Tanks have played a crucial role in shaping modern warfare, evolving significantly since their introduction in World War I. From the early designs that changed battlefield strategies to the advanced technology of today, each milestone marks a step forward in combat effectiveness and innovation. Here are 16 key milestones that highlight the remarkable evolution of tanks over the past century.
Contents
Development of the Mark I (1916)
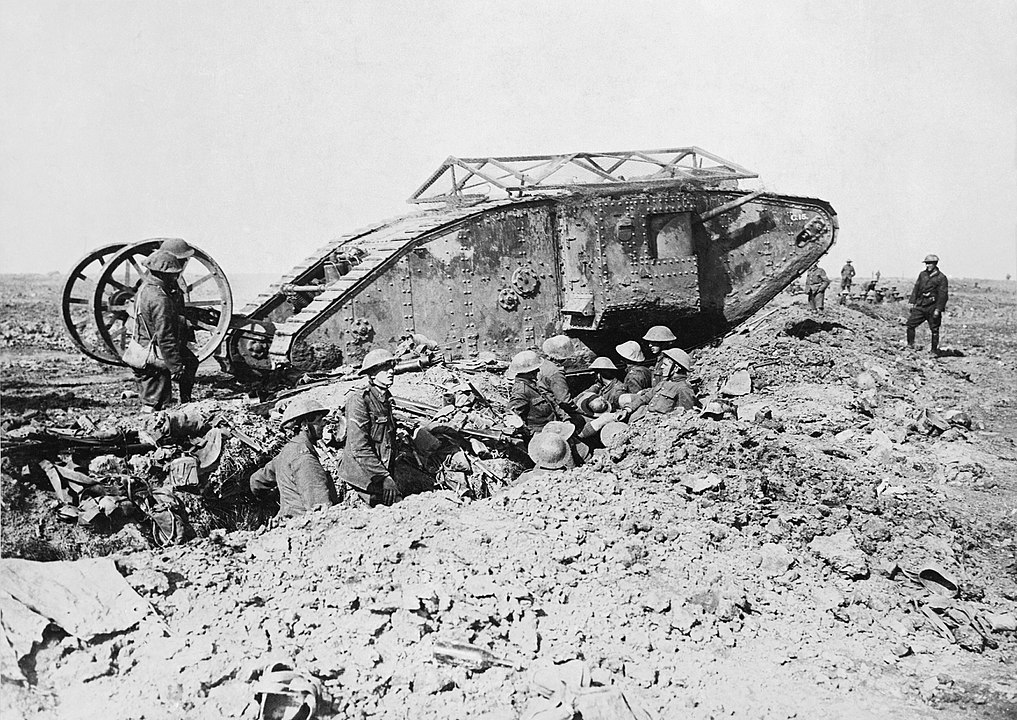

The Mark I tank, introduced by the British during World War I, was the world’s first tank. Designed to navigate the rough terrain of the Western Front, it aimed to break through enemy lines. Its distinctive rhomboid shape and track system allowed it to cross trenches and barbed wire, revolutionizing battlefield tactics. Despite its slow speed and mechanical issues, the Mark I demonstrated the potential of armored warfare.
Introduction of the French Renault FT (1917)
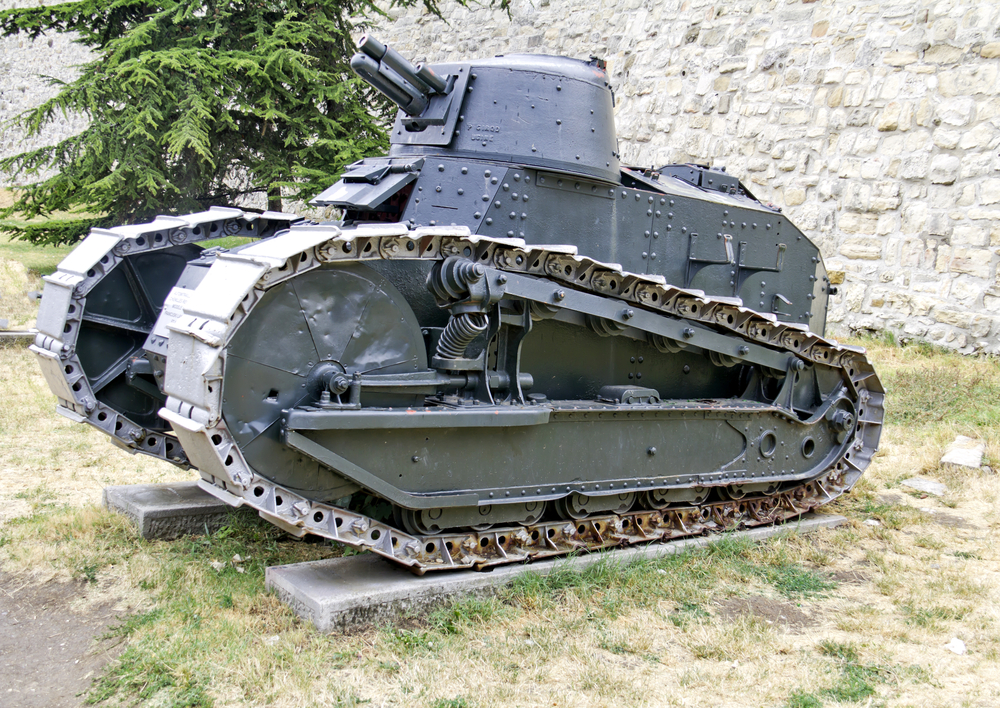

