What causes white smoke to spurt from my exhaust? We have the mystery solved for you.
The most important thing is if white smoke spews from your exhaust is to turn the car off and call your mechanic.
It is most likely that something has cracked and will do serious damage to your car if you keep driving it.

Contents
A brief outlook on car emissions
In 2019 a study was done with greenhouse gas emissions from transport in the U.S. It was found that 29% of greenhouse gas emissions came from cars. That makes cars the largest contributor in the U.S.
In August 2021 the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) put forward a proposal to toughen the greenhouse gas (GHG) emission standards for passenger cars and light trucks. The EPA proposed stricter rules for the reduction of How Targeted Vehicle Scrappage Subsidies Can Reduce Pollution Effectively GHG from Model Year (MY) of 2023 to 2026.
With GHG reductions as well as other pollutants, there will be a dramatic reduction in emissions.
The approach is to drive the car industry towards hybrid and electronic cars. This will also help the consumer with lower fuel costs. It is a positive step towards better health for the U.S.
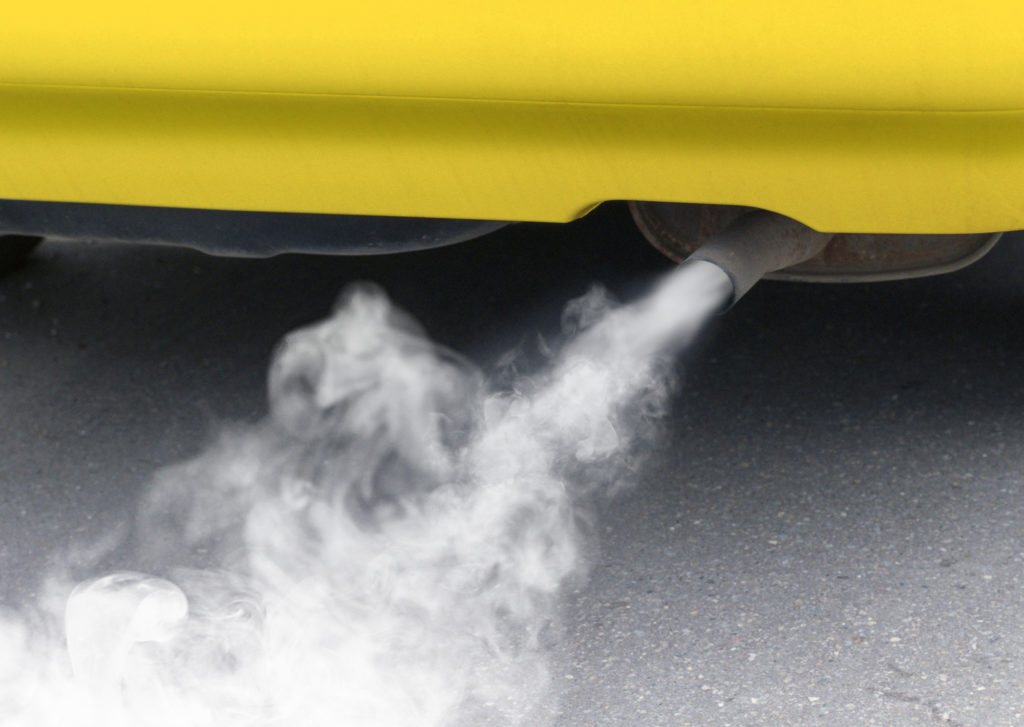
Is it normal for white smoke to come out of the exhaust on startup?
Thin wisps of white smoke emitting from your car’s exhaust on startup is acceptable. This thin white smoke is caused by a build-up in the car’s exhaust system.
The condensation build-up creates steam when the car is turned on. This looks like white smoke.
It is more serious if you have heavy and large clouds of smoke spewing from your exhaust on startup.
Possible causes of the white smoke on startup
a) Coolant Leak
A coolant leak is often the result of a blown head gasket or cracks in the head. Cracks let the coolant leak onto parts of the engine that it must not be.
If the coolant leaks out, it can cause larger problems. When your coolant reaches a very low level, your engine will seize and the car will overheat.
b) Valve Seal Leak or Piston Ring
Oil leaks happen when valve seals are leaky or when the piston rings are worn. The oil drips into the combustion chamber. The oil will mix with the fuel and cause white smoke.
If you have the necessary skills required, you can fix the issues yourself. That being said, it is highly recommended to take your car to a mechanic or service centre.
c) Faulty Fuel Injector
When the car’s fuel injector is faulty it is caused by a leaking o-ring. It can also be stuck in an open position. This will push too much fuel into the combustion chamber.
When there is too much fuel in the combustion chamber it does not burn away. Instead, the exhaust will give off white smoke.
The mechanic or service centre will replace the o-ring. The tough part is figuring out which fuel injector is faulty.
