Developing sustainable aviation is a critical step toward reducing the industry’s environmental impact, but it’s not without challenges. From high costs to technological barriers, there are numerous hurdles that need to be overcome. Let’s go through 18 major obstacles that stand in the way of creating a greener future for aviation.
Contents
High Costs of Sustainable Technologies
The development of sustainable aviation technologies comes with a hefty price tag. From research and development to implementing new systems, the costs are often prohibitively high. Technologies like biofuels and hydrogen-based propulsion systems require substantial investments. This makes it difficult for airlines operating on tight margins to adopt these innovations without external funding or government incentives.
Limited Availability of Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAF)
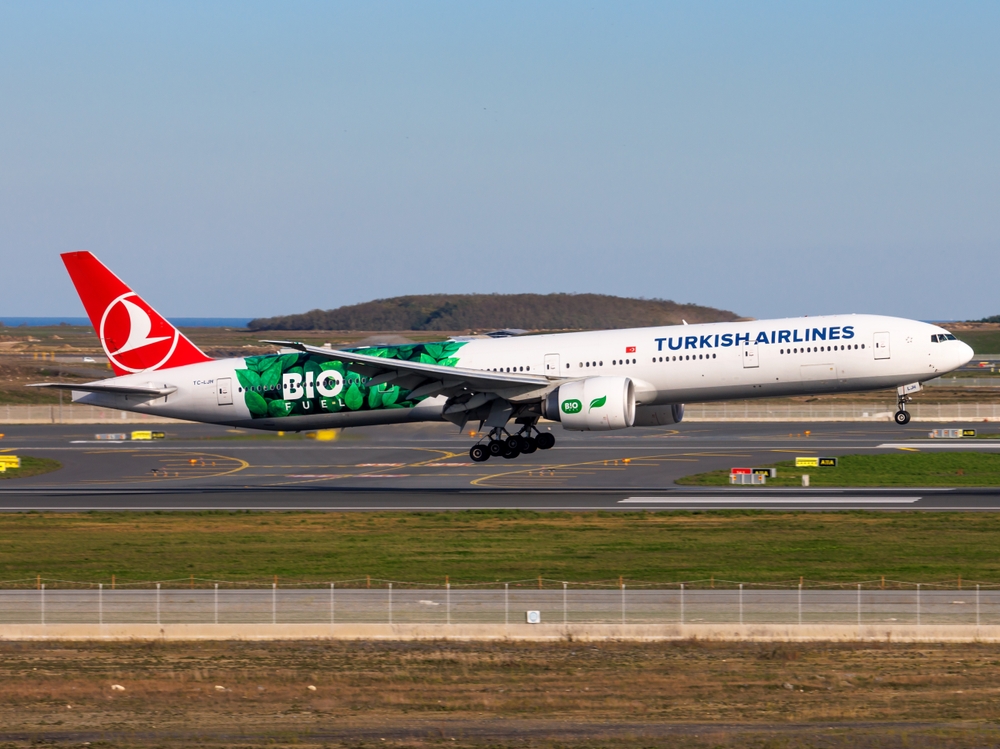

Sustainable aviation fuels (SAF) are currently produced in limited quantities. Despite their potential to reduce carbon emissions, SAF represents less than 1% of global jet fuel consumption. Production is restricted by high costs, resource availability, and complex logistics. Expanding SAF usage will require significant investment in infrastructure and feedstock development.
Infrastructure Overhaul Requirements