The Renault FT was a groundbreaking French tank that set the standard for future designs. Unlike its predecessors, the FT featured a fully rotating turret, which allowed for greater flexibility in combat. Lightweight and highly maneuverable, it was effective in various roles. The FT’s design influenced nearly all subsequent tanks, marking a significant milestone.
German Blitzkrieg Tactics (1939-1941)
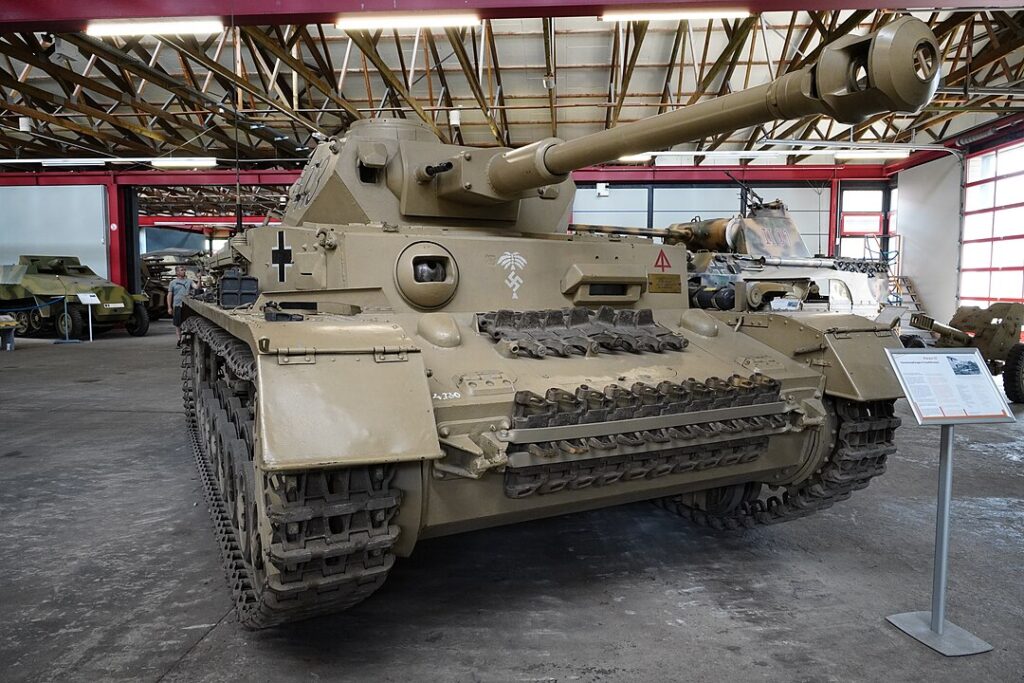

