Customizing your car with aftermarket parts can be tempting, offering the chance to enhance performance or upgrade aesthetics at a lower cost. However, many car owners overlook the potential pitfalls that can arise. What seems like a straightforward modification can sometimes lead to unexpected consequences, such as voided warranties or even safety concerns. Without realizing it, drivers may compromise the reliability and integrity of their vehicles with parts that weren’t specifically designed for their make and model.
Aftermarket components vary greatly in quality and compatibility, which makes proper research crucial before installation. Many of these parts aren’t subjected to the same rigorous testing as original manufacturer equipment, leading to issues down the road. While aftermarket upgrades can be beneficial in certain situations, a lack of careful consideration can result in reduced performance, lower resale value, and additional repair costs. Weighing these potential risks against the benefits is essential before committing to any modifications.
Contents
Voided Warranties

One of the most significant downsides of installing aftermarket car parts is the potential to void your vehicle’s warranty. Many automakers include clauses in their warranties that state any modifications using non-original parts could lead to a complete voiding of the warranty. This means that if something goes wrong with your car – even something unrelated to the part you installed – the manufacturer may refuse to cover repairs. To avoid this, it’s crucial to verify whether a part is approved by your manufacturer or if it could invalidate your coverage. Always consult with your dealership before making any modifications.
Safety Risks

Aftermarket car parts can pose significant safety risks if they are not up to standard. Parts that aren’t manufactured with the same level of quality control as original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts may not function properly or fail sooner than expected. This can lead to dangerous situations, particularly if you’re modifying critical components like brakes or suspension systems. It’s essential to ensure that any aftermarket part you install meets safety regulations and has been thoroughly tested for reliability.
Compatibility Issues

One of the hidden downsides of using aftermarket parts is the risk of compatibility issues. Cars are intricate systems where each component is designed to work in harmony with the rest of the vehicle. Installing a part that isn’t designed specifically for your make and model could lead to malfunction, reduced performance, or even damage to other parts of the car. To prevent this, always double-check the specifications of the aftermarket part to ensure it’s fully compatible with your vehicle’s systems.
Resale Value Reduction

While aftermarket modifications can appeal to some, they often reduce the resale value of a car. Many buyers are wary of purchasing a vehicle that has been modified, as aftermarket parts can raise concerns about reliability, maintenance, and warranty. Cars with extensive aftermarket parts are often considered less desirable and harder to sell. Even if the modifications enhance performance, the fact that they deviate from the manufacturer’s specifications can make potential buyers hesitant.
Quality Concerns
Aftermarket parts come from a wide range of manufacturers; unfortunately, the quality can vary significantly. Some parts may be well-made, but others can be of poor quality, leading to premature wear, malfunction, or even damage to your vehicle. Low-quality materials, lack of rigorous testing, or substandard manufacturing processes can result in parts that fail unexpectedly. To avoid these issues, it’s crucial to purchase parts from reputable brands and thoroughly research their quality before installation.
Increased Repair Costs

Installing aftermarket parts can lead to increased repair costs in the long run. If the part fails or causes damage to other components in your vehicle, you may end up spending more money on repairs than you would have if you had stuck with OEM parts. Some aftermarket parts may require specialized labor or tools to install or repair, further driving up costs. Additionally, mechanics may charge more to diagnose and fix issues related to aftermarket components because of their unfamiliarity with the part.
Insurance Complications

