Space telescopes have revolutionized our understanding of the universe, revealing secrets hidden from view for centuries. From discovering distant exoplanets to mapping the cosmic microwave background, these powerful instruments have made countless astounding discoveries. We’ll explore 10 of the most remarkable findings made by space telescopes, showcasing their profound impact on astronomy and our knowledge of the cosmos.
Contents
Exoplanets in the Habitable Zone
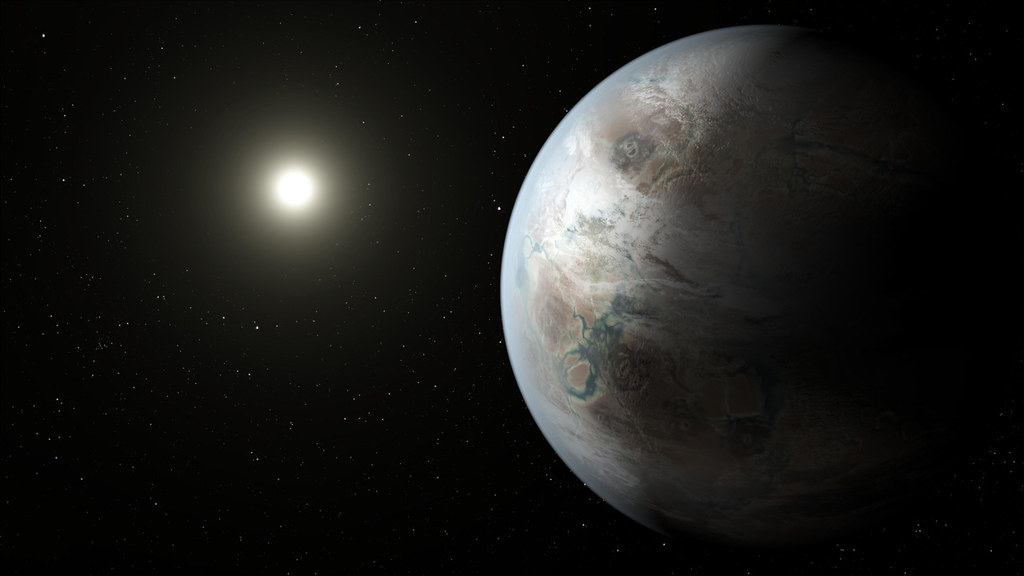

Space telescopes like Kepler have discovered exoplanets within the habitable zone of their stars, such as Kepler-452b. These planets orbit at distances where conditions might be suitable for liquid water, a crucial ingredient for life. This groundbreaking discovery suggests that potentially habitable planets could be more common than previously thought. New possibilities in the search for extraterrestrial life have emerged as a result.
The Accelerating Expansion of the Universe

The Hubble Space Telescope’s observations of distant supernovae provided evidence that the universe’s expansion is accelerating. This unexpected finding led to the concept of dark energy, a mysterious force making up about 70% of the universe’s total energy. It reshaped our understanding of the universe’s future, suggesting that galaxies are moving apart at an increasing rate. Scientists are now delving into the nature of dark energy, potentially uncovering new physics beyond the current standard model.
Black Hole in the Milky Way’s Center

