Space exploration has revolutionized our understanding of the cosmos and transformed human capabilities. From the first steps on the moon to probing the mysteries of distant planets, certain missions have left an indelible mark on history. In this article, we delve into 13 groundbreaking space missions that changed the course of science and exploration, highlighting the remarkable achievements and discoveries that continue to inspire us today.
Contents
Apollo 11 (1969)
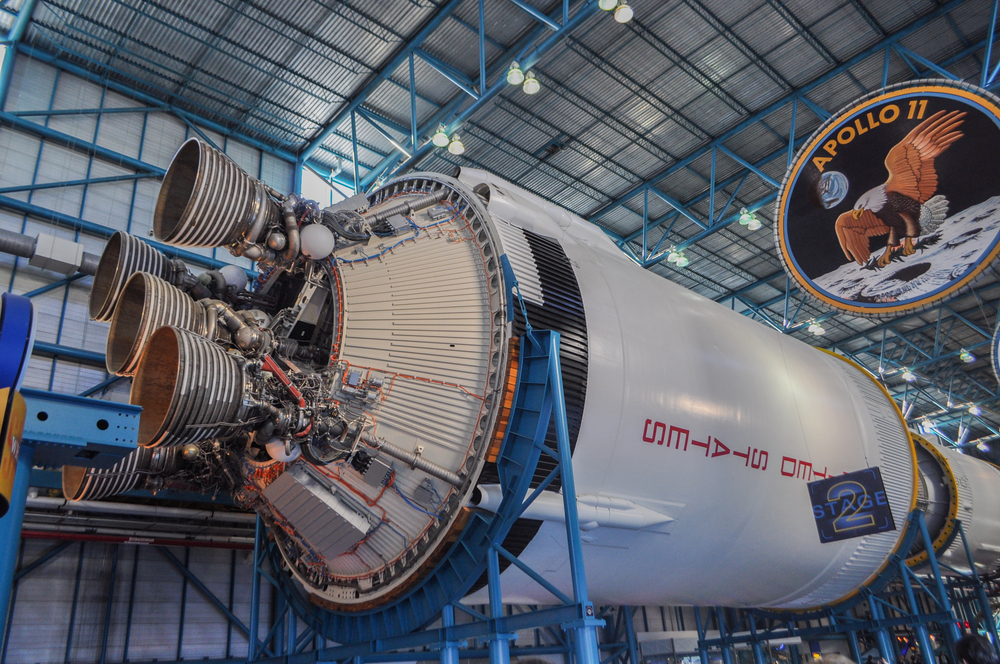

Apollo 11 was the first manned mission to land on the moon, marking a monumental achievement in human space exploration. Astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin became the first humans to walk on the lunar surface, while Michael Collins orbited above. Showcasing the capabilities of the Saturn V rocket and the Lunar Module, the mission cemented the United States’ dominance in the Space Race. It provided valuable scientific data and iconic images, such as the famous footprint on the moon.
Sputnik 1 (1957)
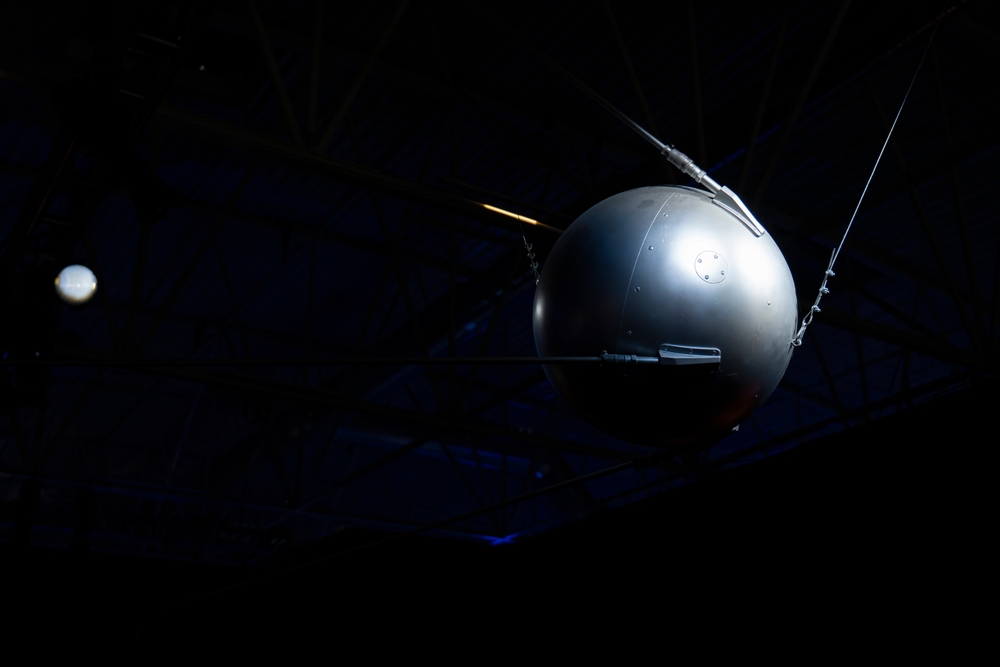

