Submarines have played crucial roles in naval history, but technology evolves and so do the vessels. In this article, we’ll explore 15 submarines that have been retired from service. These once-mighty underwater machines are now memories of the past, no longer patrolling the depths of the oceans. Let’s dive into the history of these fascinating yet outdated submarines.
Contents
USS Nautilus (SSN-571)
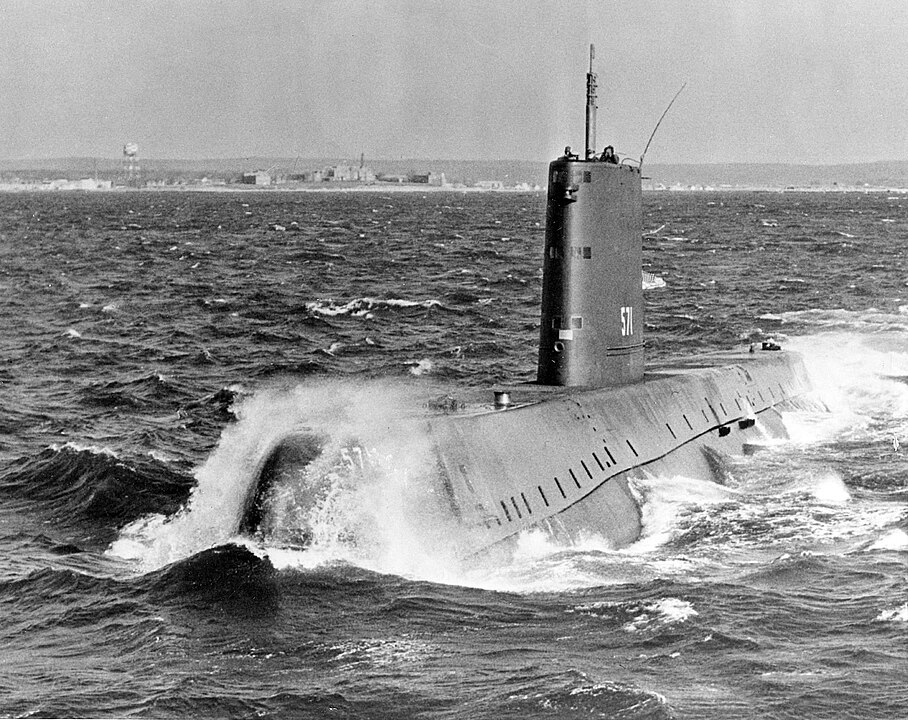

The USS Nautilus, the world’s first nuclear-powered submarine, revolutionized naval warfare when it was commissioned in 1954. Capable of remaining submerged for extended periods and traveling at unprecedented speeds, it marked a significant advancement in submarine technology. Its ability to navigate under the Arctic ice cap in 1958 demonstrated its strategic value. Retired in 1980, the Nautilus now serves as a museum ship in Groton, Connecticut, preserving its historical significance.
HMS Dreadnought (S101)
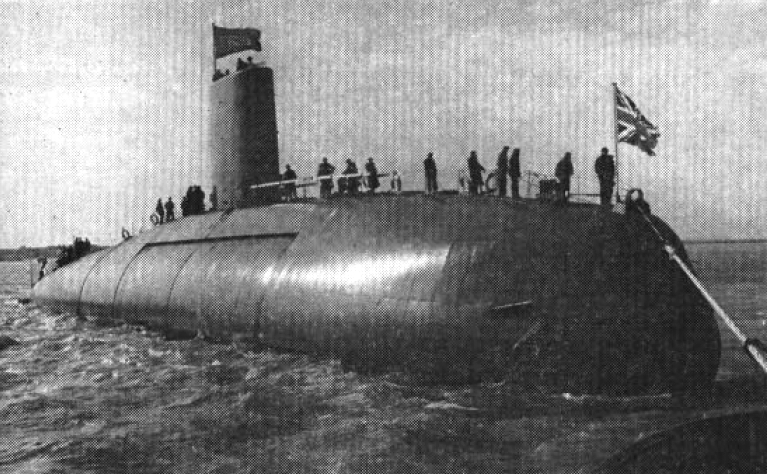
The HMS Dreadnought was the United Kingdom’s first nuclear-powered submarine, entering service in 1963. It introduced nuclear propulsion to the Royal Navy, allowing for extended submerged operations and strategic deterrence. The Dreadnought was decommissioned in 1980 after nearly two decades of service, during which it played a critical role in Cold War naval strategy. Its legacy continues to influence modern submarine design and operation.
USS Seawolf (SSN-575)