German Blitzkrieg tactics at the start of World War II showcased the effectiveness of coordinated tank assaults. Tanks such as the Panzer III and IV spearheaded rapid, deep strikes into enemy territory, supported by aircraft and mechanized infantry. This strategy allowed Germany to achieve quick victories in Poland, France, and the early stages of the Soviet invasion.
Introduction of the T-34 (1940)
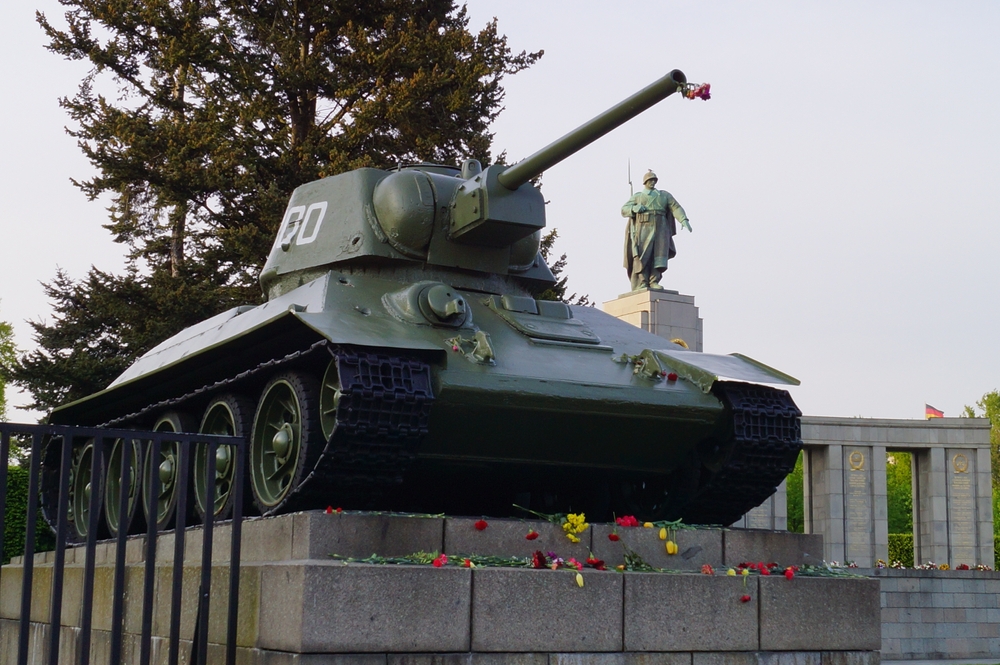

The Soviet T-34 tank, introduced in 1940, was a game-changer in armored warfare. Combining firepower, armor, and mobility, it was one of the most effective tanks of World War II. The T-34’s sloped armor increased its survivability, while its powerful 76mm gun could take on most German tanks. Mass production and widespread use of the T-34 played a crucial role in the Soviet Union’s victory over Nazi Germany.
Development of the M4 Sherman (1942)
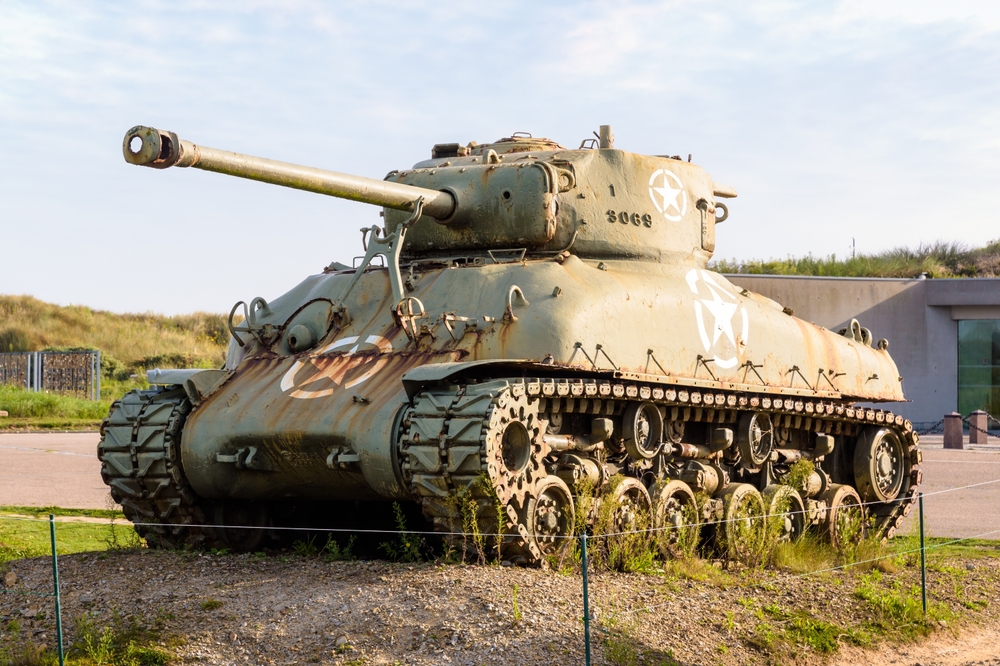