The mechanic or service centre will probably recommend replacing all the injectors as they are affordable. This will also ensure the long-term health and safety of your car.
d) Incorrect Injector Pump time (Diesel Engine)
If the injector pump time is not working correctly the engine will be “running rich”. This means that not all the fuel is being burned up.
The unburned fuel will escape out of the exhaust and cause white smoke. It can even turn to grey smoke in some cases.
In most cases, the injector will need to be reprogrammed. This can easily be done at a mechanic or service centre.
e) Cracked Cylinder Head
Coolant will leak out of the cracked cylinder head onto the engine. The coolant will mix with the fuel causing it to become contaminated. There will be a sweet smell accompanying the white exhaust smoke.
The difference between replacing a cylinder head and a head gasket is the cost. A cylinder head costs a lot more to repair than a head gasket.
A cracked cylinder head can also cause your engine to overheat and seize up. Be vigilant by checking temperature gauges often.
f) Crack in Engine Block
A cracked engine block is possibly the most costly scenario. It is essential to get your car to the mechanic or service centre as soon as possible.
A crack in the engine block can cause the oil and antifreeze to mix. This causes major problems for the engine.
If left for too long, smoke will escape out of the engine as well. The longer the issue is left, the more issues will occur.
The smoke from the engine is caused by emission fumes that have leaked through the crack instead of through the exhaust system.
This will be coupled with the loss of power from the engine.
g) Engine Taking on too Much Fluid from Vacuum Pipe or Hose
If the engine has a vacuum leak it can still run normally, however, it might idle quicker than usual. It can also idle roughly, misfire, or stall.
The car will probably not accelerate as well as it normally does. If the leak is substantial, it might stop the engine from starting at all.
The lean air-fuel ratio will burn at a hotter temperature and increase the oxide emissions. Even if the check engine light is not activated, your car can still fail an emissions test.
The engine controller will attempt to self-regulate by adding more fuel. You will notice an increase in your car’s fuel consumption.
Running the engine in this state can lead to engine damage by deteriorating pistons and bearings. The high temperatures can also cause a catalytic converter meltdown.
Braking systems can also be affected, which can make it tougher to stop your car.

Diagnosis of white smoke from exhaust on startup
There are so many variables for the cause of white exhaust smoke. It depends on the thickness and amount of exhaust smoke coming from your car.
The best thing to do is get your car to a mechanic or service centre as soon as possible.
The longer you drive your car with white smoke billowing out of the exhaust, the more dire the engine consequences. And the more costly the repairs will be.
How to fix white smoke from exhaust on startup (step-by-step guide)
a) Step 1
Check for obvious cracks in the engine, head gasket, or cylinders. These cannot be repaired and need to be replaced as soon as possible.
b) Step 2
Check for leaks coming from the engine. This might help to locate where the issue is coming from.
If there is a leak near the front or under the engine, it is most likely engine oil, transmission fluid, power steering fluid, or coolant (antifreeze).
Leaks happening near the wheels will most likely be brake fluid.
Leaks at the back of the car or the exhaust are probably leaking water or fuel.
Make sure to get your car to a mechanic or service centre if you do not have the necessary skills to fix the problem.
c) Step 3
Corrosion and rust can be damaging to the engine. Types of corrosion include;
- High-temperature corrosion
When the engine runs hot, it can lead to rust build-up. Friction is also caused by low or bad quality engine oil.
- Crevice corrosion
Found in gaps around the engine, including seals and gaskets. This is caused by deposits that slowly degrade components over time.
- Chemical corrosion
When fuel and oil mix with water molecules.
- Galvanic corrosion
This is an electromechanical reaction. It is when two different metals come into electric contact. This is unavoidable, and you do not have to worry about it too much. It has no long-term effect on your car’s engine.
This is easy to avoid by doing the following:
- Maintain your car’s service schedule. Change your car’s oil and oil filter every 12 months.
- Check the coolant (antifreeze) regularly. Also, check the reservoir and the condition of the coolant.
- Always use good quality coolant and oil.
- Maintain the fuel system. Change the fuel filter every 20,000 miles.
- Flush out the cooling system.
d) Step 4
Maintaining the integrity of your car can go a long way to preventing issues later on:
- Fuel filter (replace every 2-years or 30,000 miles)
- Engine air filter (replace every 15,000-30,000 miles)
- Cabin air filter (replace every 15,000-20,000 miles)
- Engine oil filter (replace every 3-months or 3,000 miles)
- Emission filter (replace every 100,000 miles)
e) Step 5
When it comes to fuel injection, it is best to take your car to a professional. It is frowned upon to try to change this yourself.
Most fuel injectors are faulty due to contaminated fuel. Get your fuel filter replaced at a minimum of two years or with every service.
Conclusion
Maintain your car’s service plan. Always take your car to a reputable mechanic or service center.
Always check to see what work they have done on your car. Check to see that the work has actually been done.