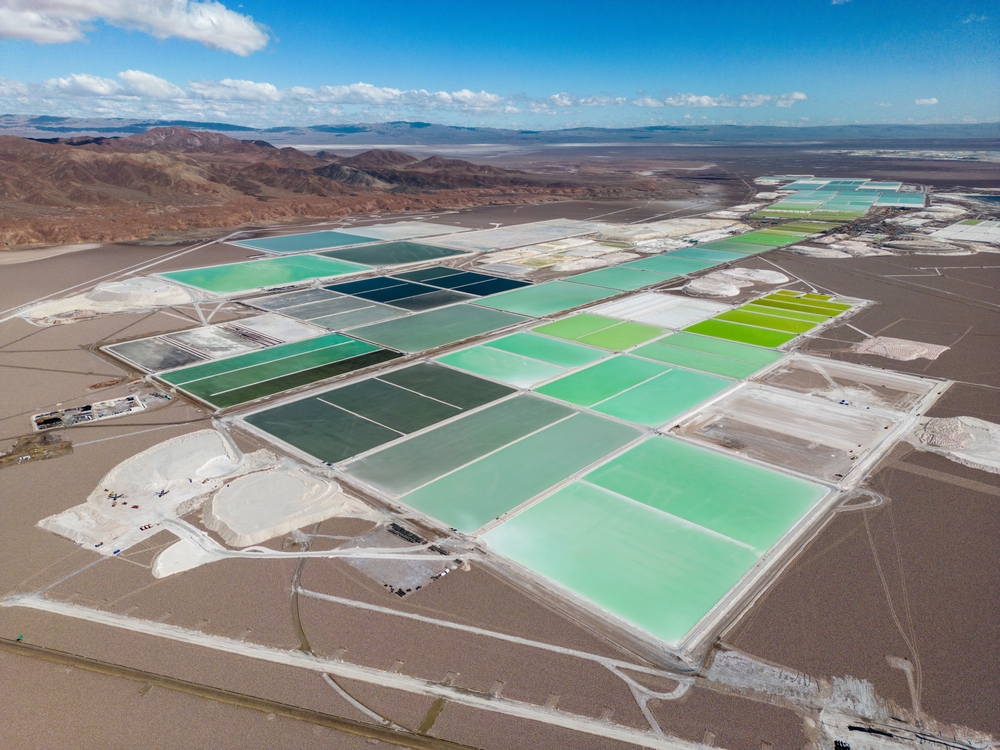

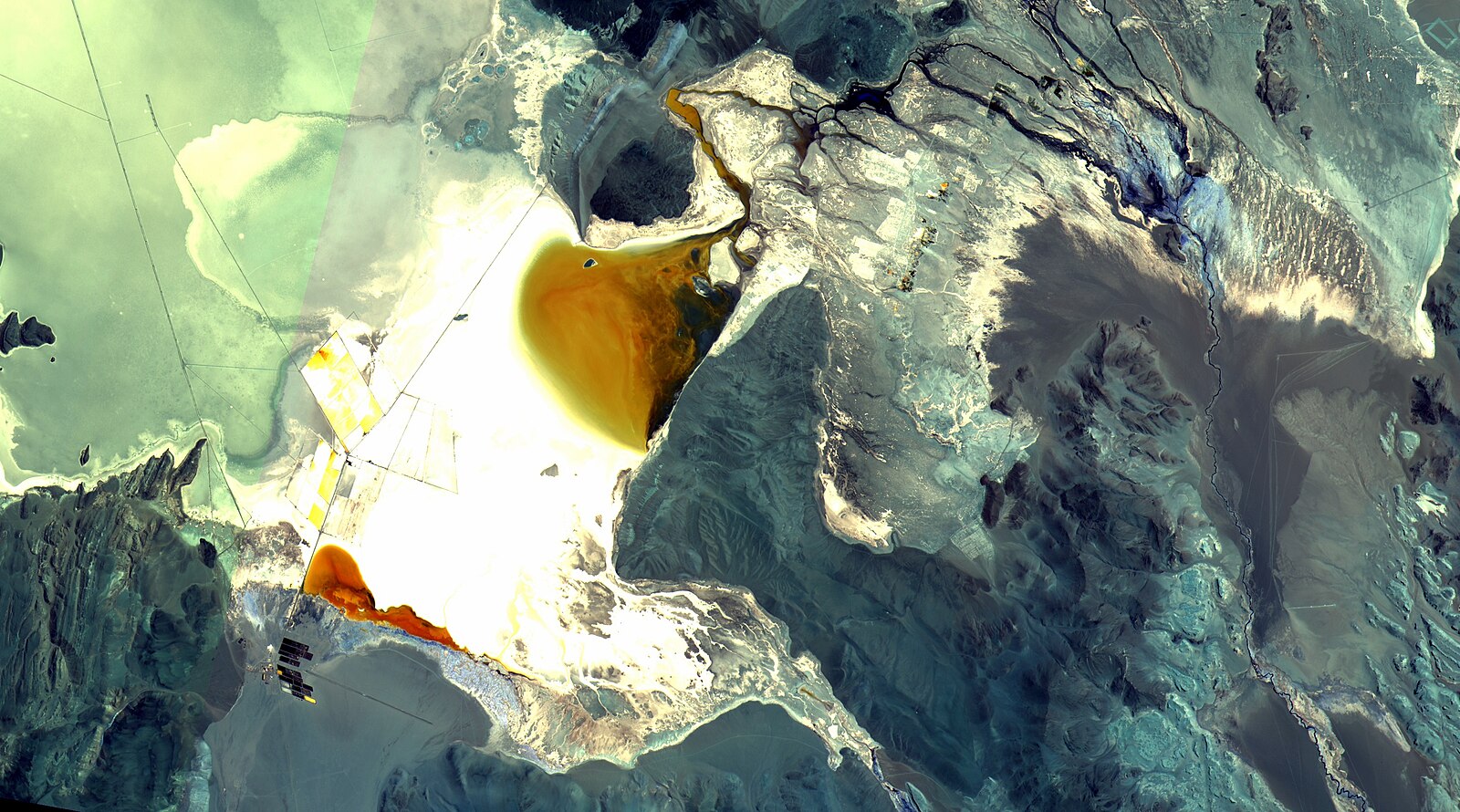
One of the major downsides of lithium mining is the significant environmental degradation it can cause. Mining activities often involve the removal of vast amounts of soil and rock, which can result in habitat destruction and loss of biodiversity. According to the United States Geological Survey, the extraction process can also contaminate soil, groundwater, and surface water with chemicals from the mining process.
Water Consumption
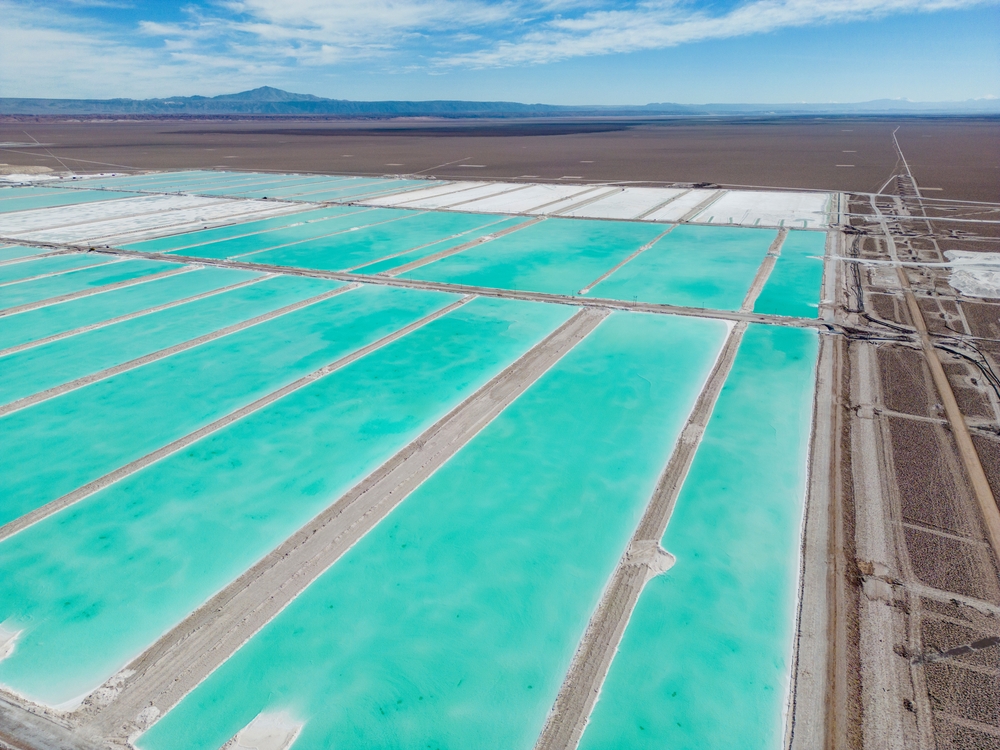

Lithium extraction, particularly through the method of lithium brine, requires enormous quantities of water. This can strain local water resources and potentially lead to water scarcity in already arid regions. A Friends of the Earth Europe report noted that extracting a ton of lithium from the Salar de Atacama in Chile consumes 65,000 liters of water, which significantly affects the local water supply.
Air Pollution

The mining and processing of lithium can lead to air pollution. The extraction process releases dust and harmful chemicals into the atmosphere, potentially affecting air quality and contributing to climate change. According to a study published in the journal Environmental Science & Technology, lithium production releases a significant amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases.
Soil Contamination

