Electric vehicles (EVs) have surged in popularity over the past decade, celebrated for their environmental benefits and advancements in automotive technology. With promises of reduced emissions and lower long-term costs, they seem to be the ideal choice for the eco-conscious consumer. However, beneath the surface of this green revolution, several challenges and drawbacks often go unnoticed in the broader conversation.
Contents
Long Charging Times
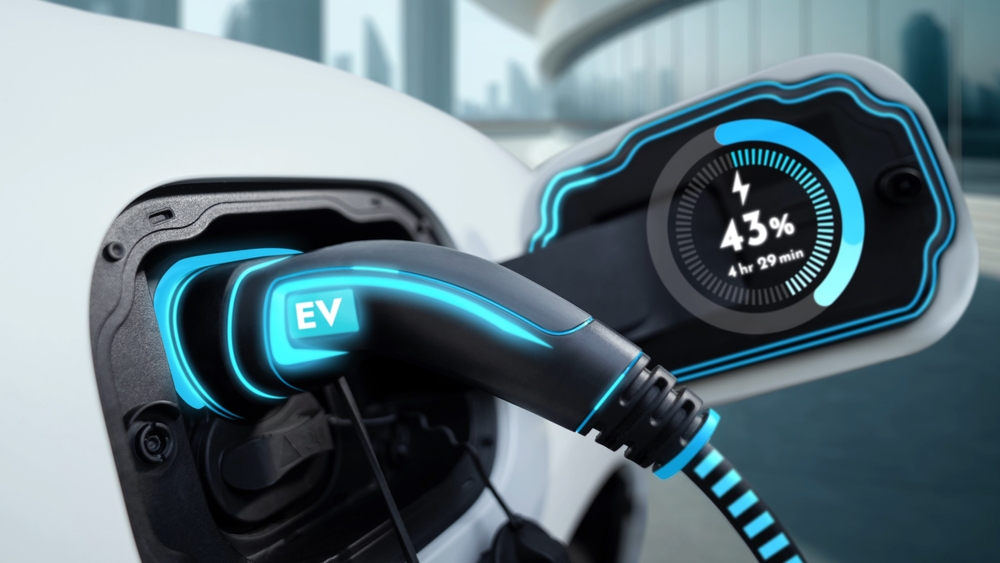

Despite advancements in battery technology, electric vehicles (EVs) still face significant issues with long charging times. Unlike traditional gasoline vehicles that can refuel in minutes, EVs can take several hours to charge fully, especially if using standard home charging units. This delay can be inconvenient for drivers, particularly on long trips or when access to fast-charging stations is limited. Even with the fastest chargers available, it can still take up to an hour to provide a substantial charge. Moreover, frequent use of fast chargers can contribute to battery degradation, which means that the convenience of faster charging can come at a cost to the longevity of the battery itself. This highlights the need for continued improvements in charging technology and infrastructure to make EVs more practical for everyday use.
Charging Infrastructure Limitations
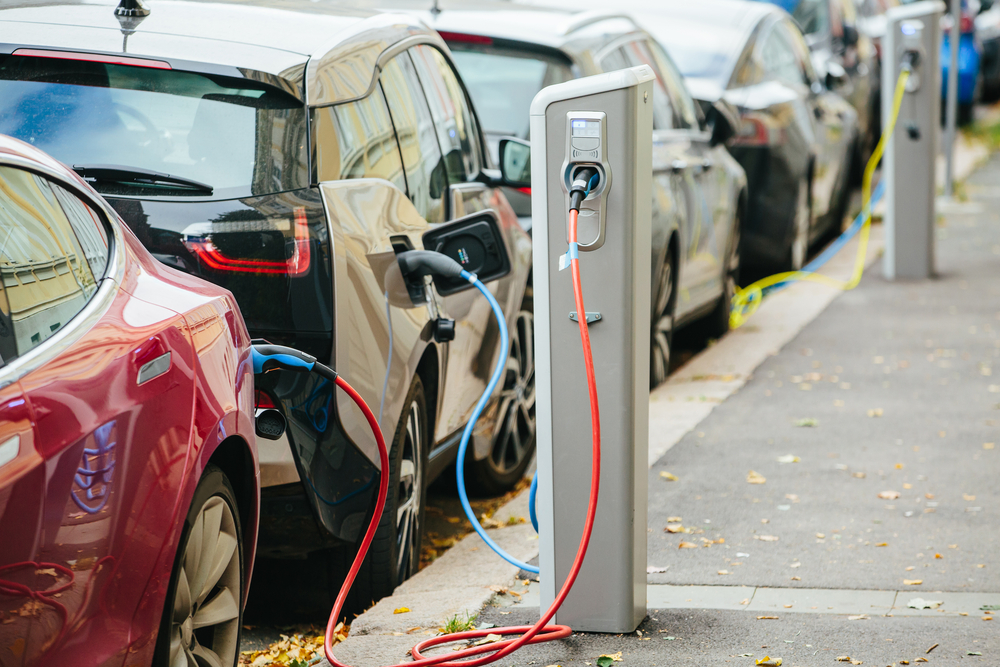

