The global demand for electric vehicle batteries is growing rapidly, but the supply chain is struggling to keep up. From raw material shortages to transportation delays, numerous challenges make production complex and costly. These problems create bottlenecks that slow down progress in the EV market. Here are 16 key issues affecting the global supply chain for electric vehicle batteries.
Contents
Limited Availability of Raw Materials

Electric vehicle (EV) batteries depend on crucial materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are found in limited quantities. These resources are highly concentrated in specific regions, creating supply bottlenecks. As demand surges, prices for these raw materials have soared, putting financial pressure on manufacturers. Additionally, the extraction processes for these minerals often cause environmental harm, further complicating production.
Geopolitical Risks

Many of the raw materials needed for EV batteries come from politically unstable regions, particularly in Africa and South America. Countries like the Democratic Republic of Congo, which supplies a large portion of the world’s cobalt, are prone to conflict and corruption. These geopolitical risks can lead to supply disruptions, sanctions, or trade restrictions, further complicating global supply chains. Political instability in key regions has made the EV battery market vulnerable to sudden changes.
Insufficient Mining Capacity

Current mining operations cannot keep up with the increasing demand for essential battery materials like lithium and cobalt. Mining expansions face numerous obstacles, including the need for significant investments and lengthy regulatory approvals. Without sufficient mining output, the battery supply chain remains strained, leading to higher prices and production delays. This lack of capacity is a bottleneck that hinders the scaling of electric vehicle production.
Environmental and Ethical Concerns

The mining of cobalt, nickel, and other essential minerals for EV batteries often results in environmental degradation and raises serious ethical concerns. In regions with weak governance, mining operations can lead to deforestation, water contamination, and human rights abuses. Child labor and unsafe working conditions plague many mining sectors, particularly in cobalt-rich areas. These issues have prompted calls for more ethical and sustainable sourcing, though implementing meaningful change is a slow process.
Battery Recycling Challenges
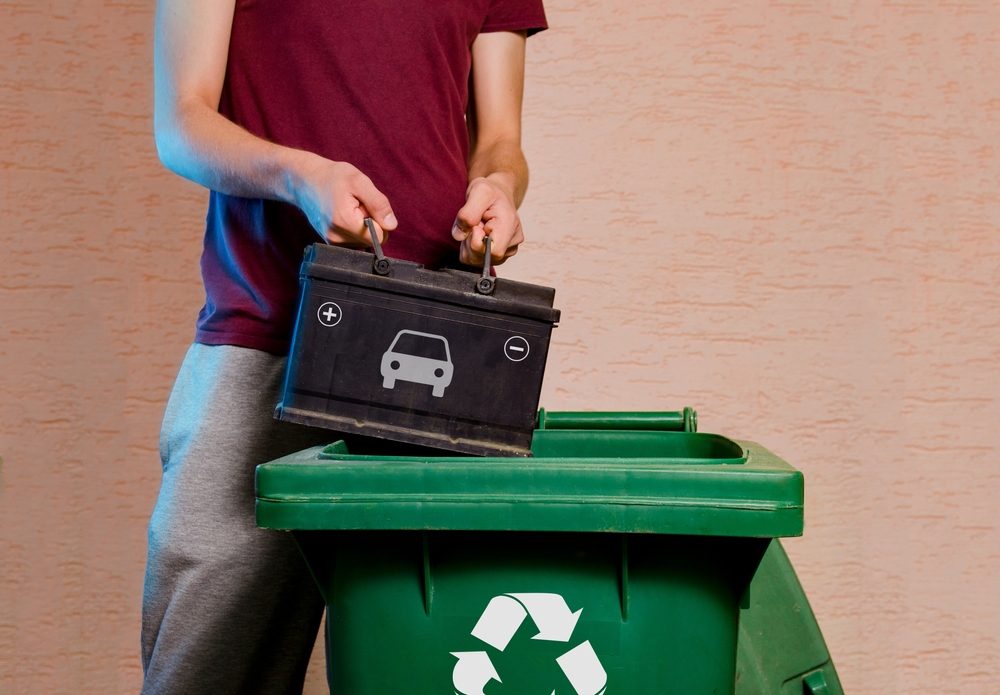