Transitioning to sustainable aviation demands a complete overhaul of existing infrastructure. Hydrogen and electric planes, for example, need specialized fueling stations and charging networks. Retrofitting airports to accommodate these changes is both costly and time-consuming. Furthermore, harmonizing these upgrades across global airports introduces additional challenges.
Energy Density Limitations of Electric Aviation
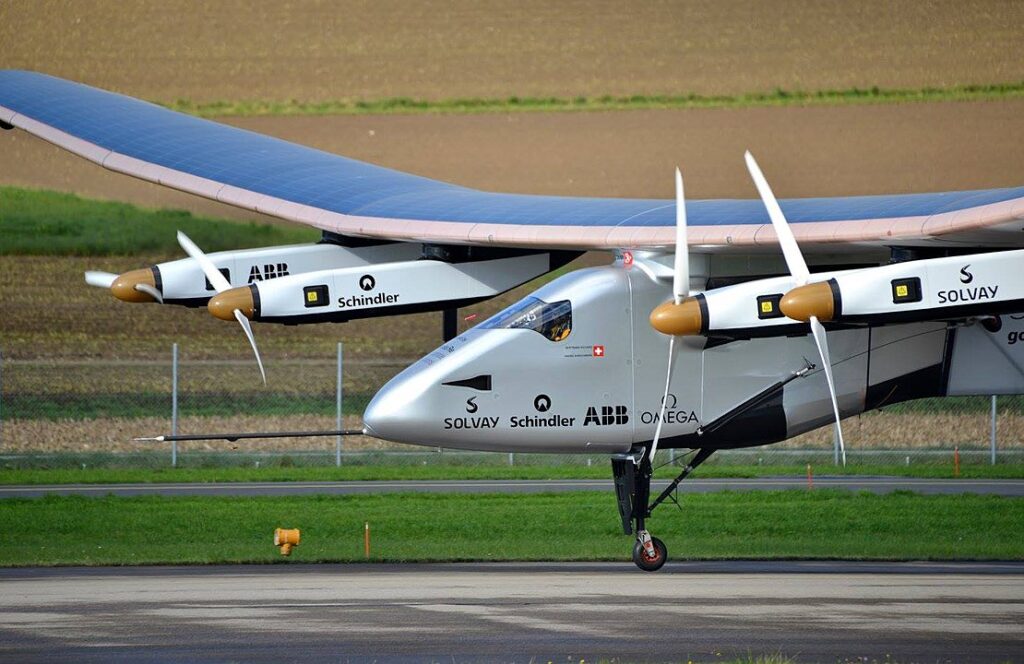

Electric aviation faces major hurdles due to current battery technology. While electric planes are a promising alternative, their batteries lack the energy density required for long-haul flights. As a result, electric aircraft are currently limited to short regional routes. Advancements in energy storage technology are critical to making electric aviation viable for longer distances.
Carbon Emissions from Aircraft Manufacturing

Even if aviation transitions to greener fuels, the aircraft manufacturing process remains a significant contributor to carbon emissions. Building airplanes involves energy-intensive processes, and the materials used, such as steel and composites, have large carbon footprints. Additionally, the disposal of outdated aircraft can further add to environmental damage unless more sustainable recycling methods are developed.
Regulatory and Policy Gaps

Inconsistent and incomplete regulations hinder the growth of sustainable aviation. While some countries have implemented green policies, others lag behind, creating disparities. Without global regulatory alignment, airlines may face difficulties adopting new technologies. Clear and consistent policies are essential for encouraging industry-wide investment in sustainability initiatives.
Public and Industry Resistance

Adopting sustainable aviation technology may face resistance from both consumers and industry stakeholders. Many passengers may balk at the higher ticket prices associated with greener travel options. Similarly, airlines are hesitant to embrace costly technological changes that disrupt existing operations. Overcoming these barriers requires education, incentives, and broader societal shifts toward sustainability.
Slow Fleet Turnover

The longevity of commercial aircraft complicates efforts to transition to sustainable aviation. Planes typically remain in service for 20 to 30 years, slowing down the rate at which greener aircraft can replace older, less efficient models. Even when new aircraft become available, airlines may be reluctant to invest in new fleets due to the high costs involved.
Technological Challenges in Alternative Propulsion Systems