The American M4 Sherman tank became the workhorse of Allied armored forces during World War II. Designed for mass production, reliability, and ease of maintenance, it was crucial in various battles. Although not the most heavily armed or armored, the Sherman’s versatility and numbers allowed it to dominate the battlefield. Supported by Allied air superiority, it helped secure victory in Europe and the Pacific.
Introduction of the Panther Tank (1943)
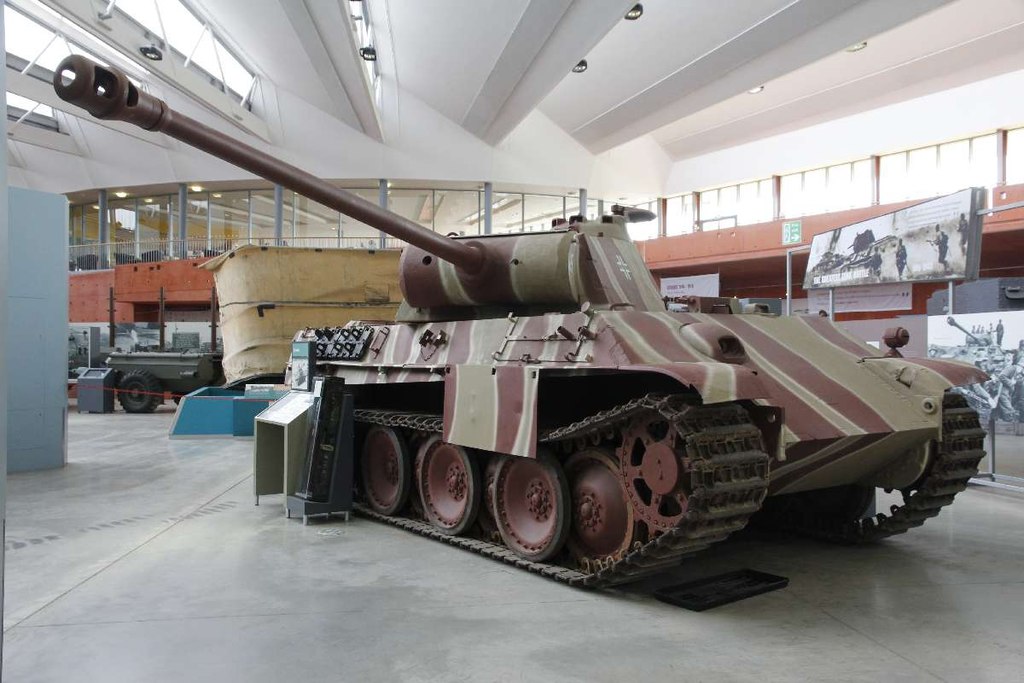

The German Panther tank, introduced in 1943, combined firepower, armor, and mobility in a balanced design. Its 75mm high-velocity gun was capable of penetrating most Allied tanks, and its sloped armor provided excellent protection. The Panther’s performance in battles like Kursk showcased its capabilities. However, production and reliability issues limited its impact.
Development of the Tiger I (1942)
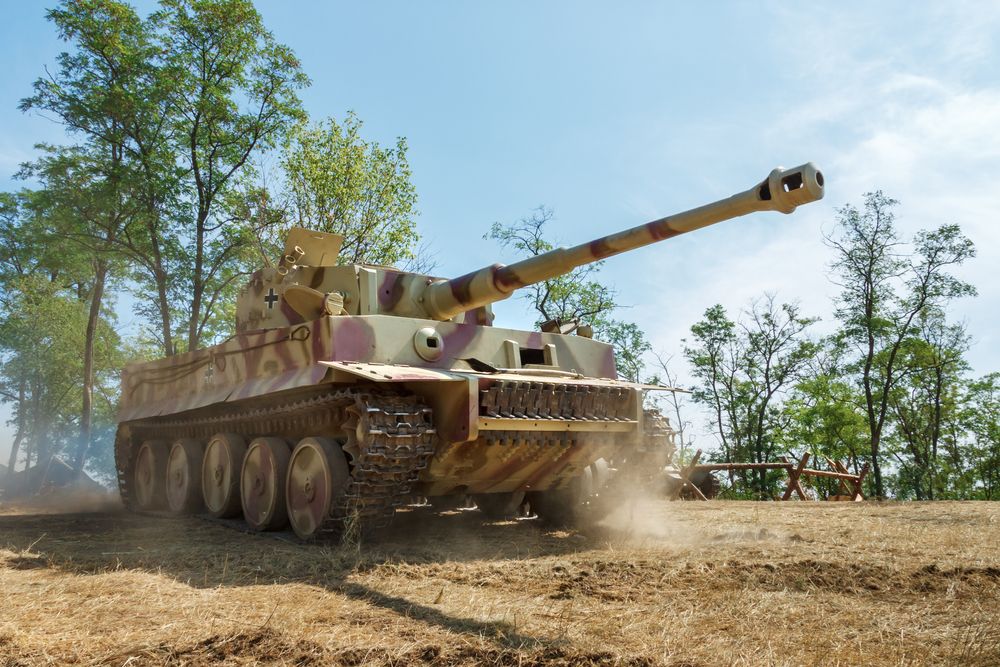