Lithium mining can lead to soil contamination, as it introduces heavy metals and other toxic substances into the ground. These substances can have detrimental effects on flora and fauna, potentially causing long-term damage to ecosystems. The process can alter the soil structure and fertility, impacting agriculture and natural vegetation in the surrounding areas.
Negative Impact on Local Communities
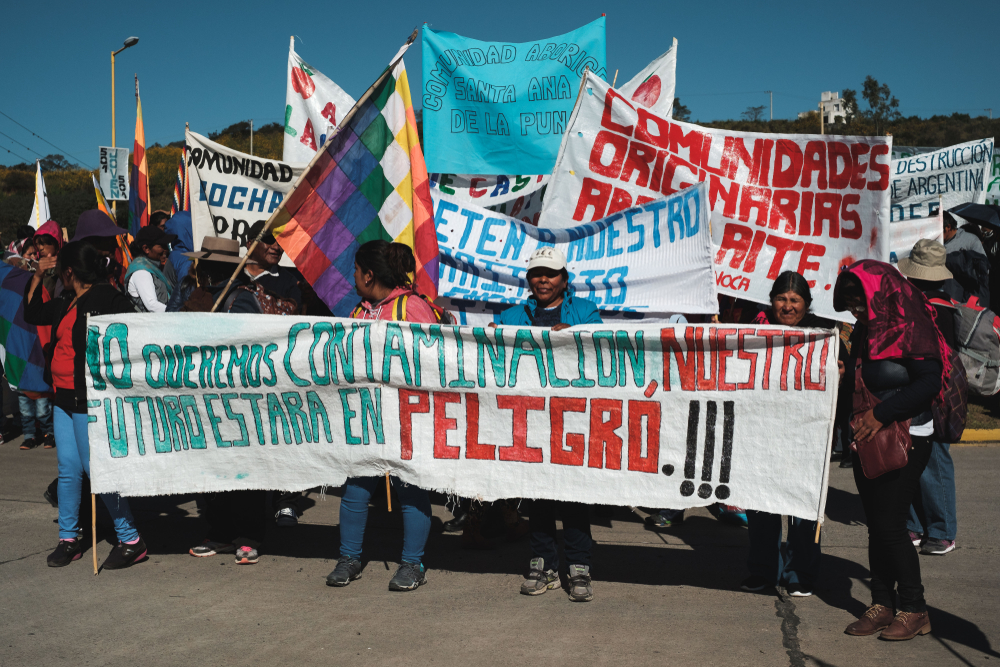

Local communities often bear the brunt of the negative impacts associated with lithium mining. Besides environmental degradation, these communities might face health issues due to exposure to pollutants and economic disparities, as the benefits of mining are not always evenly distributed. The Guardian has reported on the tensions and conflicts between mining companies and local communities, particularly in countries like Argentina.
Resource Scarcity and Geopolitical Tensions

The increasing demand for lithium, driven by the EV boom, could lead to resource scarcity and geopolitical tensions. As identified by the World Economic Forum, there are concerns that the competition for lithium resources might intensify in the coming years, potentially fostering conflicts and geopolitical tensions.
Habitat Destruction

Lithium mining often necessitates extensive land use, which can lead to habitat destruction. This is particularly concerning in areas home to endangered or endemic species. The degradation of natural habitats can lead to a loss of biodiversity, as species lose their homes and struggle to survive, according to reports by environmental organizations such as WWF.
Human Health Concerns
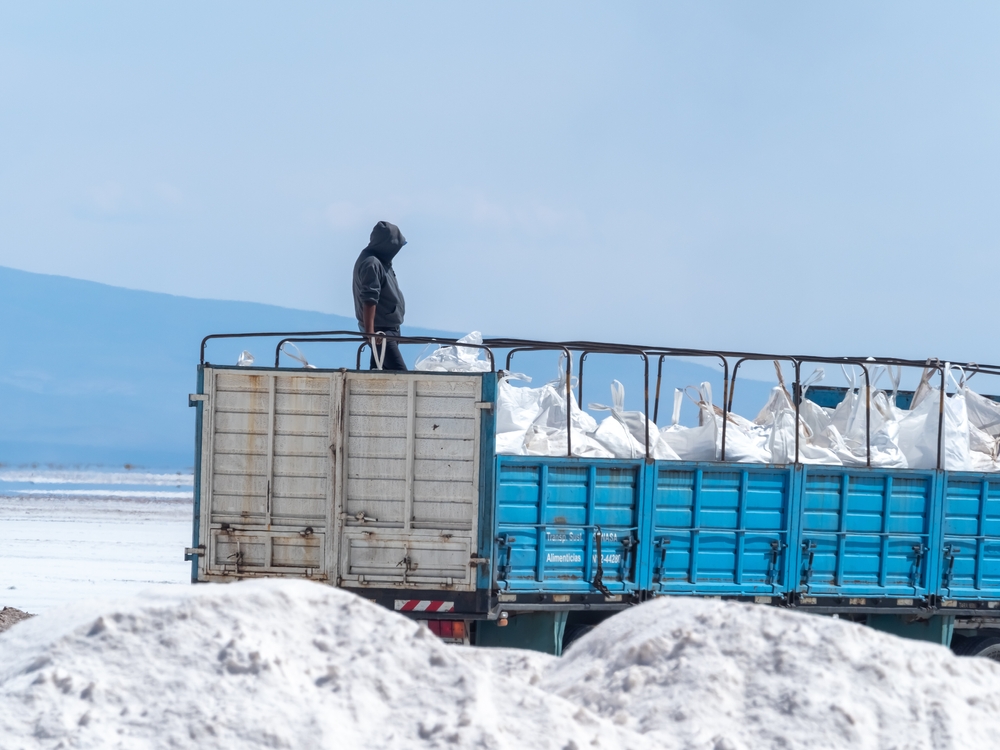