While recycling can help reduce the need for new raw materials, the infrastructure for recycling EV batteries remains underdeveloped. Current technologies are inefficient and can only recover a small percentage of battery materials. Additionally, recycling processes are costly and complex, involving hazardous chemicals that require special handling. The lack of effective recycling solutions puts additional strain on the supply of critical materials.
Long Lead Times for Equipment
Setting up battery production facilities requires specialized equipment, which often has long lead times due to high global demand. This results in significant delays for companies trying to expand or establish new manufacturing capabilities. In some cases, waiting times for critical machinery can stretch over a year, slowing down the growth of battery production capacity
Trade Barriers and Tariffs
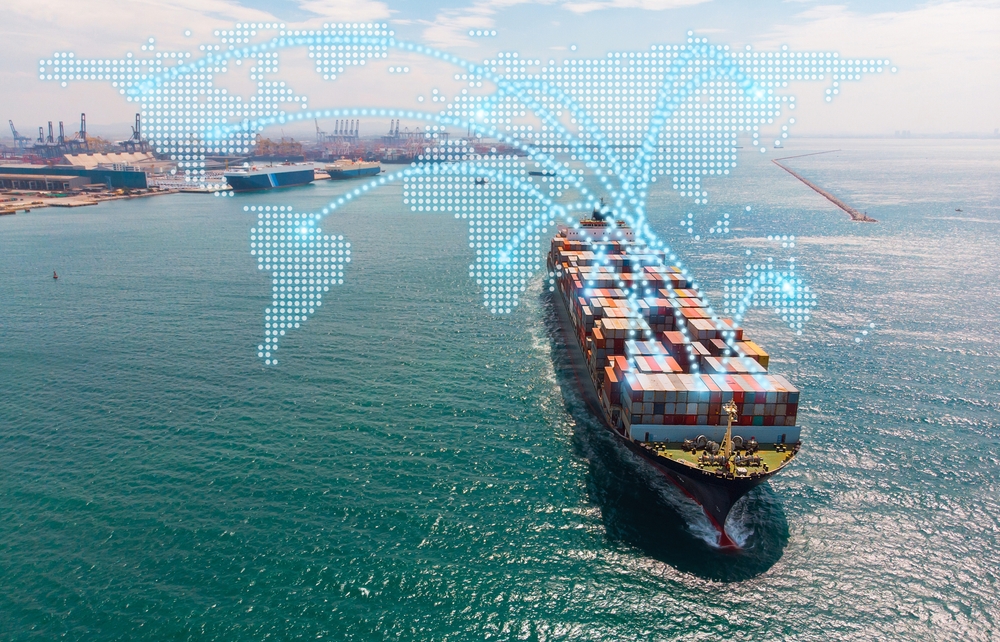