The German Tiger I tank, introduced in 1942, was renowned for its heavy armor and powerful 88mm gun. It could engage enemy tanks at long distances and withstand significant damage. Despite its mechanical complexity and production cost, the Tiger I’s psychological impact on Allied forces was substantial. It set a new standard for heavy tanks.
Advances in Tank Destroyers (1940s)
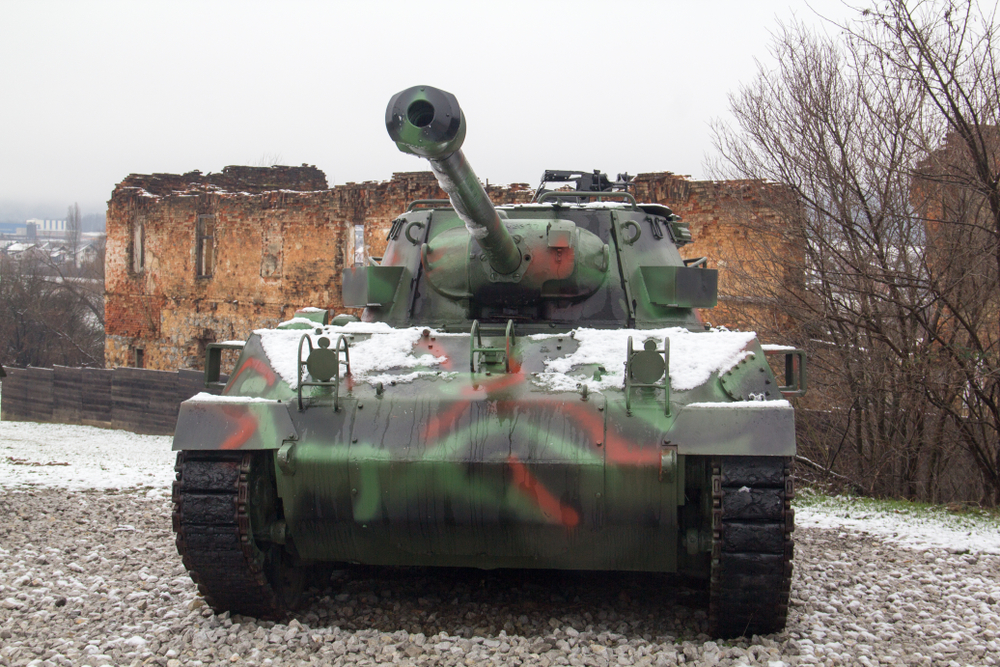

The development of tank destroyers during World War II addressed the need for specialized anti-tank capabilities. Vehicles like the German Jagdpanther and American M18 Hellcat were designed to counter enemy armor with powerful guns and mobility. These tank destroyers played crucial roles in both offensive and defensive operations. Their development highlighted the evolving nature of armored combat.
Post-War Developments and the Cold War (1945-1991)
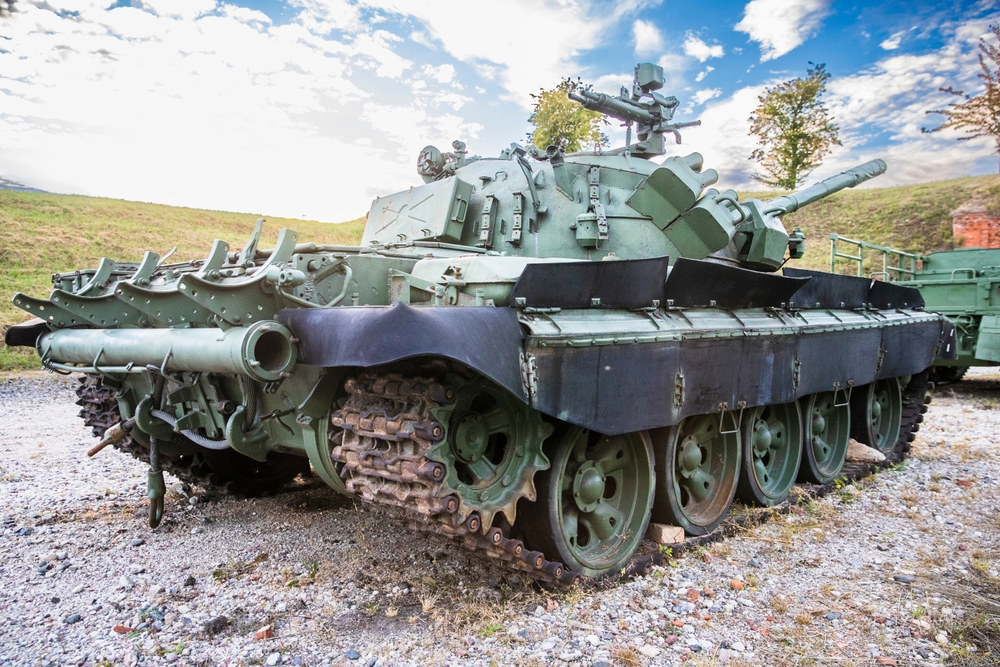