Commissioned in 1957, the USS Seawolf was the second nuclear-powered submarine in the U.S. Navy. It was initially powered by a liquid-metal-cooled reactor, which was later replaced due to operational challenges. Known for its speed and endurance, Seawolf conducted numerous covert missions during its service. Decommissioned in 1987, it remains a significant part of submarine history for its technological innovations.
USS Albacore (AGSS-569)
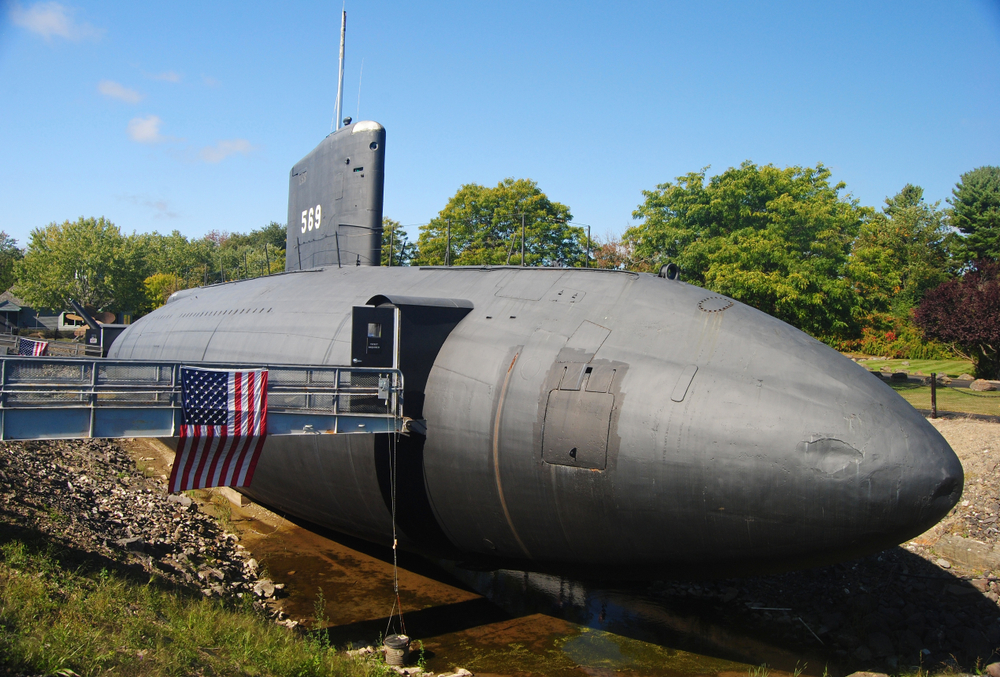