International trade tensions, especially between the U.S. and China, have introduced tariffs on battery components and raw materials, inflating costs across the supply chain. Trade barriers disrupt the free flow of materials, making it more difficult for companies to maintain efficient production. These tariffs not only increase costs but also create uncertainty for manufacturers planning long-term investments. To mitigate these issues, companies must either absorb the additional expenses or shift production to less affected regions.
Transportation and Logistics Issues
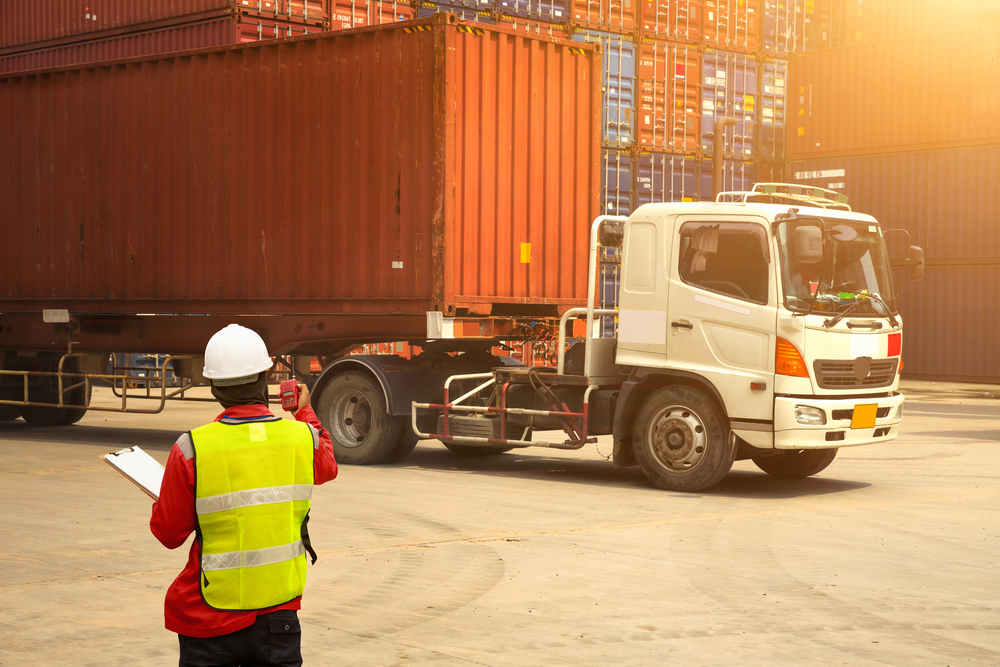

Transporting raw materials and finished batteries across the globe presents significant logistical challenges. Port congestion, labor shortages, and the rising cost of shipping all contribute to delays in moving goods through the supply chain. Additionally, hazardous materials like lithium require specialized transportation, adding complexity and expense to the process.
High Production Costs
Producing EV batteries is a resource-heavy and expensive process, primarily due to the high cost of raw materials and advanced technology. Energy consumption during production also drives up costs, making it harder for manufacturers to reduce the price of electric vehicles. Furthermore, supply chain disruptions, such as material shortages, can increase production expenses even further. These high costs are one of the key barriers to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
Lack of Standardization

The EV battery industry suffers from a lack of standardization, with manufacturers using a wide range of designs, sizes, and components. This lack of consistency creates inefficiencies in production and makes recycling more complex. Without standardized battery models, it’s difficult to streamline manufacturing processes, driving up costs and slowing production. Efforts to create industry-wide standards have been slow, but achieving greater uniformity could significantly improve the efficiency of the supply chain.
Energy-Intensive Production

Battery production is highly energy-intensive, with many factories relying on fossil fuels to power their operations. This reliance on non-renewable energy sources not only increases production costs but also undercuts the environmental benefits of electric vehicles. Until battery production can transition to more renewable energy sources, the carbon footprint of the supply chain will remain substantial. Addressing this issue is critical to ensuring that electric vehicles are truly a greener alternative to traditional cars.
Limited Supply Chain Transparency