Modifying your car with aftermarket parts can complicate your auto insurance policy. Some insurers may not cover repairs or replacements for aftermarket parts, or they may charge higher premiums for modified vehicles due to perceived increased risks. In the event of an accident, you may find that your insurance payout doesn’t cover the cost of replacing or repairing aftermarket parts. It’s important to notify your insurance company about any modifications and ensure that your policy includes coverage for those parts.
Durability Issues
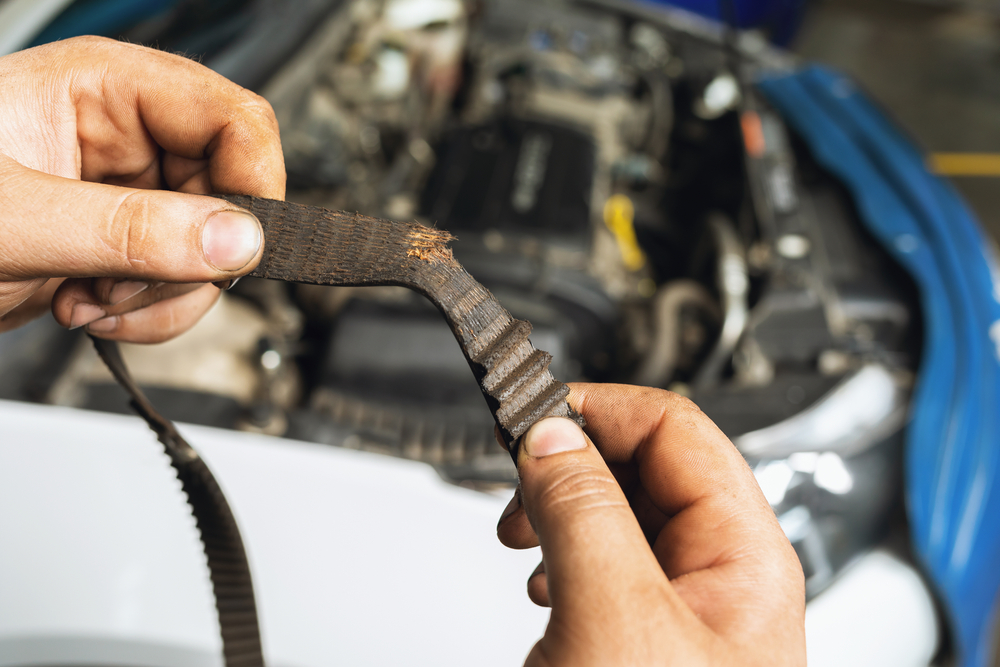

While some aftermarket parts are designed to enhance performance or appearance, they may not always be as durable as OEM parts. Many aftermarket manufacturers focus on cost-cutting to make their products more affordable, which can compromise the long-term durability of the parts. If the part wears out faster or fails prematurely, it could result in higher maintenance costs and more frequent repairs. Durability is particularly important for critical components, so be sure to research the expected lifespan of any aftermarket part before installing it.
Installation Difficulties
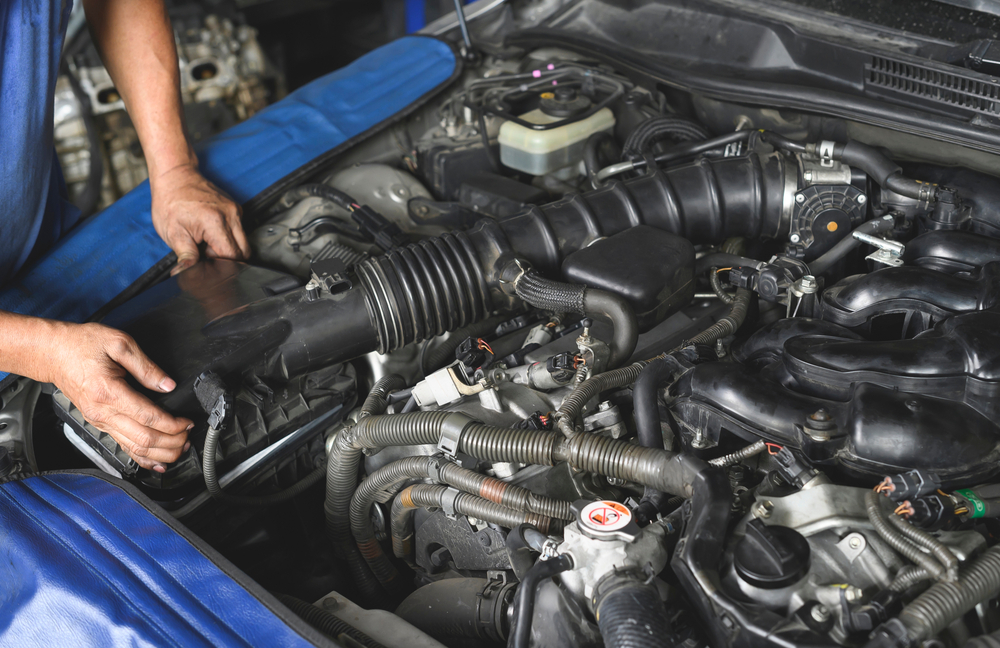

Unlike OEM parts that are designed to fit perfectly into your vehicle, aftermarket parts can sometimes be difficult to install. Poor fitment or lack of clear instructions can lead to installation errors, which can, in turn, result in malfunctions or damage to your car. In some cases, you may need to make additional modifications to your vehicle just to get the part to fit correctly. Hiring a professional mechanic with experience in aftermarket installations can help reduce these risks, but it can also drive up your costs.
Legal Restrictions