Launched by the Soviet Union, Sputnik 1 was the world’s first artificial satellite, initiating the space age. Weighing about 184 pounds, this spherical satellite transmitted radio pulses back to Earth, confirming its presence in orbit. The success of Sputnik 1 spurred the United States to accelerate its own space program, leading to the establishment of NASA. Highlighting the potential for space exploration, it demonstrated the feasibility of artificial satellites for scientific and communication purposes.
Voyager 1 (1977)
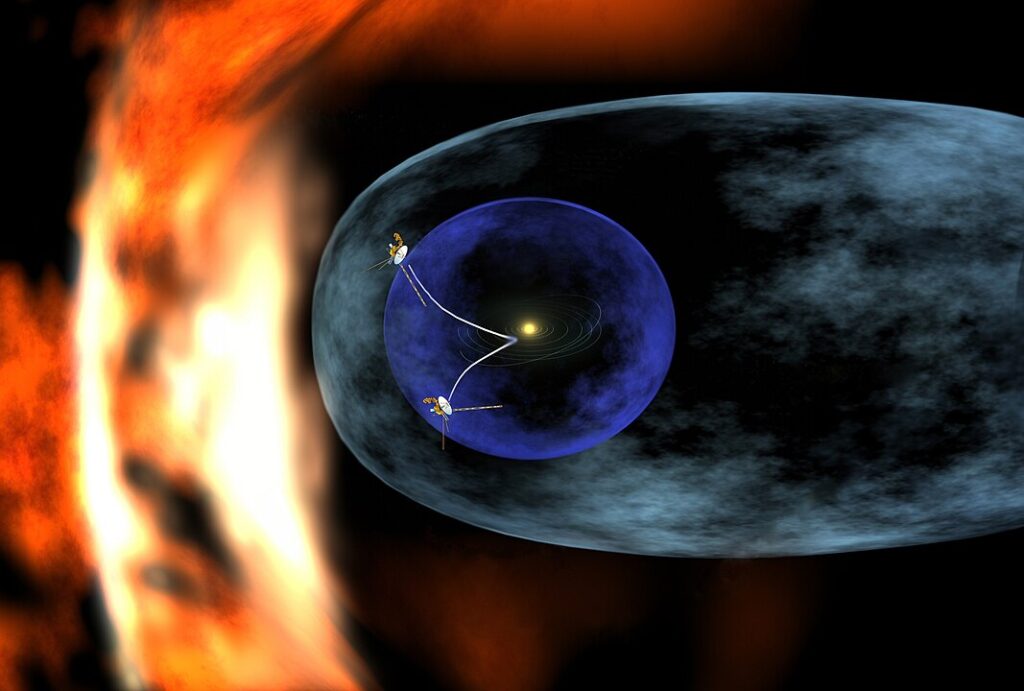
Voyager 1, launched by NASA, set out to explore the outer planets and interstellar space, and it remains one of the farthest human-made objects from Earth. Equipped with a golden record containing sounds and images from Earth, Voyager 1 provided detailed images and data from Jupiter and Saturn, including discoveries like volcanic activity on Jupiter’s moon Io. As it travels through interstellar space, the spacecraft continues to send back valuable data about the heliosphere and beyond.
Hubble Space Telescope (1990)
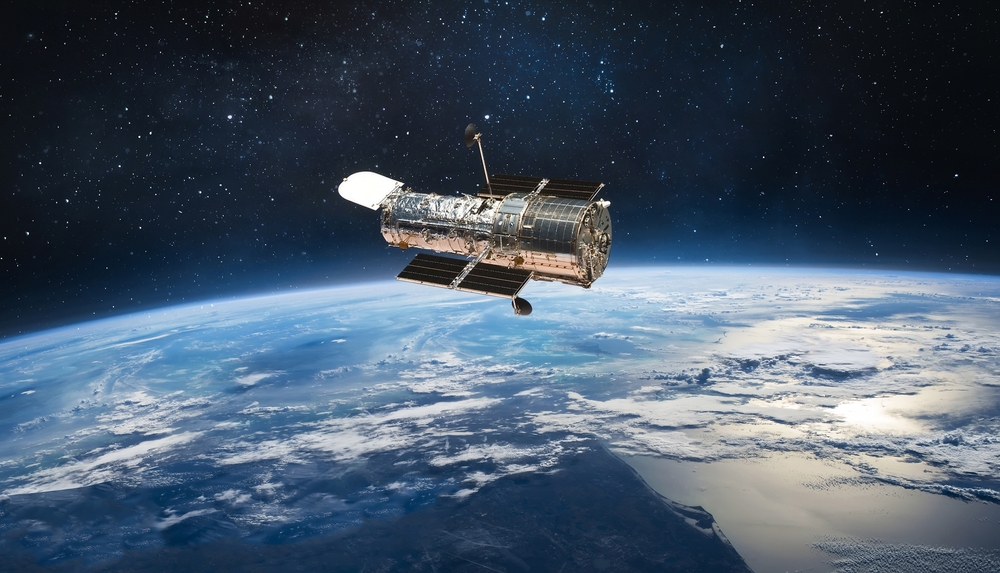