Confirmation of a supermassive black hole at the center of our galaxy, named Sagittarius A*, came from the Hubble and Chandra telescopes. This finding provided valuable insights into the role black holes play in galaxy formation and evolution. Observing the motions of stars around Sagittarius A* allowed astronomers to measure its mass and study extreme conditions near a black hole. Understanding our galaxy’s core dynamics helps us piece together the Milky Way’s history and future.
Detailed Mapping of the Cosmic Microwave Background
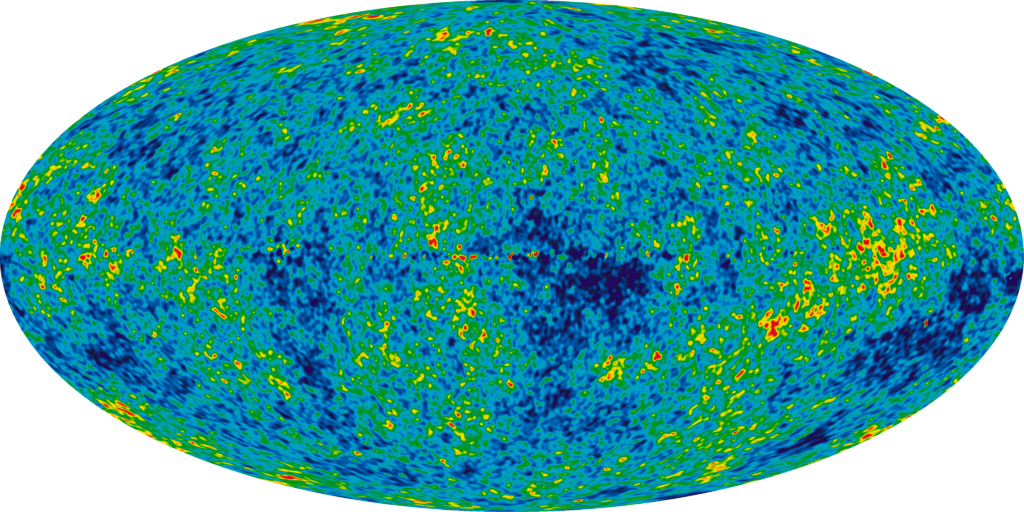
The Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) and the Planck satellite mapped the cosmic microwave background (CMB) with remarkable precision. These observations offered a detailed picture of the early universe’s composition, age, and development. By studying the CMB’s temperature fluctuations, scientists confirmed and refined the Big Bang model of cosmology. This data also illuminated the universe’s geometry, indicating it is flat and has specific amounts of ordinary and dark matter. These detailed maps are crucial for understanding the fundamental parameters governing the cosmos.
Atmospheric Composition of Exoplanets

Space telescopes like Hubble and Spitzer have enabled the study of exoplanet atmospheres, revealing their compositions. By analyzing light passing through or emitted by these distant worlds, astronomers have detected gases such as water vapor, methane, and carbon dioxide. These findings are essential for assessing exoplanets’ habitability and understanding planetary formation and evolution. Identifying various atmospheric components helps pinpoint planets that might support life.
Water Plumes on Europa

The Hubble Space Telescope detected water vapor plumes erupting from Jupiter’s moon Europa, hinting at a subsurface ocean. This discovery holds significant implications for the search for extraterrestrial life, as Europa’s ocean could potentially harbor microbial life. Observations of these plumes allow scientists to study the moon’s internal composition and dynamics without a lander. The presence of water plumes indicates ongoing geological activity, making Europa a prime target for future missions.
The Oldest Known Galaxy
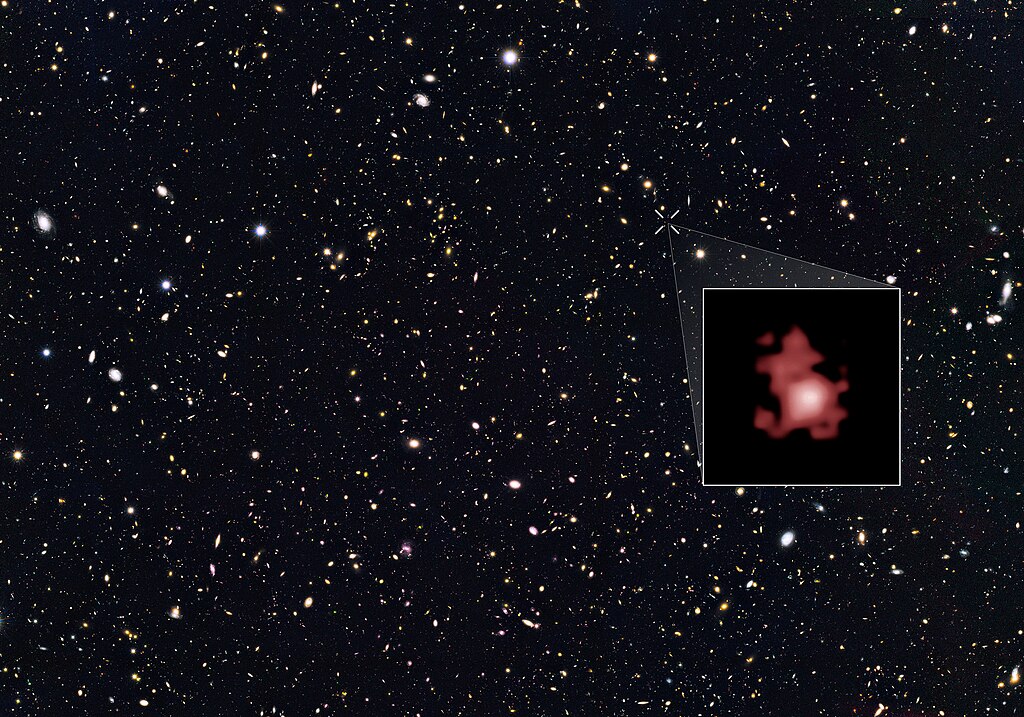