The charging infrastructure for electric vehicles is still in its developmental stages, posing a significant challenge to widespread EV adoption. While urban areas may have more charging stations, rural and less populated regions often lack sufficient infrastructure. This disparity creates “range anxiety” for EV owners, limiting their travel options and causing inconvenience. The availability of compatible chargers also varies, with some vehicles unable to use certain types of charging stations, further complicating the charging process. In addition, the existing infrastructure can be unreliable, with broken or occupied chargers causing delays. The inconsistency in charger locations and compatibility issues underscores the need for a standardized and more extensive network of charging stations to support the growing number of EVs on the road.
Limited Range in Extreme Temperatures
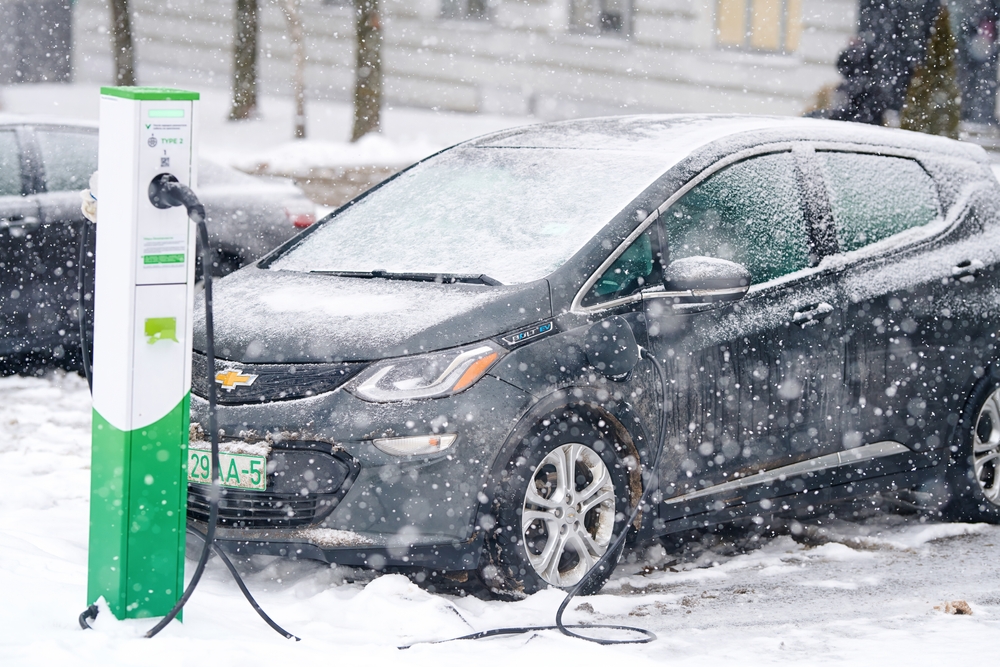