The Hubble Space Telescope, a joint project of NASA and ESA, has revolutionized our understanding of the universe with its stunningly detailed images. Orbiting Earth, Hubble has captured breathtaking views of galaxies, nebulae, and supernovae, leading to discoveries about the expansion of the universe and the presence of dark energy. Its advanced instruments have allowed astronomers to peer into the distant past, observing light from billions of years ago.
Apollo 13 (1970)
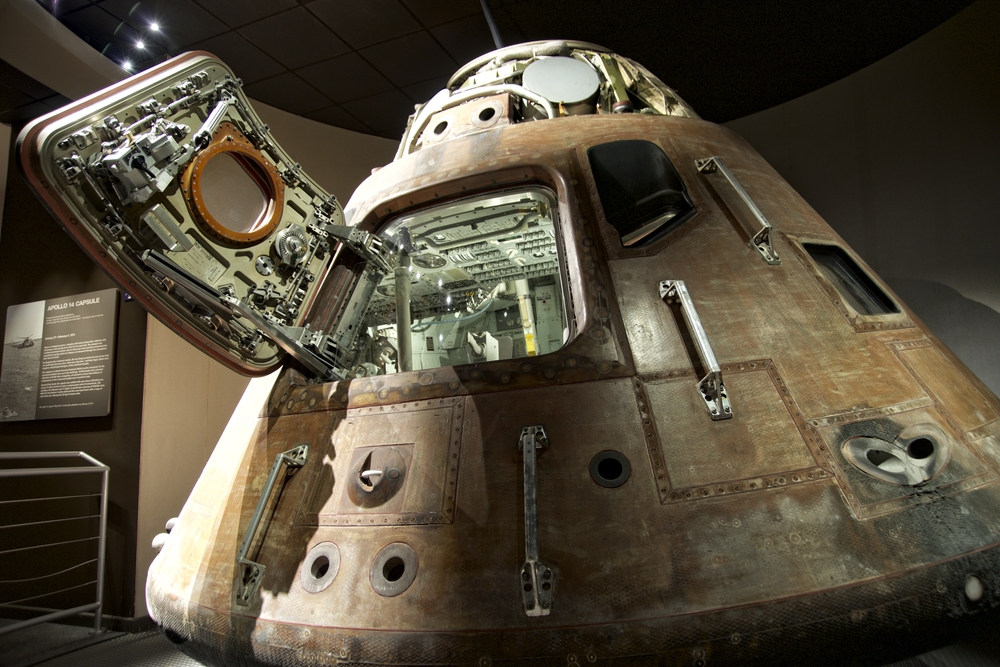