The extraction and processing of lithium can pose health risks to workers and nearby communities. Exposure to lithium can have adverse effects on the human respiratory system and skin. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), chronic exposure to lithium can lead to pulmonary conditions and other health issues.
Economic Instability Due to Market Fluctuations

The lithium market is subject to price volatility and fluctuations, which can cause economic instability in countries that heavily rely on lithium exports. According to a report by Reuters, the lithium market has experienced significant price swings, affecting the economies of lithium-producing countries.
High Energy Consumption in Production

The production of lithium is energy-intensive, requiring substantial amounts of energy to extract and process the metal. This high energy consumption contributes to the overall carbon footprint of electric vehicles, somewhat counteracting the environmental benefits of transitioning to EVs. A study in the journal “Nature Communications” indicated that the carbon footprint of lithium-ion batteries is quite significant, largely due to the energy-intensive production process.
Ecosystem Disruption

The disruption of local ecosystems is a major concern in areas where lithium is mined. In regions like the Atacama Desert, the extraction process can alter the natural drainage patterns, affecting plant and animal life that depend on these water sources. To mitigate such impacts, companies can adopt more sustainable mining practices that involve minimal water usage and rehabilitate ecosystems post-mining.
Cultural Heritage Impact

Lithium mining can also affect indigenous communities whose lands overlap with mining sites. These communities may face disruptions to their traditional ways of life and loss of access to ancestral lands. Strengthening the enforcement of corporate social responsibility policies and ensuring community consent and participation in mining projects can help protect cultural heritage.
Economic Dependency
Regions that depend heavily on lithium mining for economic growth can experience economic instability due to market fluctuations in lithium prices. Diversifying local economies and developing other sustainable income sources can reduce this dependency.
Land Scarcity
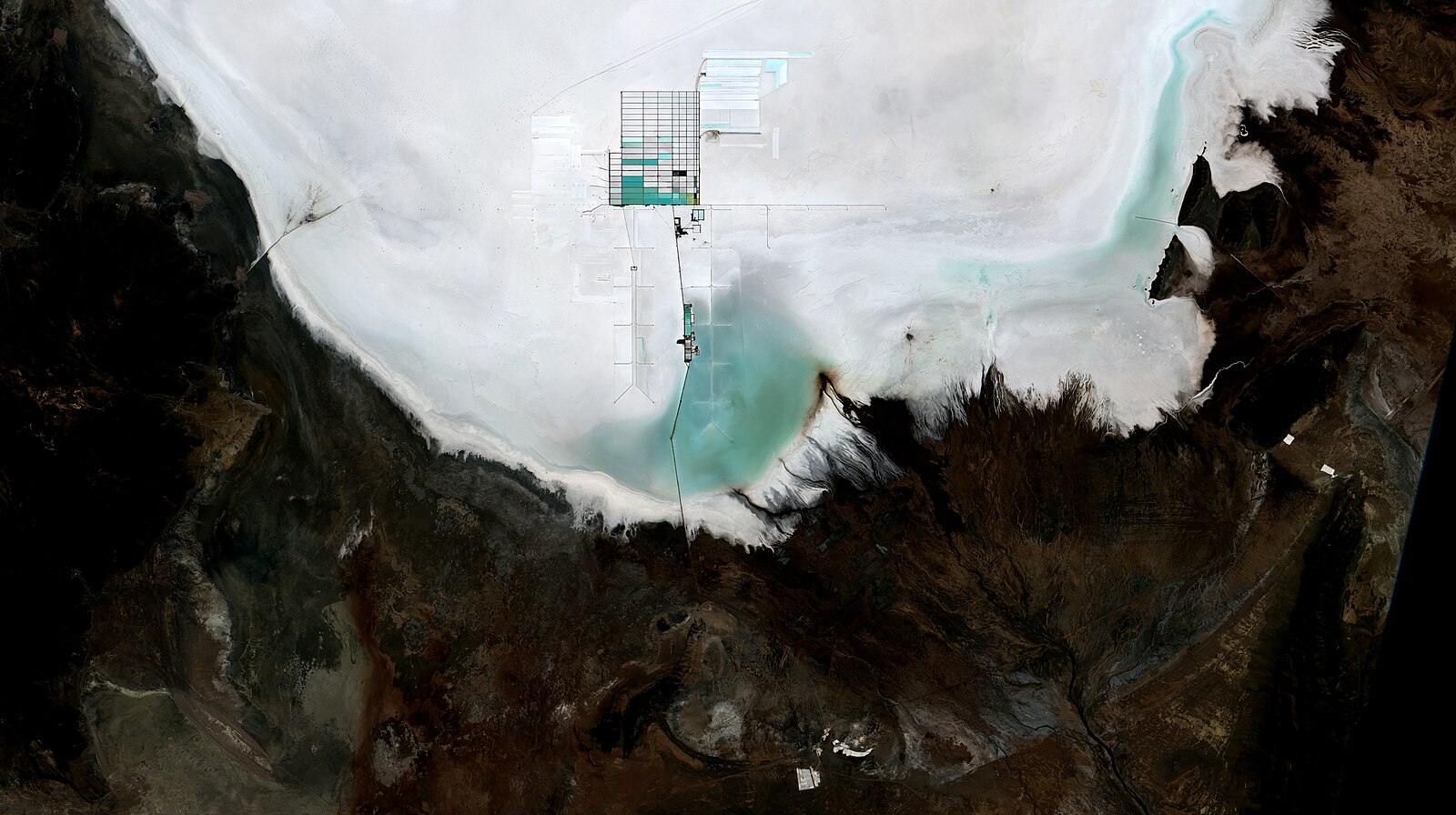