Electric vehicles often suffer from reduced range in extreme temperatures. Both cold and hot weather can significantly impact battery performance, leading to a shorter driving range than advertised. In cold weather, the battery’s chemical reactions slow down, reducing efficiency and increasing energy consumption for heating. Similarly, in hot climates, cooling systems drain the battery to maintain optimal temperatures. These fluctuations can be problematic for drivers in regions with harsh climates, making EVs less reliable for long-distance travel in such conditions. Additionally, preconditioning the battery and cabin can also consume a significant amount of energy, further reducing the effective range of the vehicle. This makes it essential for manufacturers to develop more resilient battery technologies that can withstand a wider range of environmental conditions without significant performance loss.
High Upfront Costs
The high upfront cost of electric vehicles remains a barrier for many potential buyers. Despite lower operating costs and government incentives, the initial purchase price of an EV can be significantly higher than that of a comparable gasoline vehicle. This cost disparity is mainly due to the expensive battery technology and lower economies of scale in EV production. While prices are gradually decreasing as technology improves, the current financial barrier still deters many consumers from making the switch to electric vehicles. Additionally, the higher cost of EVs can affect the affordability of insurance and financing options, further complicating the purchase decision. This highlights the importance of continued research and development to reduce production costs and increase the affordability of EVs for a broader audience.
Limited Model Options

Compared to traditional gasoline vehicles, the range of electric vehicle models available is relatively limited. While major manufacturers are expanding their EV lineups, the variety and customization options are still not as extensive as those for gasoline cars. This limitation can make it challenging for consumers to find an EV that meets all their preferences and needs, particularly for those seeking specific features or styles. The lack of options in segments such as trucks, sports cars, and luxury vehicles can also deter potential buyers who have particular requirements. Furthermore, the limited availability of different body styles and performance levels restricts consumer choice, which can slow down the adoption of electric vehicles. Expanding the variety of EV models will be crucial to appealing to a broader range of consumers and accelerating the transition to electric mobility.
Battery Degradation Over Time
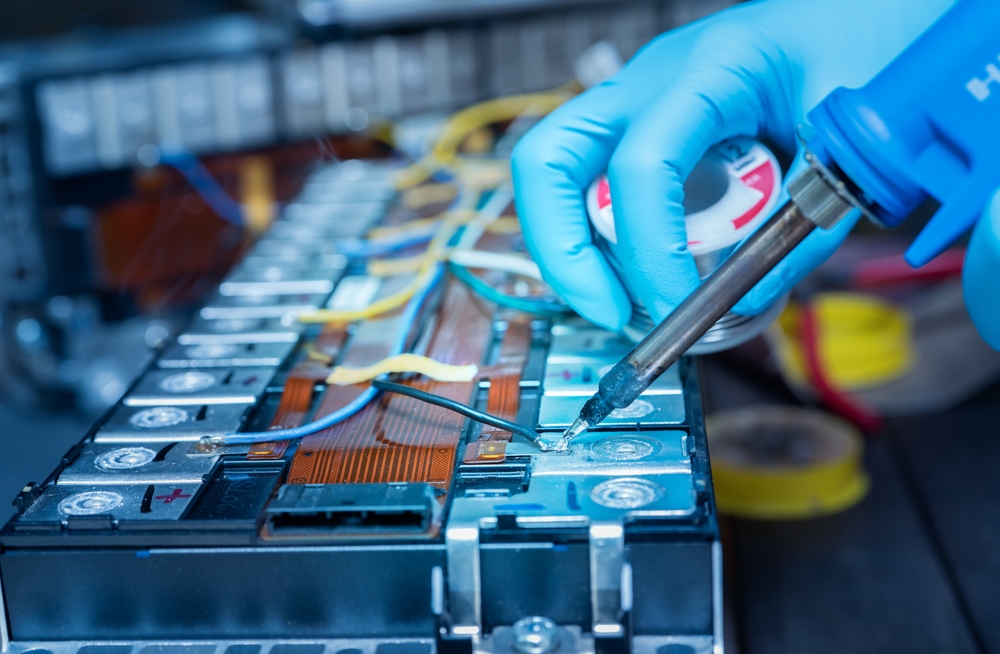

Battery degradation is a concern for electric vehicle owners, as the performance of lithium-ion batteries declines with age and use. Over time, this degradation leads to reduced driving range and overall efficiency. The rate of degradation varies based on factors such as driving habits, charging frequency, and environmental conditions. This issue raises concerns about the long-term value and sustainability of EVs, as replacement batteries can be costly. Regular fast charging and high-temperature exposure can accelerate degradation, making it essential for owners to manage their charging habits and storage conditions carefully. The prospect of significant performance loss over the vehicle’s lifetime can affect resale values and overall consumer confidence in EV technology. Ongoing advancements in battery chemistry and management systems are needed to improve the longevity and reliability of EV batteries.
Limited Availability of Used EVs