Astronomers discovered GN-z11, a galaxy dating back to just 400 million years after the Big Bang, using the Hubble Space Telescope. This makes it the oldest and most distant galaxy ever observed, offering a glimpse into the early universe. Studying such ancient galaxies helps scientists understand galaxy formation and evolution over cosmic time. This discovery also sheds light on conditions in the young universe, revealing processes that led to the first stars and galaxies’ formation.
The Structure of Nebulae
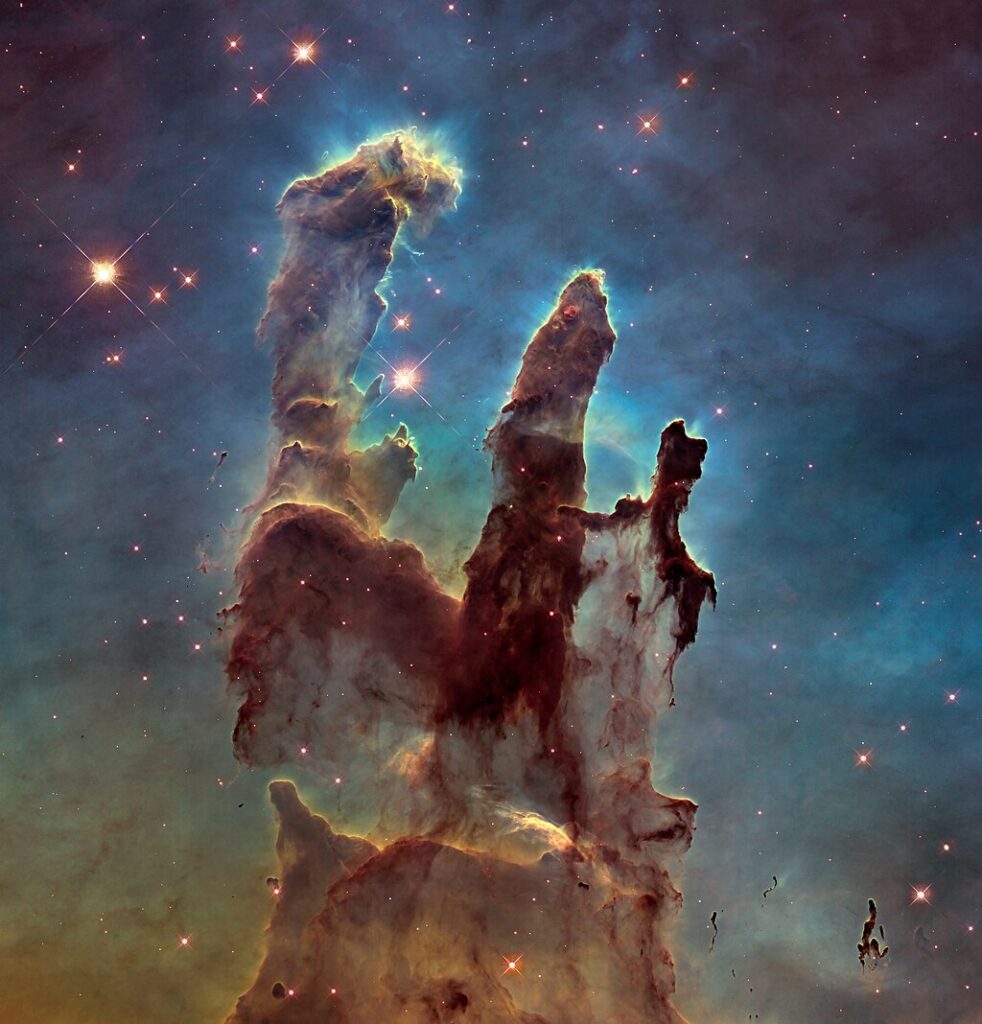