The Cold War era saw significant advancements in tank technology, driven by the arms race between NATO and Warsaw Pact countries. Innovations included improved armor, such as composite and reactive armor, and more powerful, accurate guns. Tanks like the American M60 and Soviet T-55 became iconic symbols of this period. The Cold War spurred continuous improvements in tank design.
Introduction of the Main Battle Tank (1950s)
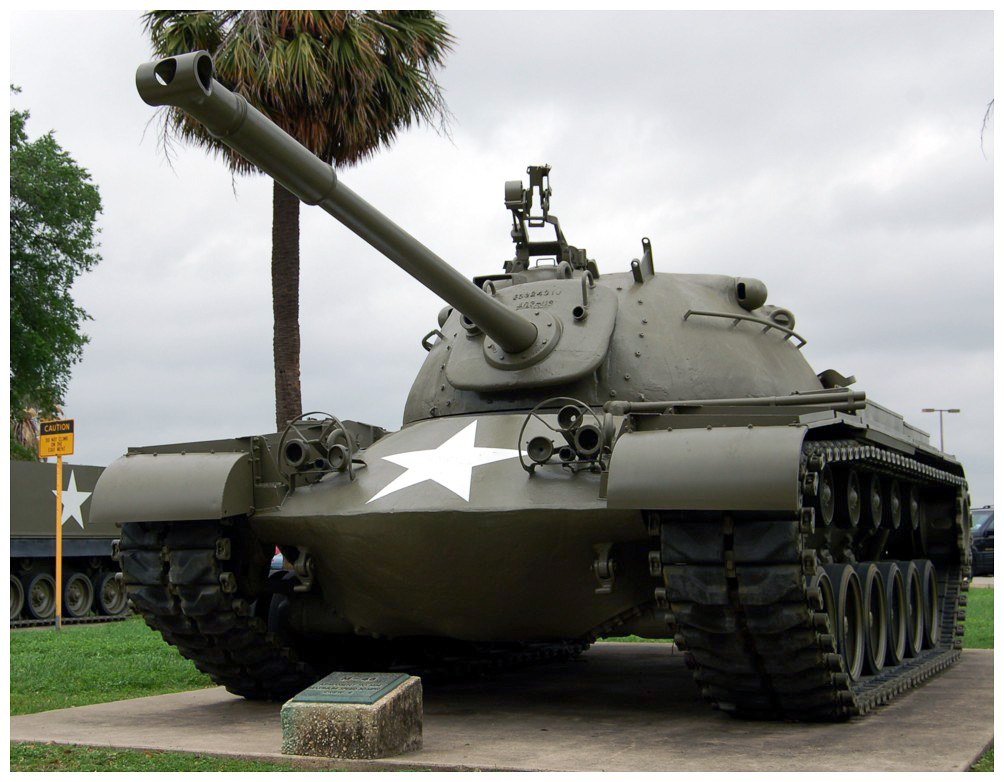

The concept of the main battle tank (MBT) emerged in the 1950s, combining the roles of light, medium, and heavy tanks into a single platform. MBTs like the American M48 Patton and Soviet T-62 featured powerful guns, thick armor, and high mobility. This shift streamlined tank forces and enhanced their versatility on the battlefield. The MBT concept remains the cornerstone of modern armored forces.
Development of Composite Armor (1960s)
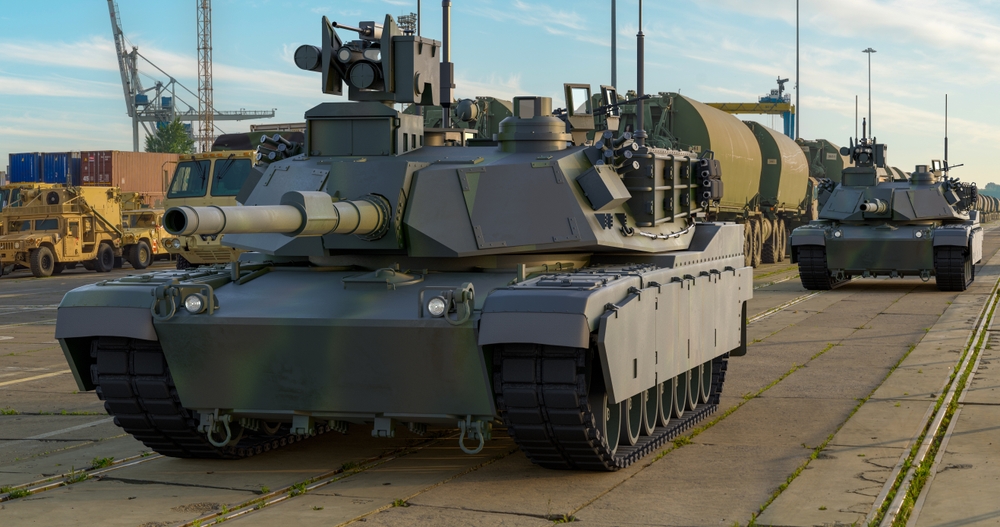