The market for used electric vehicles is still developing, with fewer options available compared to the extensively used gasoline vehicle market. This limited availability can make it difficult for budget-conscious consumers to find affordable EV options. Additionally, the potential for battery degradation in older models can further complicate the decision to purchase a used EV, as buyers must weigh the cost of future battery replacements. The uncertain resale value and varying levels of remaining battery life can deter potential buyers, making the used EV market less attractive. This highlights the need for transparency in battery health information and the development of reliable secondary markets for EV batteries. As the market matures, increasing the availability and reliability of used EVs will be crucial for expanding access to electric mobility for a wider range of consumers.
Higher Insurance Costs

Insurance premiums for electric vehicles can be higher than those for traditional cars. The higher costs are due to several factors, including the expensive battery technology, specialized repair processes, and the higher overall value of EVs. Insurance companies often factor in these risks, resulting in increased premiums for EV owners. This added expense can offset some of the savings gained from lower fuel and maintenance costs. The limited availability of specialized repair shops and parts can also contribute to higher repair costs, which insurers consider when setting premiums. Addressing these issues will require increased investment in EV repair infrastructure and the development of more cost-effective insurance solutions tailored to electric vehicles.
Limited Towing and Payload Capacity
Electric vehicles often have limited towing and payload capacities compared to their gasoline counterparts. The additional weight of the battery and the need to preserve driving range can restrict the amount of cargo an EV can carry or tow. This limitation can be a significant drawback for consumers who require vehicles for heavy-duty tasks or those who frequently tow trailers, reducing the versatility of EVs for certain use cases. Manufacturers are working on developing more capable electric trucks and SUVs, but the current offerings may not meet the needs of all potential buyers. Improving the towing and payload capacities of electric vehicles will be essential to appeal to a broader range of consumers and increase EV adoption in various segments.
Limited Availability of Fast Chargers
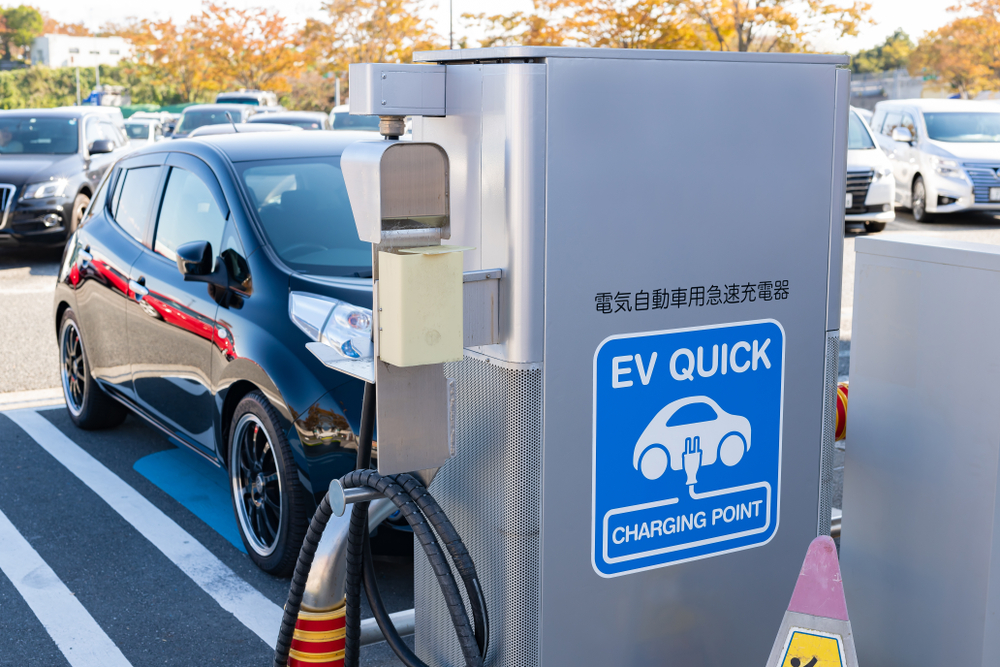