The USS Albacore was an experimental submarine that played a pivotal role in developing modern submarine hull design. Commissioned in 1953, its teardrop-shaped hull significantly improved underwater speed and maneuverability. Albacore’s design principles are still used in contemporary submarines. It was decommissioned in 1972 and now serves as a museum in Portsmouth, New Hampshire.
USS Halibut (SSGN-587)
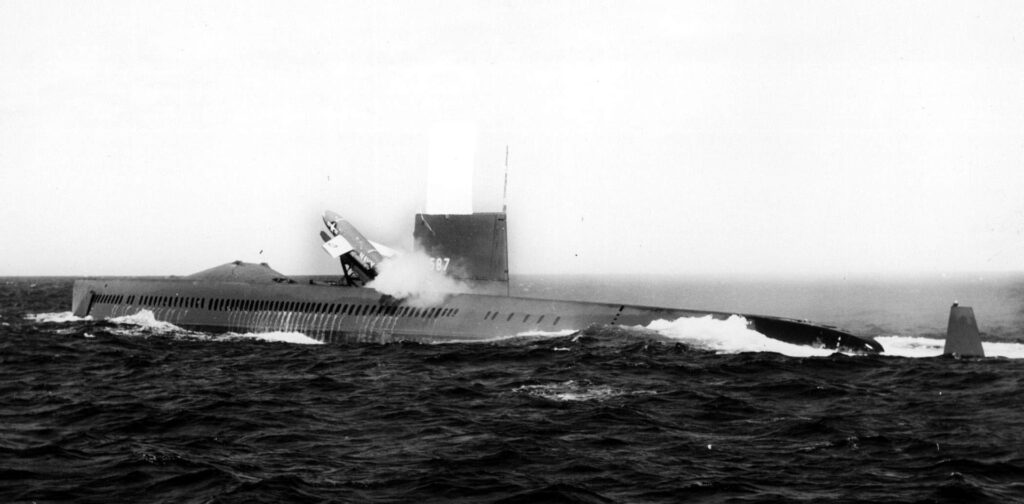

Originally commissioned as a guided missile submarine in 1960, the USS Halibut was later converted into a special operations platform. It carried out several secretive Cold War missions, including tapping undersea communication cables. Its distinctive role and advanced technology made it a unique asset. Decommissioned in 1976, Halibut’s contributions to naval intelligence remain classified.
HMS Resolution (S22)
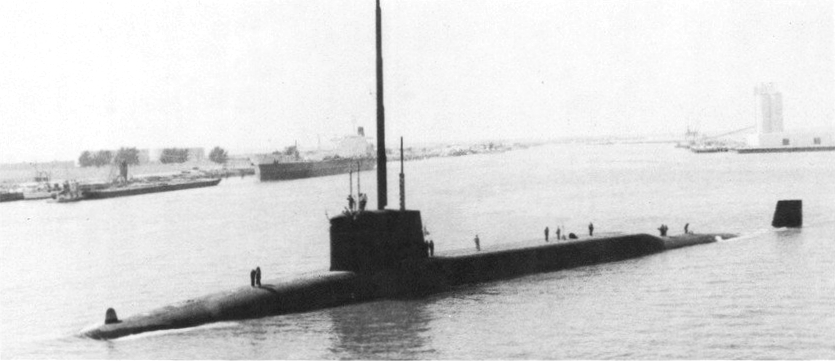
The HMS Resolution was the lead boat of the Royal Navy’s Resolution-class ballistic missile submarines, commissioned in 1967. It provided the United Kingdom’s nuclear deterrent during the Cold War with its Polaris missiles. Decommissioned in 1994, Resolution’s service marked a significant period in British naval history, ensuring national security through strategic deterrence.
USS Skate (SSN-578)