Although Apollo 13 did not achieve its intended lunar landing, it became a landmark mission in human spaceflight due to the crew’s dramatic survival. An oxygen tank explosion crippled the spacecraft, forcing NASA to abort the moon landing and focus on safely returning the astronauts to Earth. The mission showcased the ingenuity and problem-solving capabilities of NASA engineers and astronauts, who used the Lunar Module as a lifeboat. Against all odds, Apollo 13’s successful return is a testament to human resilience and innovation.
Mars Rover Curiosity (2012)
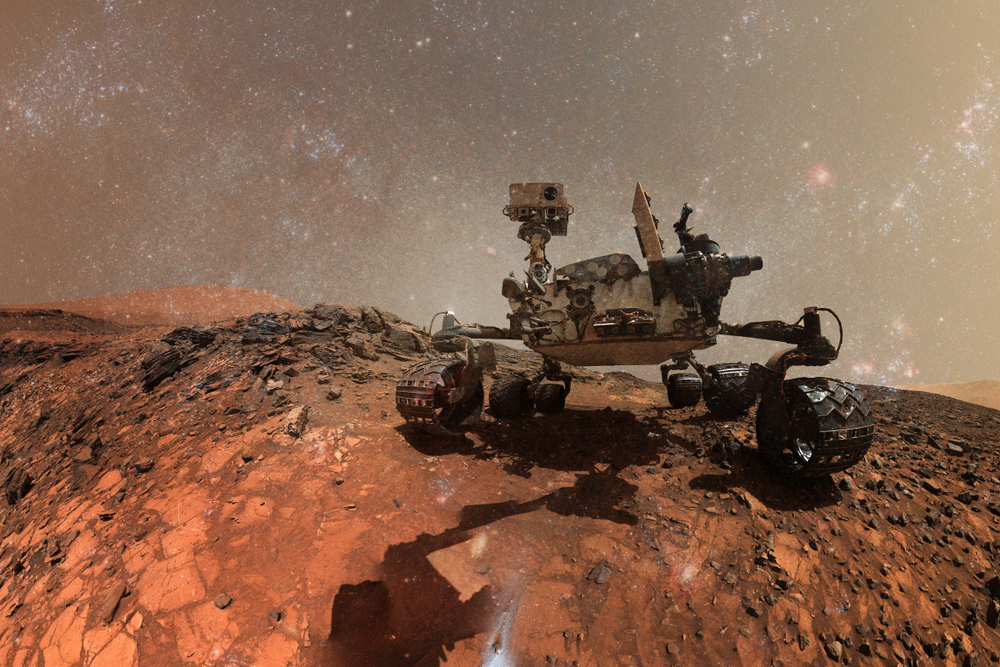

Curiosity, part of NASA’s Mars Science Laboratory mission, was designed to explore Gale Crater on Mars and assess the planet’s habitability. Equipped with advanced scientific instruments, Curiosity has analyzed soil and rock samples, providing evidence of ancient water flows and organic molecules. The rover’s discoveries have significantly advanced our understanding of Mars’ geology and climate, informing future missions and the potential for human exploration.
International Space Station (1998)
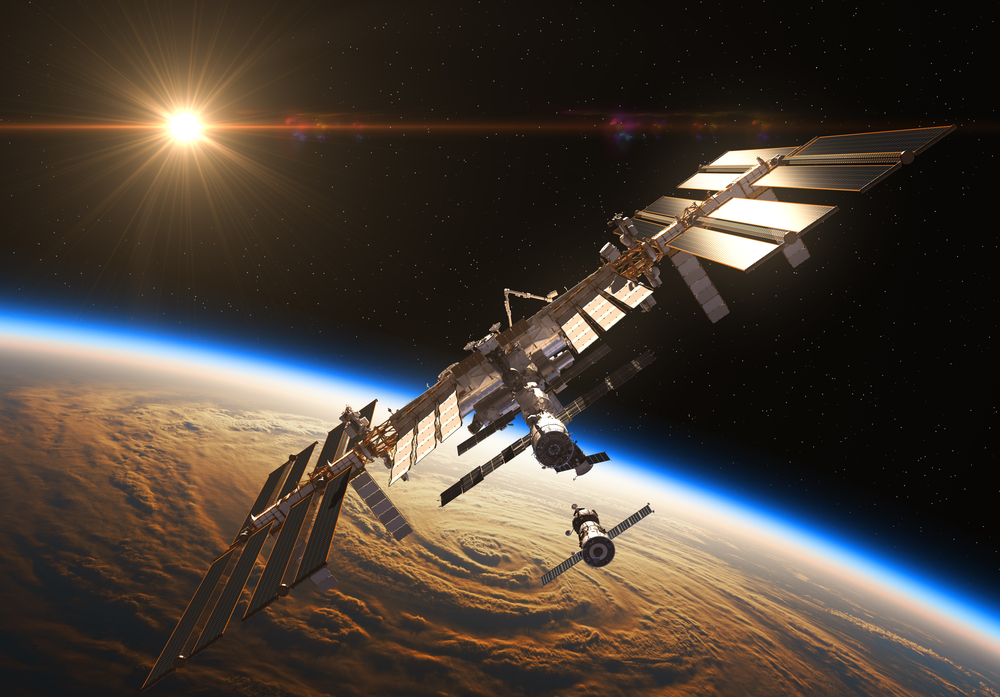