Hydrogen and electric propulsion systems face complex technological obstacles. Hydrogen, for instance, requires cryogenic storage, adding weight and complexity to aircraft designs. Electric planes, on the other hand, struggle with battery limitations. These challenges slow the development and deployment of alternative propulsion systems, hindering their adoption on a larger scale.
Lack of Research and Development Funding

The progress of sustainable aviation hinges on research and development, yet securing adequate funding remains a challenge. Compared to other industries, aviation has historically received less R&D investment for green technologies. Without more financial support, breakthroughs in sustainable fuels and propulsion systems will remain elusive.
Inconsistent Global Cooperation

Sustainable aviation requires countries around the world to work together, but cooperation has been uneven. Nations have different priorities, resources, and environmental policies, making global alignment difficult. This lack of coordination hampers efforts to standardize sustainable aviation practices. A more united approach is needed to tackle the global nature of aviation’s environmental impact.
Aircraft Weight and Energy Efficiency

Reducing aircraft weight is a key factor in boosting energy efficiency, but achieving this balance is complex. Lightweight materials can lower fuel consumption, but they are expensive and difficult to produce at scale. In addition, incorporating these materials into existing fleets is not always practical. As a result, improvements in weight reduction are progressing more slowly than other technological advances.
Environmental Impact of Aircraft Noise

Noise pollution from aircraft remains an issue even with sustainable advancements. While new technologies reduce carbon emissions, they often fail to address the problem of noise, especially around airports. Excessive noise can have health impacts on local communities, complicating sustainability efforts. Sustainable aviation must balance both emissions and noise reduction to fully mitigate its environmental footprint.
Competition with Other Industries for Renewable Resources

The aviation industry competes with other sectors, such as automotive and energy, for limited renewable resources. This competition can drive up costs and restrict access to critical materials like biofuels or hydrogen. In regions with constrained supplies, prioritizing aviation over other industries can lead to conflicts and hamper broader sustainability goals.
Supply Chain Disruptions

The global nature of aviation means that disruptions in the supply chain can have major repercussions. Recent events like the COVID-19 pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in the production and distribution of aviation technologies. Such disruptions can slow the adoption of sustainable solutions, especially when critical components or materials are affected.
Passenger Expectations for Faster Travel

Passengers often prioritize convenience and speed, which can clash with sustainable aviation solutions. Technologies like electric and hydrogen-powered planes may reduce carbon emissions but often come with trade-offs in terms of slower travel times. Convincing travelers to accept these changes will require airlines to balance sustainability with passenger expectations.
Limited Availability of Renewable Energy for Airports

Many airports are not equipped with renewable energy sources to support sustainable ground operations. Transitioning to renewable energy—such as solar or wind—requires significant investments in infrastructure. Without these upgrades, airports cannot fully support the green technologies needed for a sustainable aviation industry. More investment is necessary to power airports sustainably.
Air Traffic Management and Efficiency

Air traffic management (ATM) inefficiencies result in excess fuel consumption, increasing the aviation industry’s carbon footprint. Updating ATM systems to use modern, more efficient routing and scheduling is critical. However, this requires international coordination and investment. Streamlined air traffic systems could significantly reduce unnecessary fuel burn and emissions.
This article originally appeared in MyCarMakesNoise.
More from MyCarMakesNoise
20 Design Flaws in Iconic Sports Cars

Even the most iconic sports cars aren’t without their flaws. Despite their legendary status, some of these vehicles have design issues that impact performance, comfort, or reliability. Read More.
19 High-Performance Electric Cars That Deliver Incredible Value

In today’s fast-paced world, electric cars are proving that you don’t have to compromise performance for sustainability. With advancements in technology, many high-performance electric vehicles now offer incredible value, blending speed, efficiency, and affordability. Read More.
Top 15 Modifications to Increase Fuel Efficiency in Your Vehicle

Improving your vehicle’s fuel efficiency not only saves you money but also reduces your environmental impact. By making a few strategic modifications, you can enhance your car’s performance and get more miles per gallon. Read More.