While fast-charging stations are becoming more common, their availability is still limited compared to traditional gas stations. The scarcity of fast chargers can lead to longer wait times at charging stations and inconvenience for drivers, especially during long trips or in areas with high EV adoption rates. This limitation underscores the need for continued investment in charging infrastructure to support the growing number of electric vehicles on the road. Additionally, the uneven distribution of fast chargers can create regional disparities in charging convenience, affecting the practicality of EVs in certain areas. Expanding the fast-charging network and ensuring consistent availability will be crucial for enhancing the overall user experience and supporting widespread EV adoption.
Depreciation Concerns
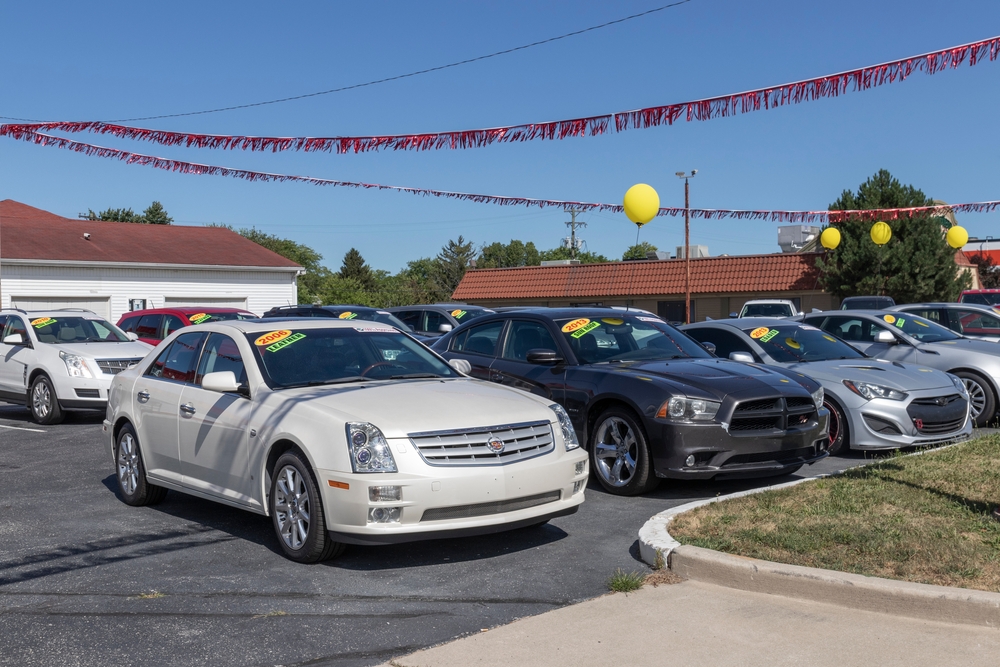

Electric vehicles can experience higher depreciation rates than traditional cars, primarily due to concerns about battery life and technological advancements. As newer models with improved battery technology and features become available, older EVs may lose value more quickly. This rapid depreciation can affect the resale value of electric vehicles, making them a less attractive investment for some consumers. Additionally, the potential for costly battery replacements can further impact the perceived value of used EVs. Ensuring the long-term durability and performance of EV batteries, as well as offering affordable replacement options, will be critical for addressing depreciation concerns and maintaining consumer confidence in the value of electric vehicles.
Limited Repair and Maintenance Facilities
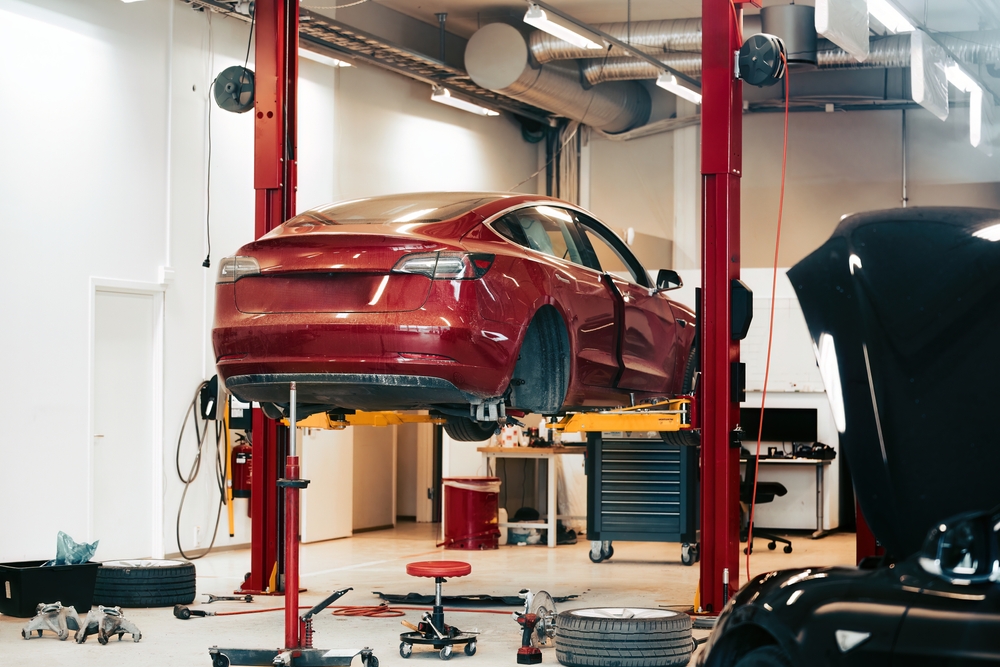