The expansion of lithium mining operations can lead to land scarcity for local agriculture, driving up land prices and displacing farmers. Implementing strict land use policies that prioritize agricultural and residential land use over industrial can help manage this issue.
Chemical Leaks and Spills

The mining and processing of lithium involve hazardous chemicals, which can leak or spill, contaminating local environments. Regular monitoring, stringent regulatory compliance, and having emergency containment strategies in place can reduce the risks of chemical accidents.
Noise Pollution
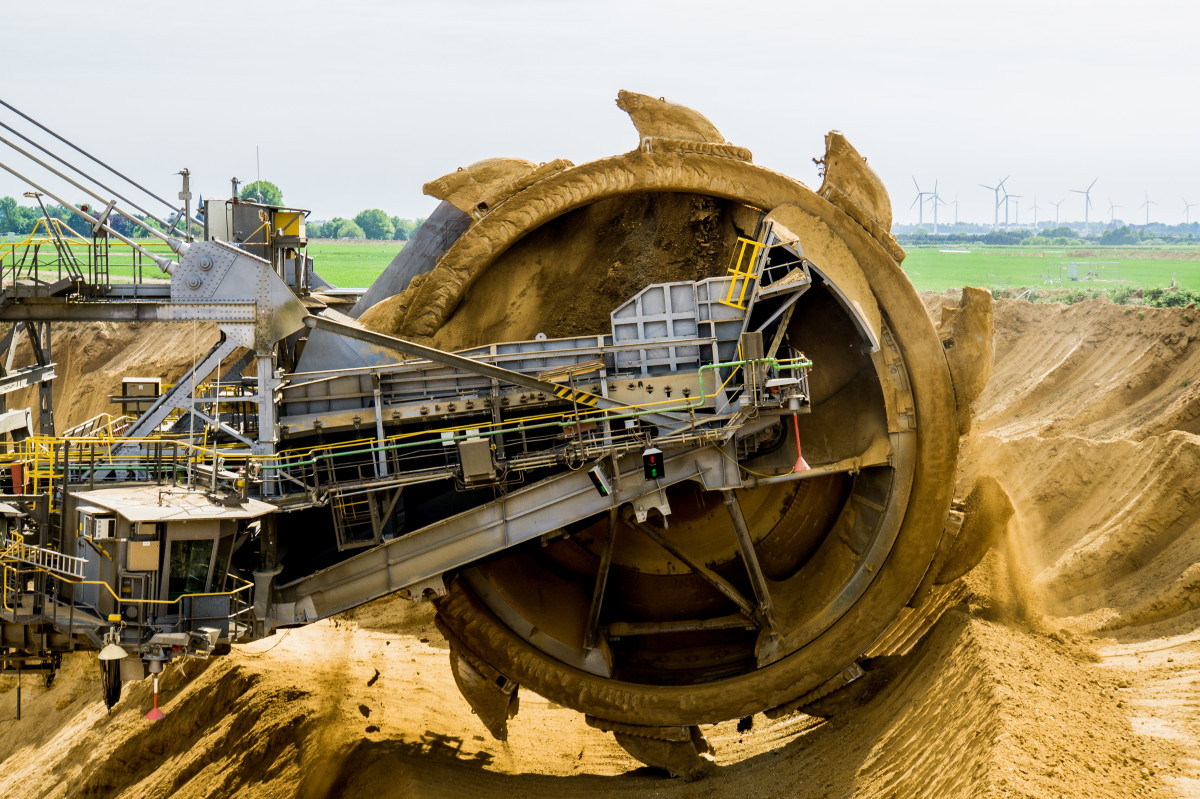