Composite armor, developed in the 1960s, significantly enhanced tank survivability. Unlike traditional steel armor, composite materials offer better protection against both kinetic and shaped charge threats. The British Chieftain and American M1 Abrams were among the first tanks to incorporate this technology. Composite armor’s effectiveness in combat demonstrated the importance of continuous innovation.
Introduction of the T-72 (1973)
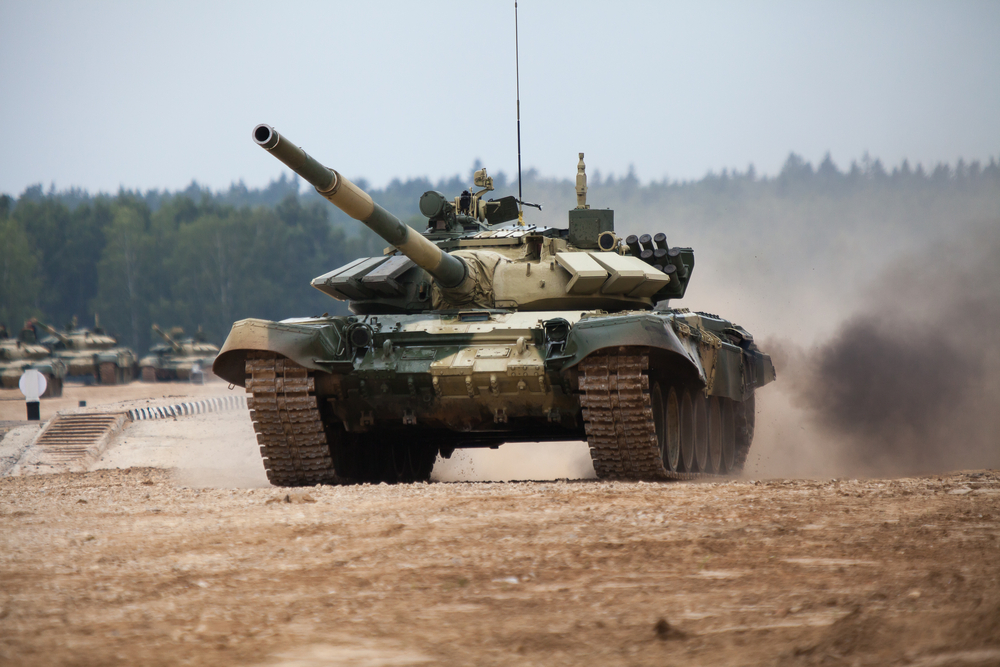