Space telescopes like Hubble have captured stunning images of nebulae, revealing their intricate structures and dynamics. These observations have provided insights into star formation processes and stars’ life cycles. For instance, the detailed images of the Eagle Nebula’s “Pillars of Creation” have become iconic, showcasing regions where new stars are born. Understanding nebulae’s structure and composition helps astronomers piece together stellar systems’ history and future.
Gamma-Ray Bursts
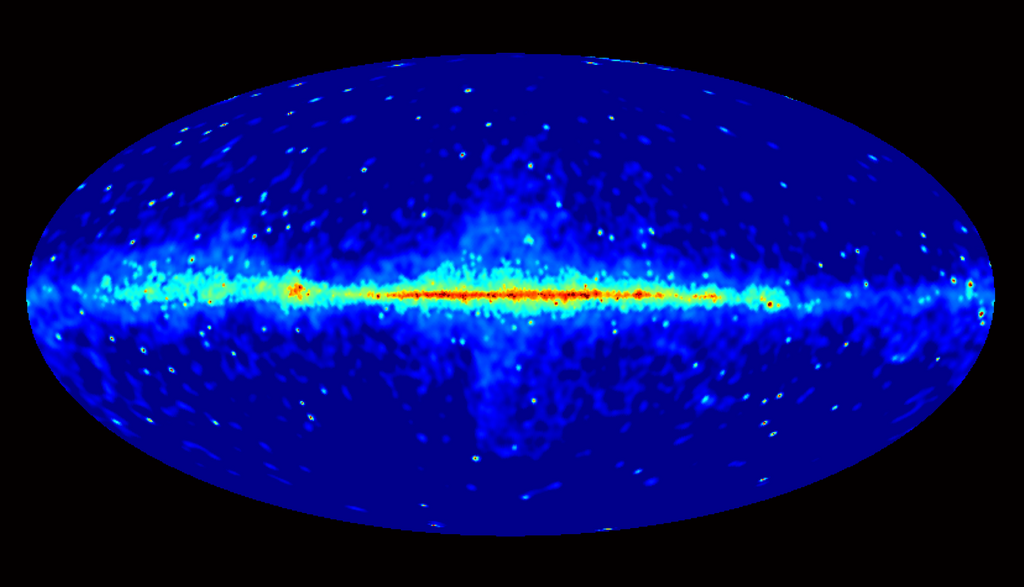
Space telescopes like the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope have identified and studied gamma-ray bursts, the universe’s most energetic explosions. These bursts, originating from collapsing massive stars or merging neutron stars, release enormous energy. Observing gamma-ray bursts helps scientists understand extreme conditions and processes producing such powerful phenomena. These studies also provide insights into black hole formation and matter behavior under extreme conditions.
The Lifecycle of Stars

Space telescopes have captured detailed images of star clusters, nebulae, and supernova remnants, revealing the full lifecycle of stars. From stars’ birth in dense molecular clouds to their explosive deaths in supernovae, these observations provide a comprehensive view of stellar evolution. Studying stars’ lifecycle helps astronomers understand element formation processes and matter distribution in galaxies. Detailed images of stellar nurseries and remnants also inspire a deeper appreciation for the universe’s dynamic nature.
The Detection of Water on Mars

The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, equipped with high-resolution imaging and spectrometers, detected evidence of liquid water on Mars. This discovery has profound implications for the possibility of life on Mars and the planet’s habitability. Observations of seasonal dark streaks, known as recurring slope lineae, suggest liquid water may flow on the Martian surface under certain conditions. Water’s presence is crucial in the search for past or present life on Mars and informs future exploration missions.
This article originally appeared on MyCarMakesNoise.
More from MyCarMakesNoise
Exploring the 15 Rarest Nissan Cars Ever Produced

Nissan has produced some truly remarkable cars over the years, but some models are so rare that even die-hard fans might not know about them. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the 15 rarest Nissan cars ever produced. Read More.
20 Fascinating Facts About the Golden Age of Aviation

Step back in time to the Golden Age of Aviation, an era marked by groundbreaking innovations and the glamorous allure of air travel. Spanning from the 1920s to the 1950s, this period transformed aviation with daring feats and technological breakthroughs. Read More.
22 Tips for Affordable Car Maintenance

Maintaining your car efficiently and affordably is simpler than it seems. Seasoned auto mechanics provide invaluable tips to keep your vehicle in top shape without breaking the bank. From routine inspections to preventative measures, these expert insights can extend your car’s life, enhance its performance, and help you avoid costly repairs. Read More.