The specialized technology and components in electric vehicles require specific expertise and equipment for repairs and maintenance. As a result, there are fewer service centers and qualified technicians available to work on EVs compared to traditional gasoline vehicles. This limitation can lead to longer wait times for repairs and higher service costs, adding to the overall ownership expenses for EV drivers. The scarcity of repair facilities can also discourage potential buyers who are concerned about the availability of convenient and reliable service options. Expanding the network of EV-certified repair shops and increasing the training and certification of technicians will be essential for supporting the growing EV market and ensuring a positive ownership experience.
Safety Concerns with Battery Fires
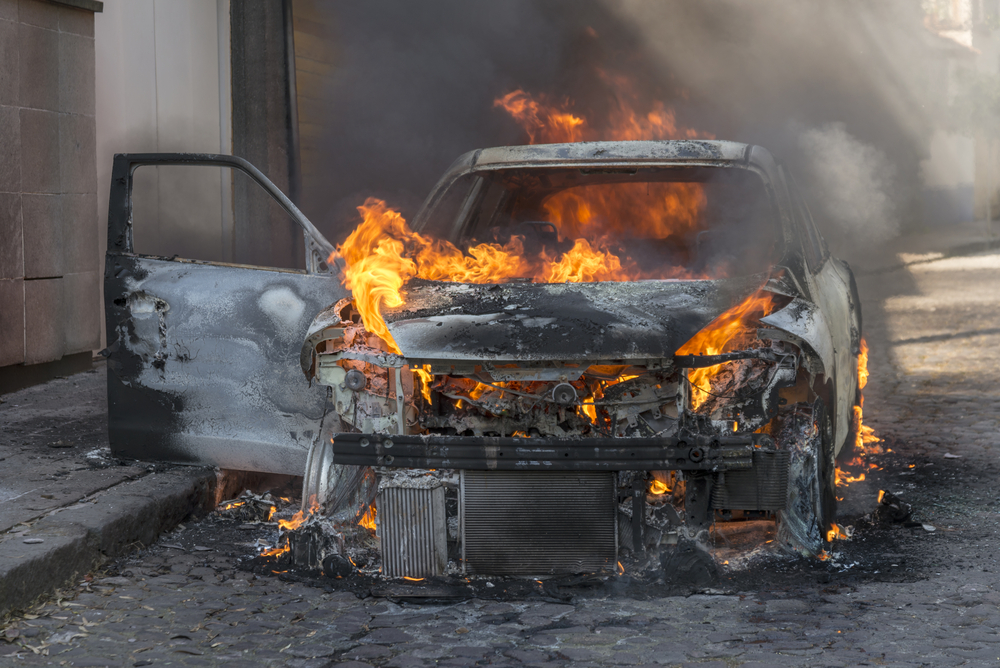