The International Space Station (ISS) represents a monumental international collaboration, providing a unique laboratory for scientific research in microgravity. Orbiting Earth, the ISS has hosted astronauts from around the world, conducting experiments in biology, physics, astronomy, and other fields. It has also served as a platform for testing technologies for future space exploration, including missions to Mars.
Cassini-Huygens Mission (1997)
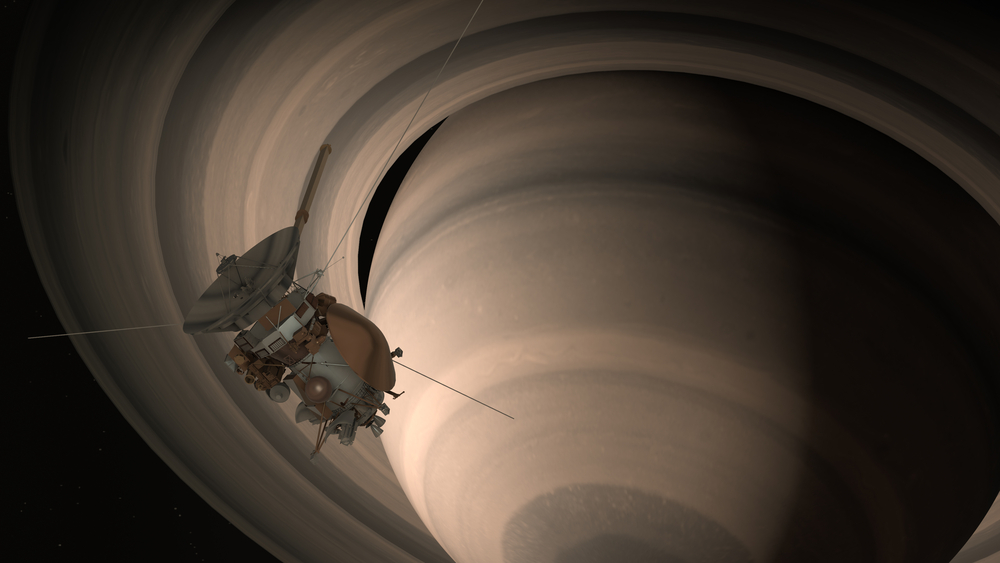

The Cassini-Huygens mission, a collaboration between NASA, ESA, and ASI, explored Saturn and its moons, delivering groundbreaking discoveries. Cassini orbited Saturn for over 13 years, capturing detailed images and data of the planet’s rings, atmosphere, and magnetic field. The Huygens probe landed on Titan, Saturn’s largest moon, revealing its surface and providing insights into its atmosphere.
New Horizons (2006)
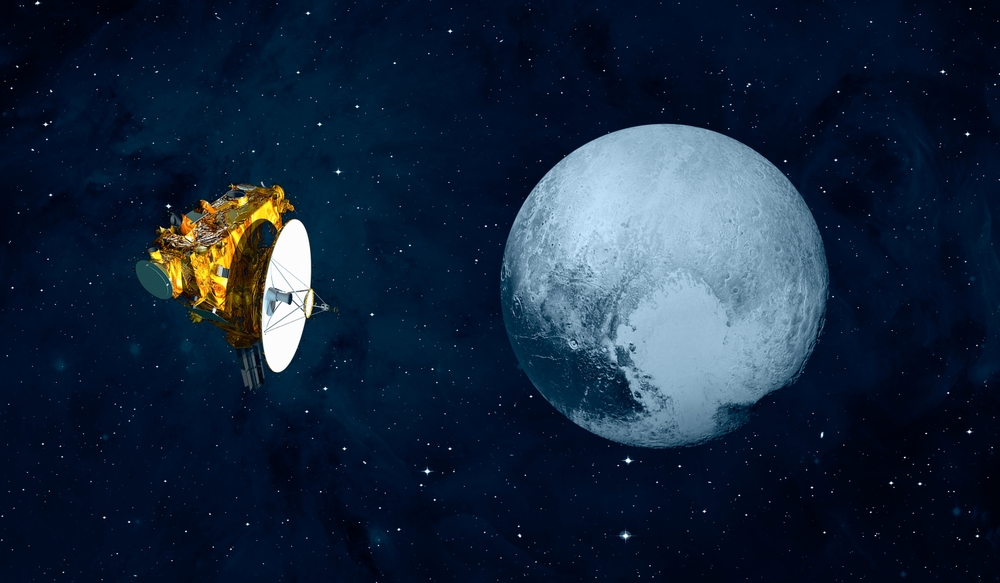