Lithium mining operations often generate significant noise, which can disturb both human populations and wildlife nearby. Employing noise reduction technologies and setting up buffer zones around populated areas can help minimize noise pollution.
Energy Use in Material Transport
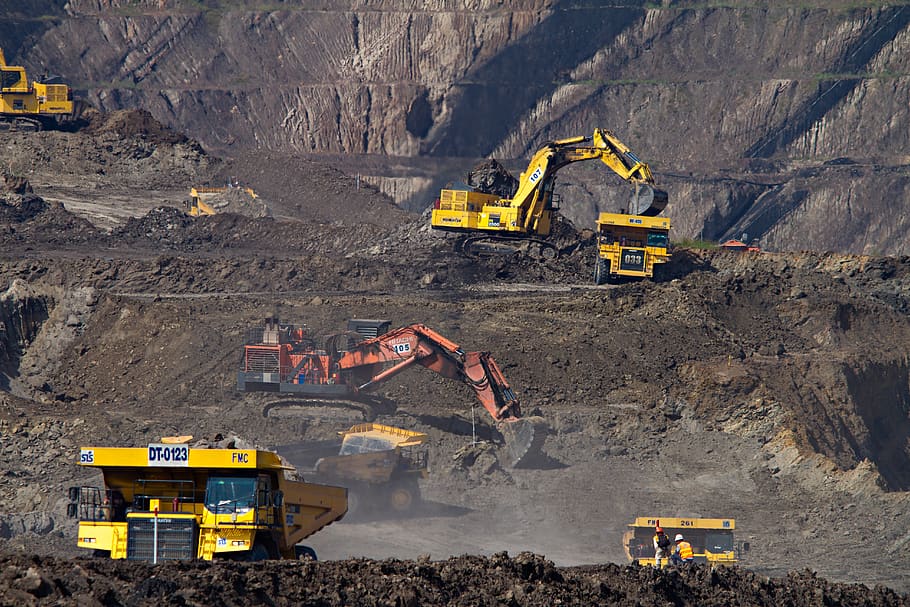

Transporting lithium and other raw materials from mining sites to processing facilities and then to manufacturing plants consumes significant energy, contributing to overall emissions. Optimizing logistics, using energy-efficient transport modes, and localizing supply chains can decrease energy use and emissions.
Depletion of Non-Renewable Resources
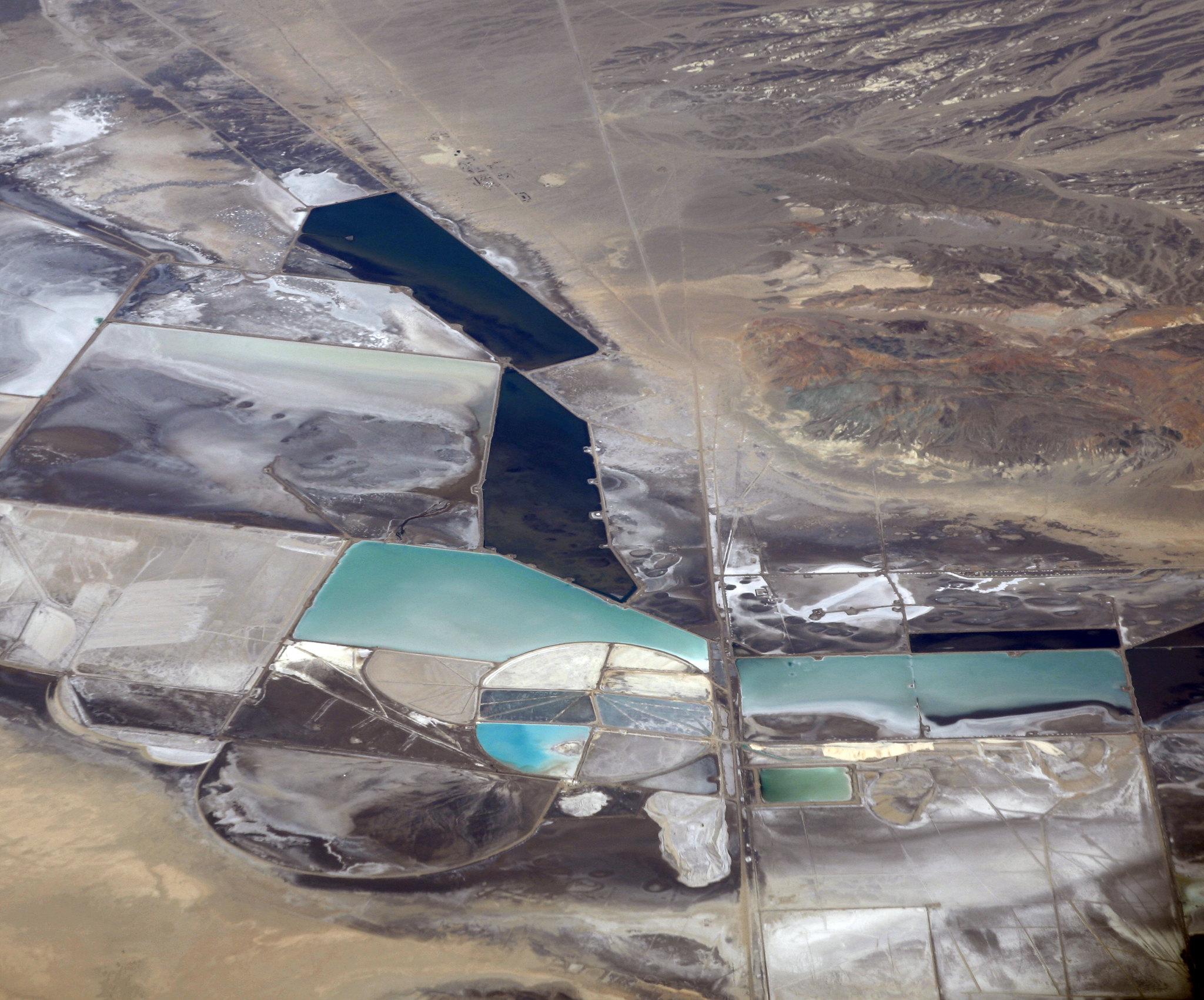