Depending on where you live, there may be legal restrictions on the types of aftermarket parts you can install on your vehicle. Some states or countries have strict emissions standards, safety regulations, or noise ordinances that prohibit certain modifications. For example, exhaust systems, engine components, or lighting kits that don’t meet local laws could result in fines or even the impoundment of your vehicle. Before making any modifications, check local regulations to ensure that your aftermarket parts are legal in your area.
This article originally appeared on MyCarMakesNoise.
More from MyCarMakesNoise
20 Futuristic Car Designs That Didn’t Live Up to the Hype
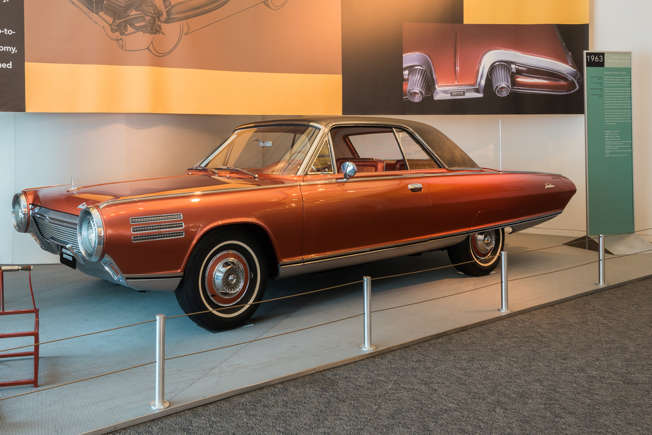

Futuristic car designs often promise cutting-edge technology and groundbreaking aesthetics, but not all of them live up to the hype. Many ambitious concepts have fallen short of expectations, disappointing enthusiasts and buyers alike. Read More.
20 Legendary Off-Road Vehicles Still in Use
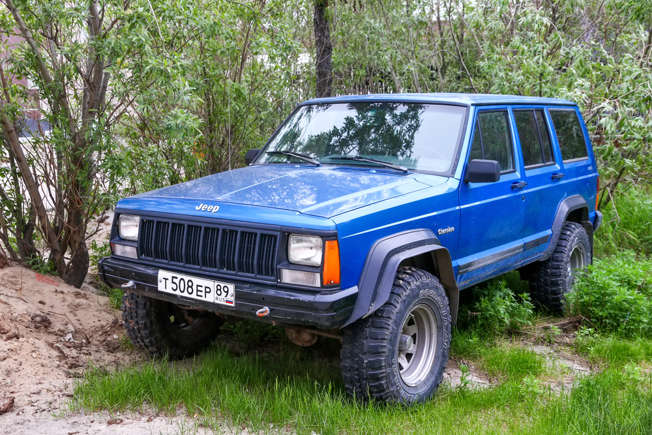

Off-road vehicles have a special place in the hearts of adventurers and thrill-seekers. From rugged trails to remote landscapes, these machines are built to handle the toughest conditions. Read More.
10 Iconic Vehicles Powered by the Legendary 426 Hemi Engine
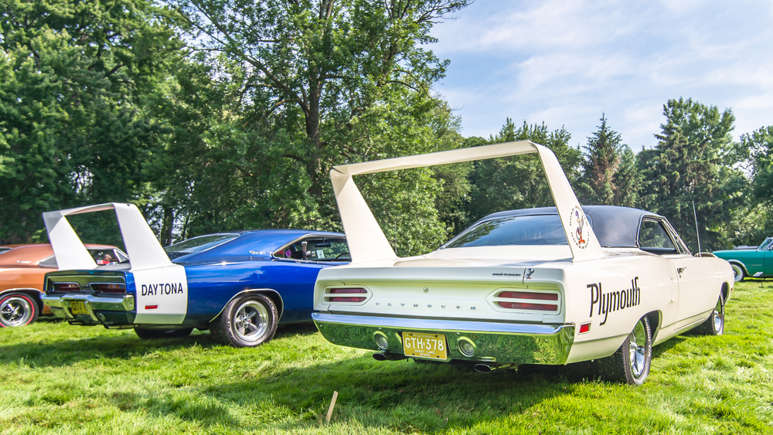

The 426 Hemi engine, synonymous with raw power and unmatched performance, stands as a towering figure in the world of muscle cars. Crafted by Chrysler, this legendary V8 engine redefined automotive performance, making it a favorite among car enthusiasts and racers alike. Read More.