NASA’s New Horizons mission provided the first close-up images and data of Pluto and its moons, revolutionizing our understanding of this distant world. The spacecraft’s flyby revealed a complex and geologically active surface, with features such as mountains, plains, and potential ice volcanoes. New Horizons also explored the Kuiper Belt, offering insights into the early solar system.
Vostok 1 (1961)
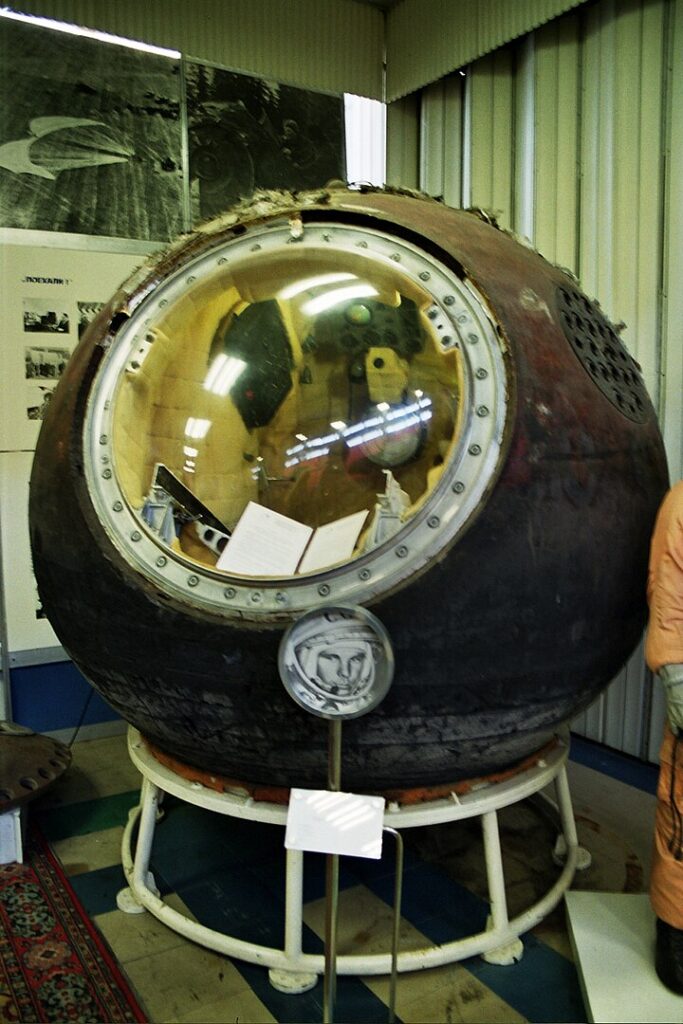