The complex and fragmented nature of the global battery supply chain makes it difficult for companies to trace the origins of their materials. Without full transparency, it’s challenging to ensure that materials are sourced responsibly, and free from human rights abuses or environmental harm. Implementing robust tracking and reporting systems across such a sprawling network is an expensive and technically difficult task. However, as consumers become more conscious of ethical sourcing, improving supply chain transparency will be essential.
Inadequate Workforce Training
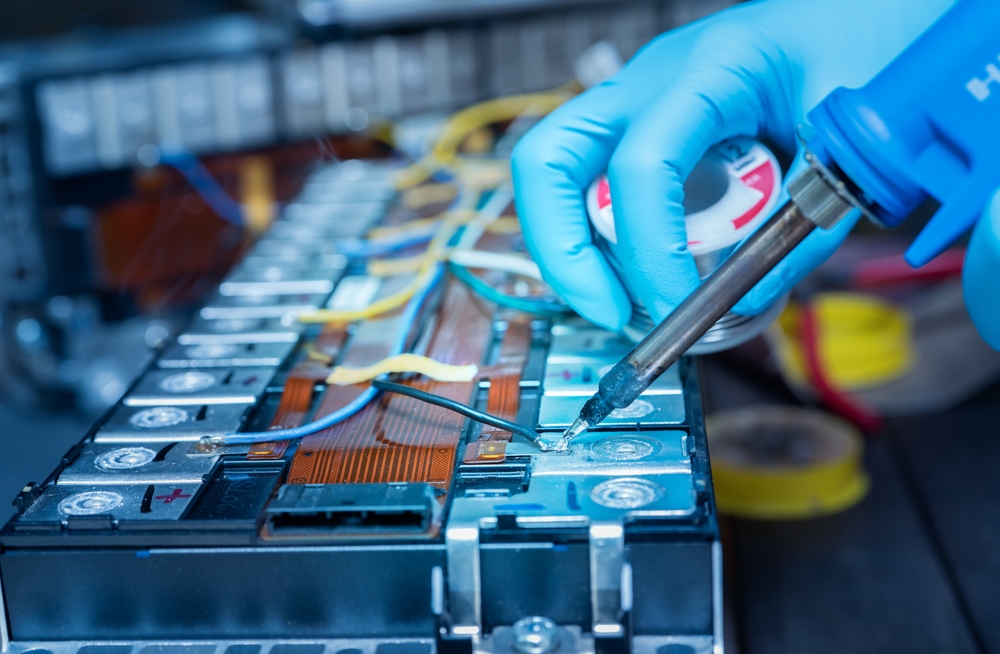

Battery production requires a highly skilled workforce, but many regions lack sufficient training programs to meet industry demands. As the EV market continues to grow, the shortage of trained workers becomes a major constraint on expanding production. Skilled technicians are needed to operate the complex machinery involved in manufacturing, and without them, efficiency suffers.
Cybersecurity Threats

As battery production facilities become increasingly automated and interconnected, they are also more vulnerable to cyberattacks. A breach in the digital infrastructure could disrupt production lines, steal sensitive data, or even cause physical damage to machinery. The global nature of the supply chain also makes it difficult to safeguard all points of vulnerability, increasing the risk of cyber threats. Strengthening cybersecurity protocols is essential to protect the integrity of the supply chain. Any major attack could cause widespread disruptions in the EV market.
Regulatory Hurdles

Countries have different regulations governing the production, transportation, and disposal of batteries, making compliance a complicated and expensive process. Navigating this web of rules can slow down the movement of goods through the supply chain and increase operational costs. Stricter regulations, particularly those aimed at improving environmental safety, are necessary but can further complicate production processes.
Volatile Commodity Prices

The prices of essential materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel are subject to extreme fluctuations due to changes in global demand, geopolitical tensions, and supply disruptions. These price swings make it difficult for manufacturers to forecast costs and plan long-term production. When prices rise sharply, it directly impacts the cost of producing EV batteries, making them more expensive for consumers.
This article originally appeared in MyCarMakesNoise.
More from MyCarMakesNoise
20 Car Features Drivers Are Begging Automakers to Remove

Not all car features are welcomed by drivers. Some can be more annoying than useful, adding complexity or distraction. Read More.
17 Historic Tractors That Transformed Agricultural Practices

Tractors have been at the heart of farming for over a century, revolutionizing how we cultivate and harvest crops. Over the years, certain models have stood out for their innovation, durability, and impact on agricultural practices. Read More.
18 Transport Aircraft Designs That Crews Struggle With

Operating transport aircraft isn’t always smooth flying, especially when certain designs present unexpected challenges. From complex systems to cumbersome loading procedures, these aircraft often test the skills and patience of their crews. Read More.