While electric vehicles are generally safe, there have been incidents of battery fires, particularly in severe accidents. Lithium-ion batteries can catch fire if damaged, leading to safety concerns for drivers and passengers. Although advancements in battery technology and safety features are addressing these risks, the potential for battery fires remains a point of concern for some consumers considering an EV. The high energy density of lithium-ion batteries means that any failure can result in a significant thermal event, requiring robust safety measures and protocols. Continued research and development are needed to improve the safety and resilience of EV batteries, as well as to educate consumers about best practices for preventing and responding to battery-related incidents.
Limited Range for High-Performance Models

High-performance electric vehicles, designed for speed and acceleration, often face trade-offs in terms of driving range. The additional power required for high performance can drain the battery more quickly, reducing the overall range of the vehicle. This limitation can be a drawback for enthusiasts who want both performance and practicality from their electric cars. Balancing the demands of high performance with the need for adequate range presents a technical challenge for manufacturers. Developing more efficient powertrains and battery management systems will be essential for creating high-performance EVs that can also offer competitive driving ranges.
Complex Charging Networks
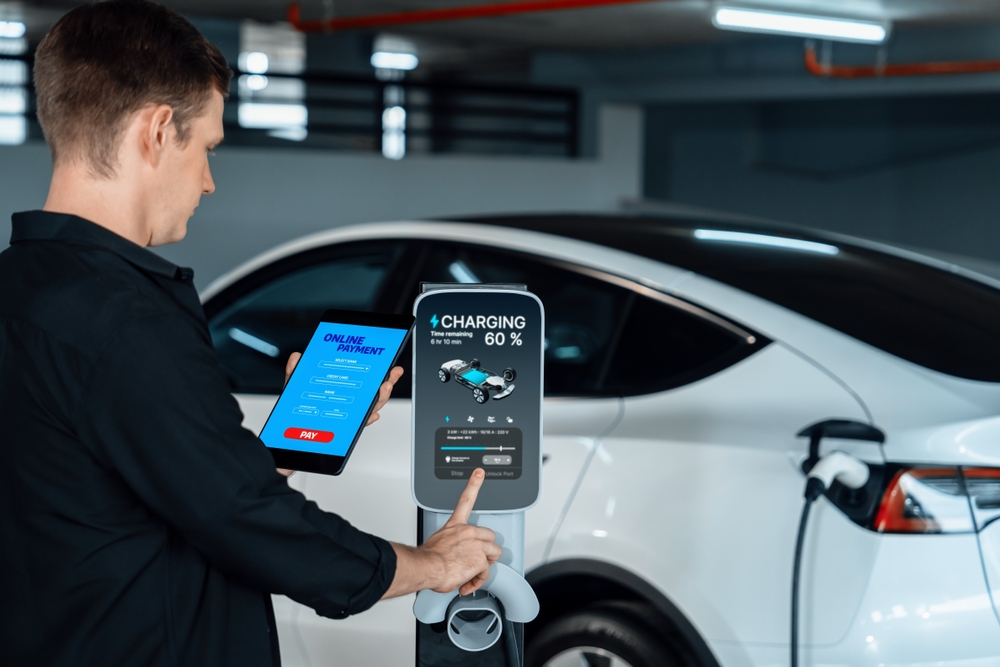

Navigating the various charging networks and their associated payment systems can be confusing for electric vehicle owners. Different networks may require separate memberships or payment methods, complicating the charging process. This complexity can be frustrating for drivers who need a seamless and straightforward charging experience. The lack of interoperability between charging networks can also limit the availability of charging options for EV owners, further complicating travel plans. Standardizing charging network access and payment methods will be crucial for simplifying the charging experience and supporting the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
This article originally appeared on MyCarMakesNoise.
More from MyCarMakesNoise
10 Car Modifications That Will Transform Your Vehicle

In the realm of automotive enthusiasts, personalizing an import car is more than just a hobby; it’s an expression of individuality and passion. This article is a guide tailored for those looking to elevate their vehicles beyond the ordinary. Read More
10 Companies Revolutionizing Self-Driving Vehicles

The automotive landscape is undergoing a transformative shift as the autonomous era unfolds, with technology paving the way for self-driving vehicles. In this dynamic and groundbreaking industry, several companies are at the forefront, driving innovation and shaping the future of transportation. Read More
10 Impressive Car Brands You Might Not Know About

In the vast world of automobiles, beyond the well-trodden path of renowned brands, lies a trove of lesser-known car manufacturers that offer exceptional value without compromising on quality and performance. Read More