The USS Skate was the lead ship of its class and the first nuclear submarine to surface at the North Pole in 1958. Commissioned in 1957, it demonstrated the feasibility of extended Arctic operations, a crucial strategic capability. Decommissioned in 1986, Skate’s achievements in polar exploration and nuclear propulsion set the stage for future submarine missions.
USS Triton (SSRN-586)
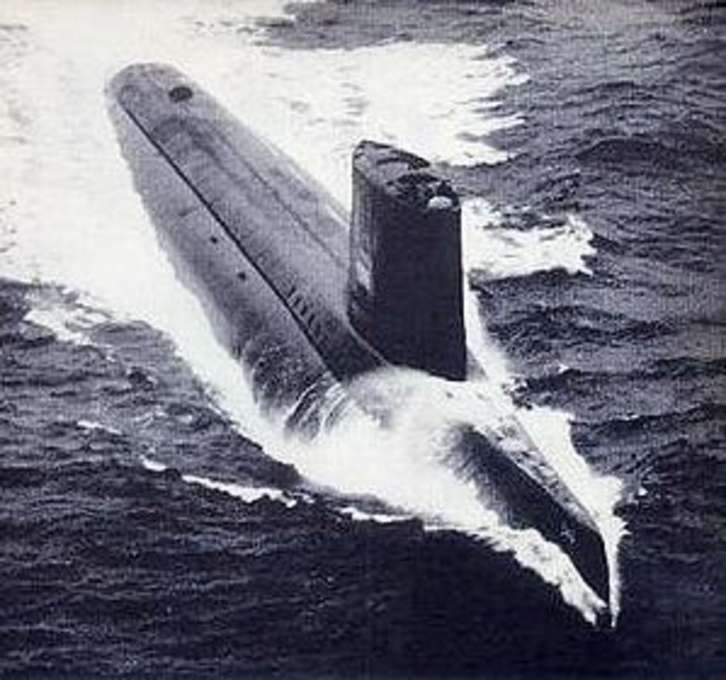

The USS Triton, commissioned in 1959, was unique as the only U.S. submarine powered by two nuclear reactors. It gained fame for completing the first submerged circumnavigation of the globe in 1960. Designed initially for radar picket duties, its role became obsolete with advancements in radar technology. Decommissioned in 1969, Triton remains a landmark in naval exploration.
USS George Washington (SSBN-598)
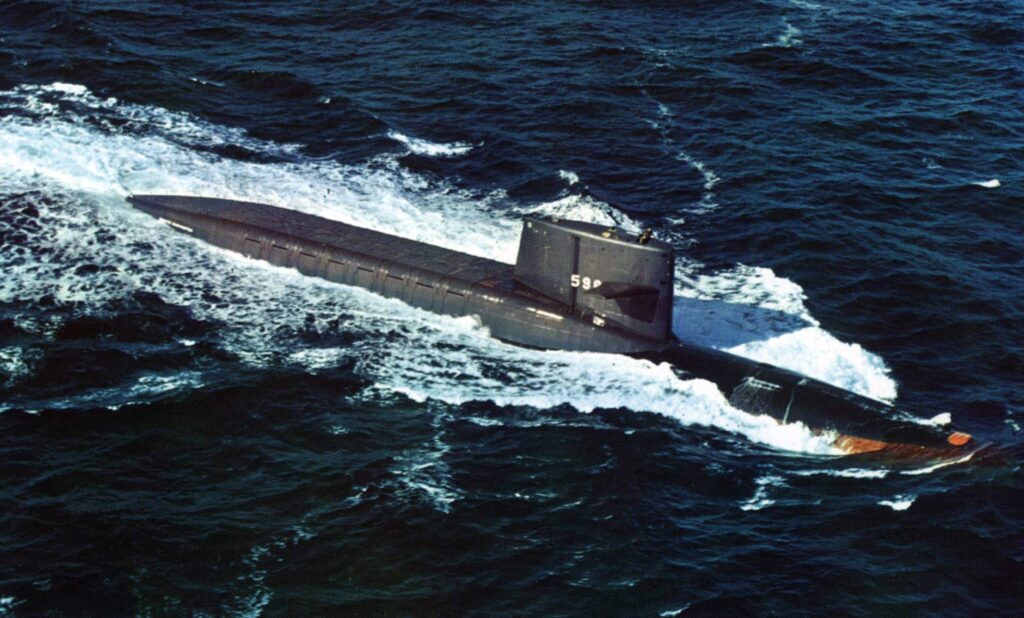