While lithium is abundant, the accessible high-grade deposits are finite and are being depleted rapidly due to the surging demand for EVs. Investing in recycling technologies to recover lithium from used EV batteries can help reduce the demand for primary lithium extraction.
Worker Safety Issues
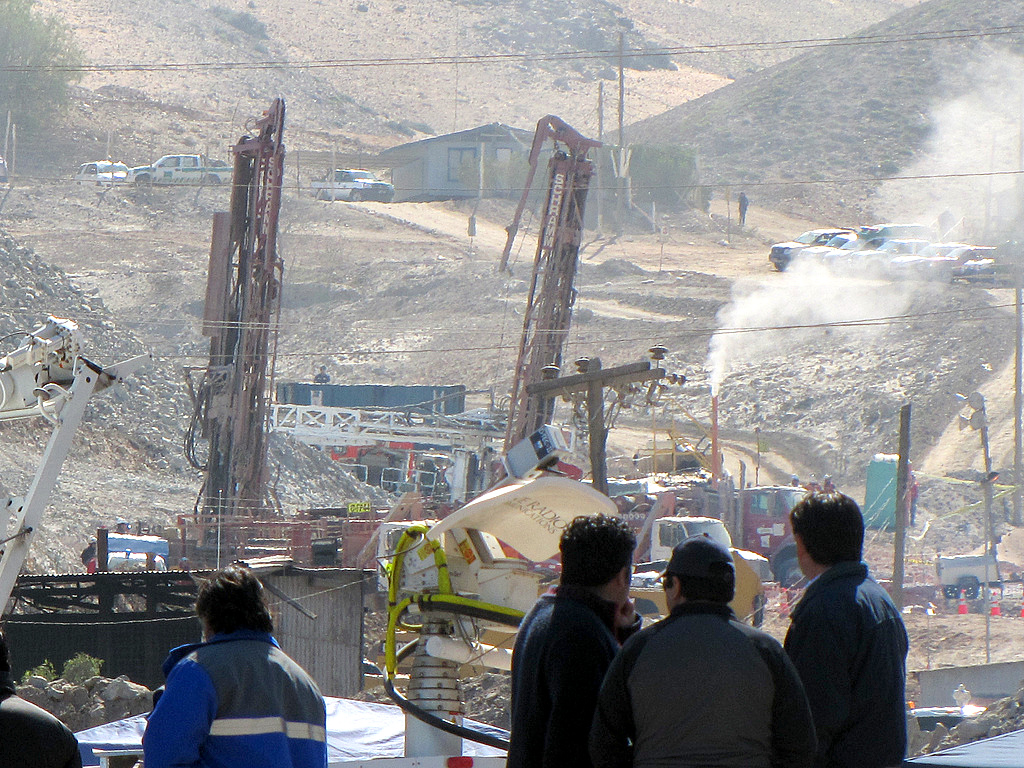