Vostok 1, launched by the Soviet Union, was the first human spaceflight, with Yuri Gagarin becoming the first person to orbit Earth. Gagarin’s 108-minute flight demonstrated the feasibility of human space travel and marked a significant achievement in the Space Race. The mission’s success showcased the Soviet Union’s technological prowess and inspired future manned space missions.
Mars Pathfinder (1996)
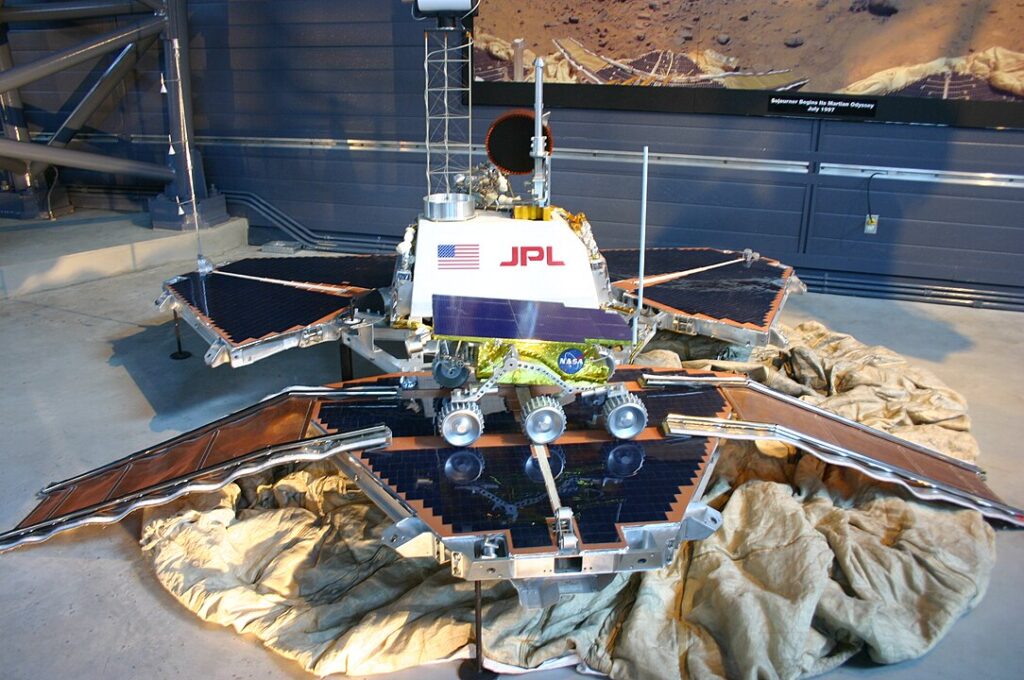

Mars Pathfinder, a NASA mission, successfully delivered the Sojourner rover to the Martian surface, demonstrating the viability of low-cost exploration. The mission provided detailed images and data of the Martian terrain and atmosphere, helping to shape future Mars exploration strategies. Sojourner’s mobility allowed it to analyze various rocks and soil, contributing to our understanding of Mars’ geology.
Galileo (1989)
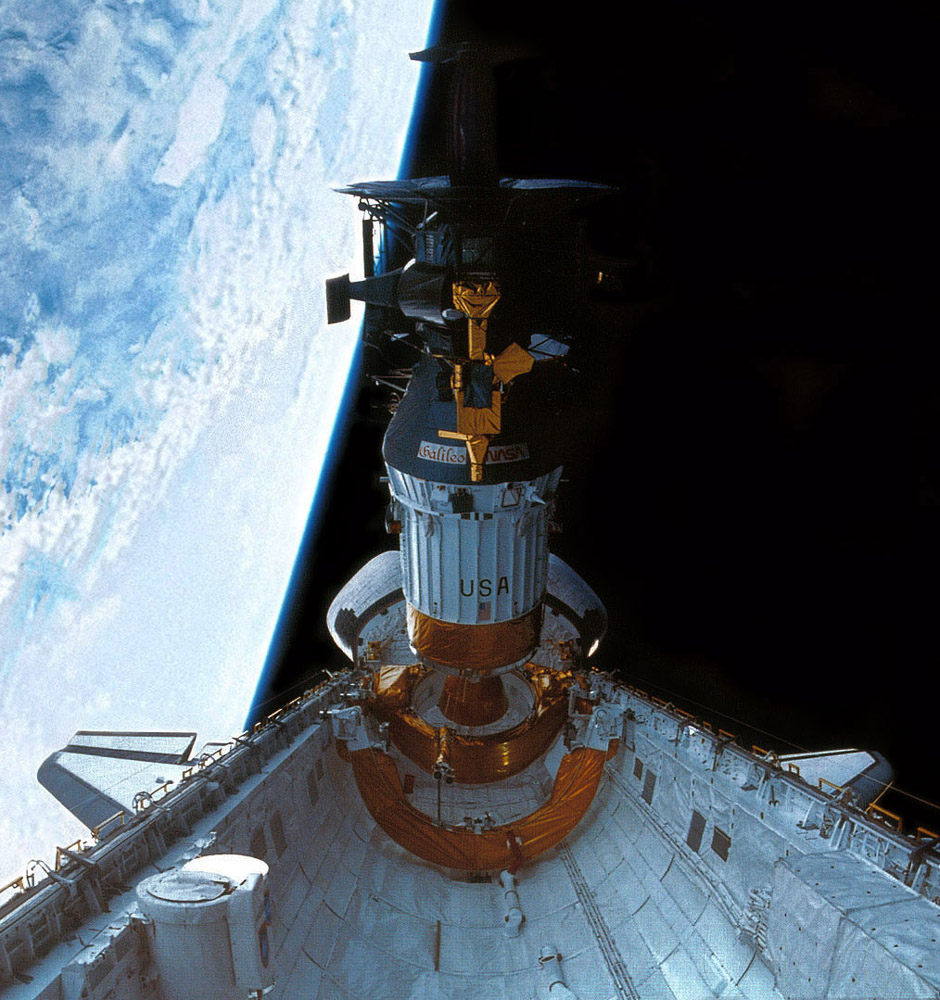