The USS George Washington was the world’s first operational ballistic missile submarine, commissioned in 1959. Equipped with Polaris missiles, it provided a powerful nuclear deterrent during the Cold War. Its ability to launch missiles while submerged changed naval strategy profoundly. Decommissioned in 1985, it set the standard for subsequent ballistic missile submarines.
USS Parche (SSN-683)

Commissioned in 1974, the USS Parche was one of the most decorated submarines in U.S. naval history. It specialized in covert operations, including intelligence gathering and undersea cable tapping. Parche’s missions remain largely classified, highlighting its crucial role in Cold War espionage. Decommissioned in 2004, it left a legacy of exceptional service.
USS Tang (SS-563)

The USS Tang, commissioned in 1951, was the lead ship of its class and featured numerous technological advancements, including improved sonar and torpedo systems. It set a new standard for post-World War II submarine design. Decommissioned in 1980, Tang’s innovations influenced subsequent generations of submarines.
USS Grayback (SSG-574)
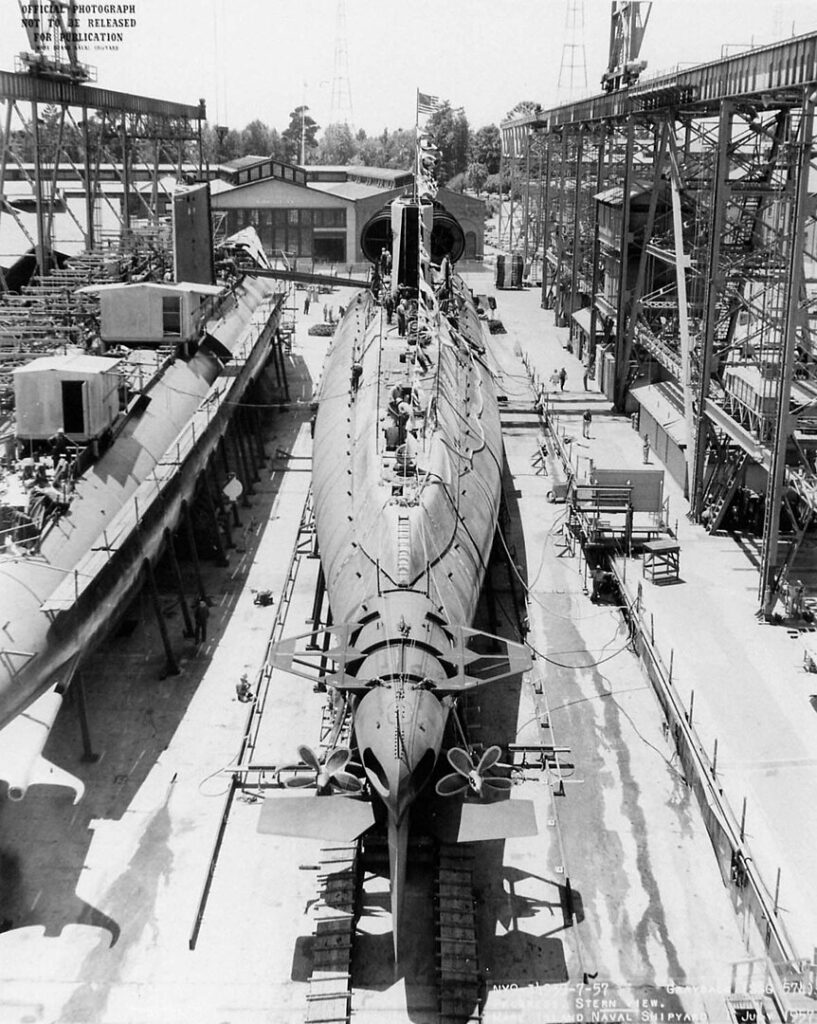