Mining is one of the most dangerous industries, with risks of accidents and exposure to toxic chemicals. Enhancing safety protocols, providing proper protective equipment, and continuous worker training can improve safety in lithium mining operations.
Long-term Environmental Liability
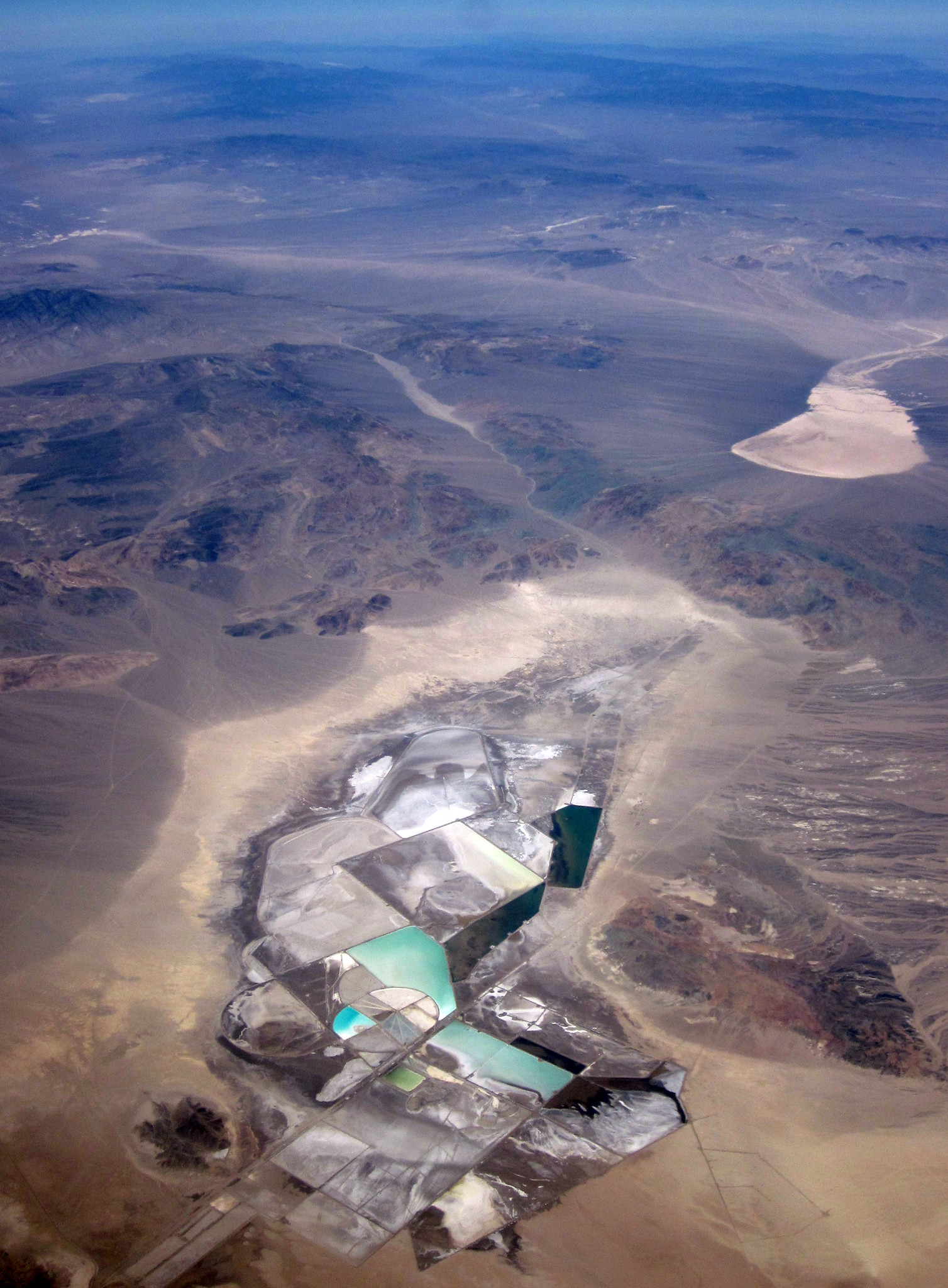

The long-term environmental impacts of lithium mining, such as groundwater contamination and ecosystem degradation, can persist long after mines have closed. Establishing funds for long-term environmental monitoring and remediation, required as part of the mining approval process, can ensure that mining companies remain responsible for environmental impacts.
This article originally appeared on MyCarMakesNoise.
More from MyCarMakesNoise
Exploring the Most Badge-Engineered Cars Ever

From economic tactics to global expansions, this article explores the most notable badge-engineered cars and the stories behind their shared identities. Read more.
The Coolest Tri-Wheelers on the Road

Whether you’re an auto enthusiast craving something different or a casual observer intrigued by their peculiar design, these quirky machines will surely capture your interest. Read More.
The Best Cars Engineered for Maximum Survival

From impeccable structural designs to intelligent, responsive systems, this article spotlights the marvels of modern engineering that prioritize your safety above all. Read More.