NASA’s Galileo mission provided unprecedented insights into Jupiter and its moons, revealing the complexities of the Jovian system. The spacecraft conducted detailed observations of Jupiter’s atmosphere, magnetic field, and rings, as well as close flybys of its major moons, including Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. Galileo’s discoveries, such as evidence of subsurface oceans on Europa, have profound implications for the potential for life beyond Earth.
Pioneer 10 (1972)
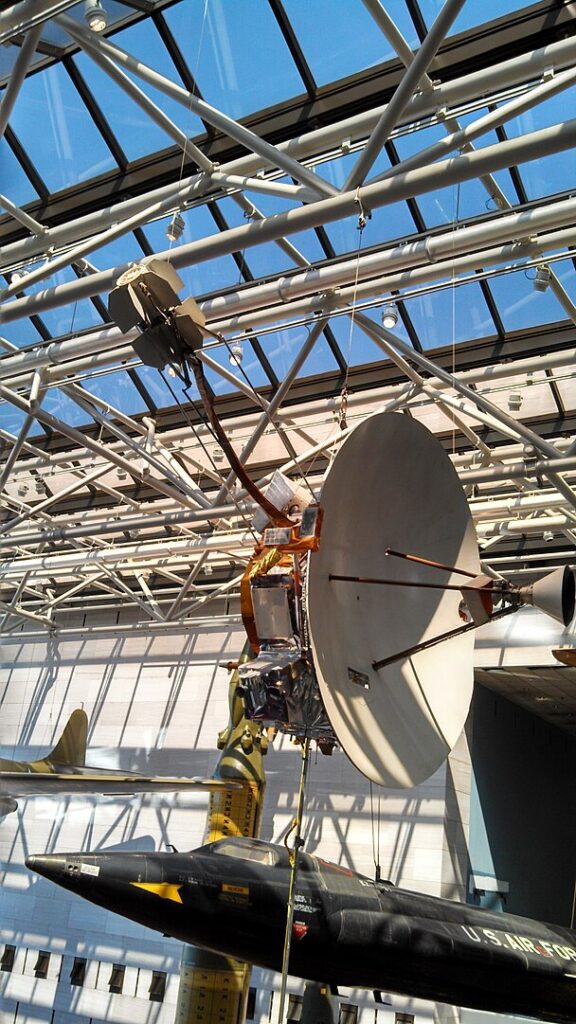

Pioneer 10 was the first spacecraft to travel through the asteroid belt and make a close approach to Jupiter, sending back the first detailed images of the gas giant. The mission provided valuable data on Jupiter’s atmosphere, magnetic field, and moons, laying the groundwork for future missions to the outer planets. Pioneer 10’s success demonstrated the feasibility of long-distance space travel and interplanetary exploration.
This article originally appeared on MyCarMakesNoise.
More from MyCarMakesNoise
Top 15 Motorcycles with Exceptional Fuel Efficiency for Long Rides

Embarking on long motorcycle journeys requires a bike that combines robust performance with excellent fuel efficiency. This selection of touring motorcycles is known for their ability to cover vast distances with fewer fuel stops. Read More.
Top 20 Must-Have Accessories for Long-Distance Motorcycle Riding

Embarking on a long-distance motorcycle journey requires more than just a spirit of adventure. Being well-equipped is essential for ensuring safety, comfort, and convenience on the open road. Read More.
10 Iconic Race Cars That Defined Motorsport History

In the world of motorsport, certain race cars stand out for their groundbreaking design, technological innovations, and dominant performances. These machines transcended their eras, revolutionizing racing and capturing the imaginations of fans worldwide. Read More.