Initially commissioned as a guided missile submarine in 1958, the USS Grayback was later converted to support special operations forces. It conducted several covert missions during the Cold War, emphasizing versatility and adaptability. Decommissioned in 1984, Grayback’s service included significant contributions to naval intelligence and special operations.
USS Salmon (SSR-573)
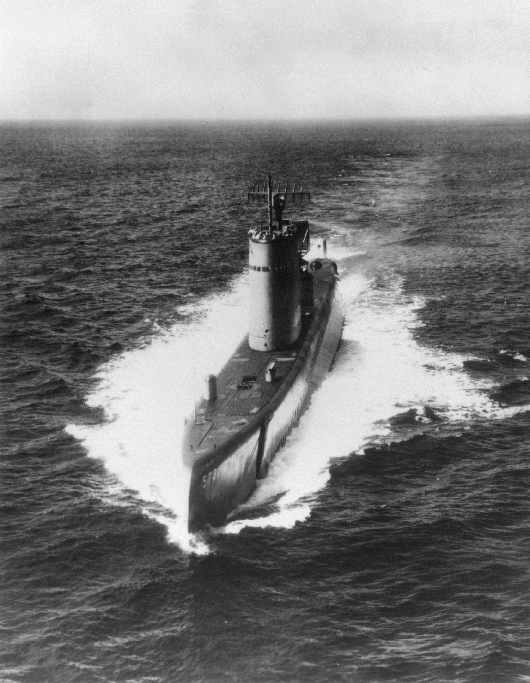
Commissioned in 1956, the USS Salmon was designed as a radar picket submarine to extend the radar coverage of carrier battle groups. With the advent of more advanced radar systems and aircraft, its role became redundant. Decommissioned in 1977, Salmon represents a unique phase in submarine development focused on electronic warfare.
HMS Vanguard (S28)
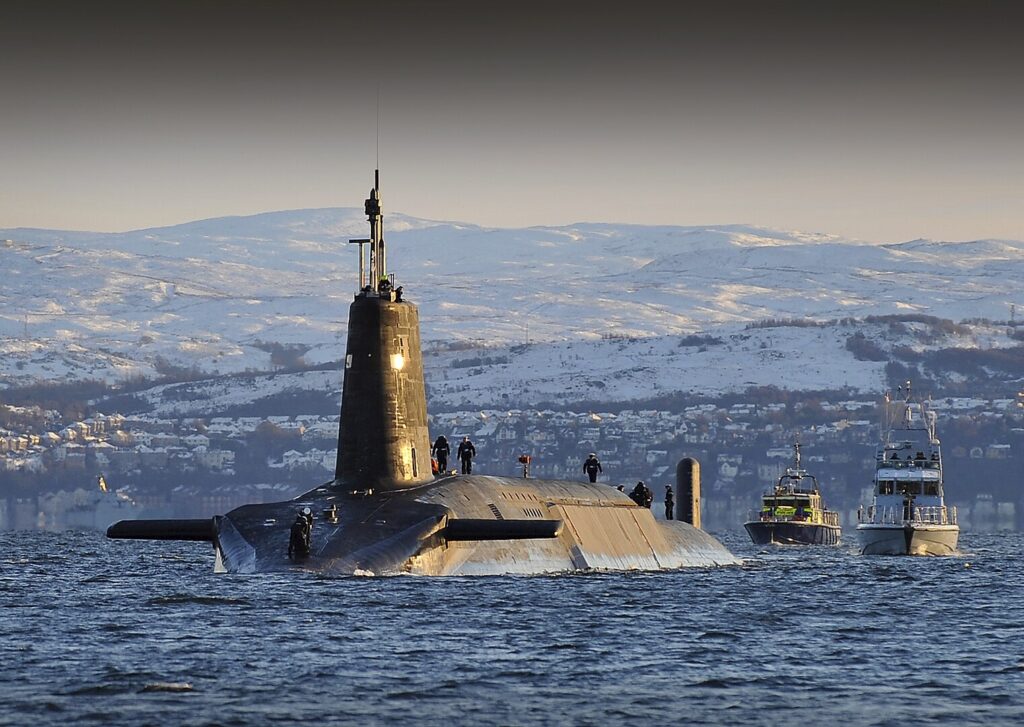

The HMS Vanguard, commissioned in 1993, was the lead boat of the Vanguard-class ballistic missile submarines. Equipped with Trident missiles, it played a key role in the United Kingdom’s nuclear deterrent. Decommissioned as newer submarines came online, Vanguard’s service highlighted the evolution of strategic deterrence in the post-Cold War era.
USS Narwhal (SSN-671)
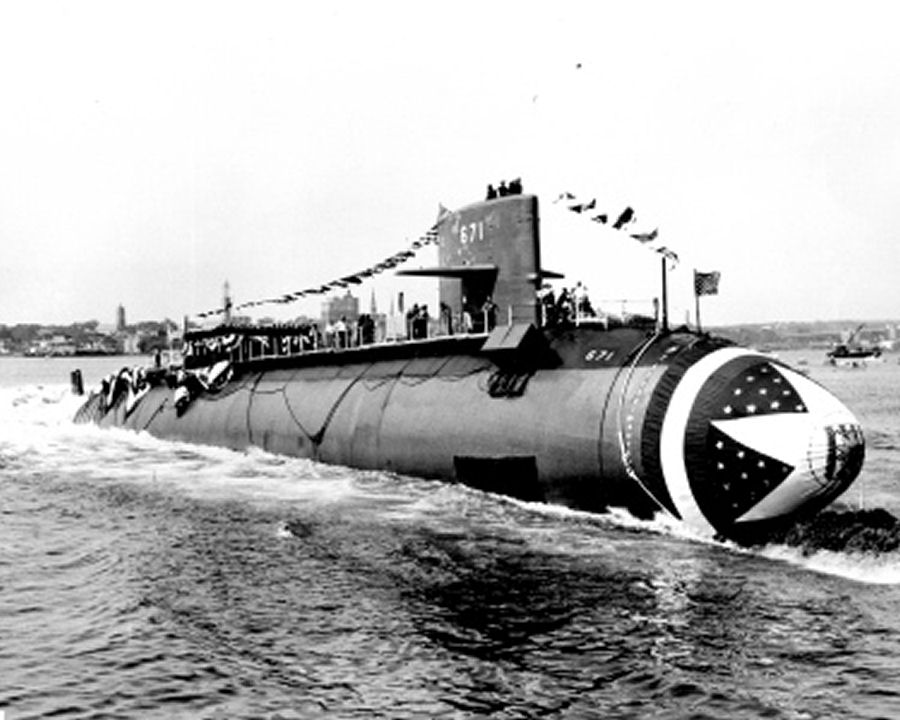
The USS Narwhal, commissioned in 1969, featured a unique reactor design that allowed for exceptionally quiet operation, enhancing its stealth capabilities. It served in various covert missions and demonstrated innovations in submarine propulsion. Decommissioned in 1999, Narwhal’s contributions to submarine technology and tactics remain influential.
This article originally appeared in MyCarMakesNoise.
More from MyCarMakesNoise
20 Misconceptions About Race Cars You Probably Believe

Race cars have long been the subject of fascination and intrigue, but with that comes a host of misconceptions. From the belief that they are simply souped-up street cars to the idea that they are only about speed, many myths surround these high-performance machines. Read More.
12 Unmanned Space Probes Exploring Our Solar System

The exploration of our solar system has been significantly advanced by unmanned space probes. These remarkable spacecraft have journeyed to distant planets, moons, and even beyond the solar system, providing invaluable data and breathtaking images. Read More.
15 Iconic Airplanes from Classic Aviation Movies

Aviation has always captivated audiences, and classic movies have brought some of the most iconic airplanes to the big screen. From World War II fighters to modern jets, these films showcase the beauty and power of aviation history. Read More.