The Soviet T-72 tank, introduced in 1973, became one of the most widely produced and exported tanks in history. Its combination of firepower, protection, and affordability made it popular among the Warsaw Pact and other allied nations. The T-72’s advanced autoloader system and powerful 125mm gun made it a formidable opponent. Its widespread use in conflicts worldwide showcased its effectiveness.
Development of the M1 Abrams (1980)
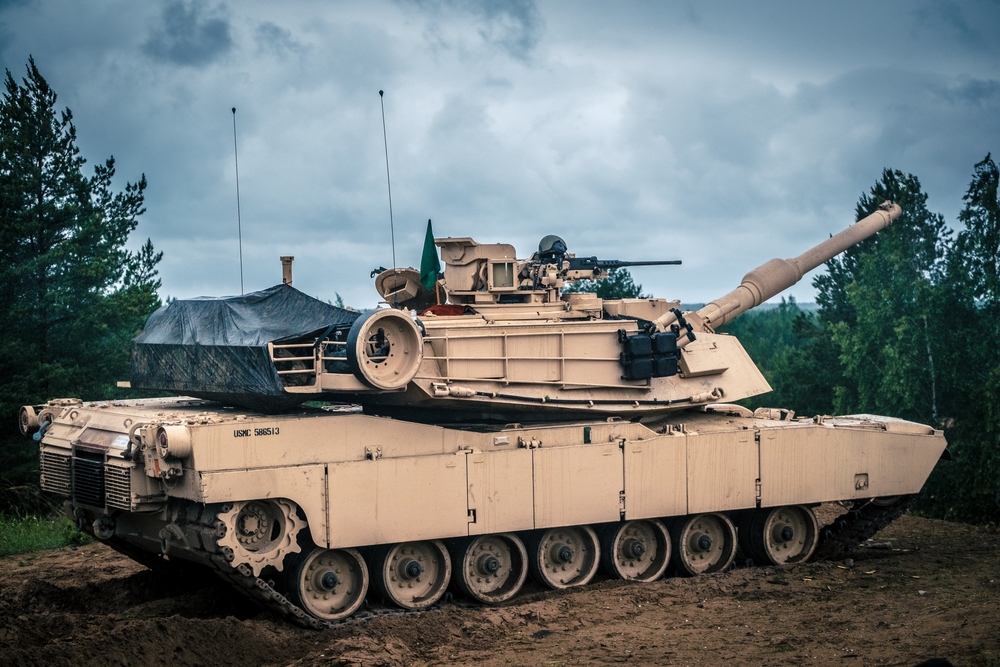

The American M1 Abrams, introduced in 1980, set new standards for tank design with its advanced armor and powerful 120mm smoothbore gun. The use of a gas turbine engine provided exceptional speed and mobility. The Abrams’ performance in conflicts like the Gulf War demonstrated its superiority in modern armored warfare. Continuous upgrades have kept it at the forefront of tank technology.
Development of the Leopard 2 (1979)
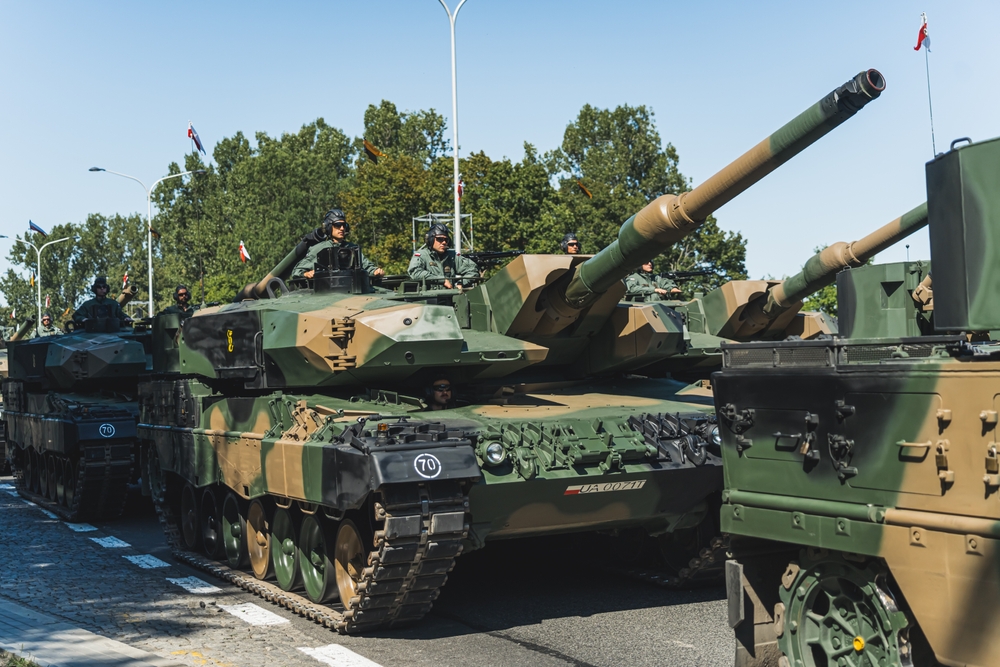

The German Leopard 2, introduced in 1979, is renowned for its balance of firepower, protection, and mobility. Its 120mm smoothbore gun and advanced targeting systems provide exceptional accuracy and lethality. The Leopard 2’s modular armor design allows for easy upgrades, ensuring its relevance in modern combat. Its widespread adoption by NATO countries underscores its effectiveness and reliability.
Introduction of Urban Warfare Modifications (2000s)

The challenges of urban warfare led to specialized modifications for tanks, enhancing their effectiveness in close-quarter combat. Additions like slat armor, remote weapon stations, and improved situational awareness systems became standard. These modifications improved tank survivability and lethality in complex urban environments. The adaptation to urban combat scenarios underscores the versatility and evolving role of tanks.
Introduction of the Armata T-14 (2015)
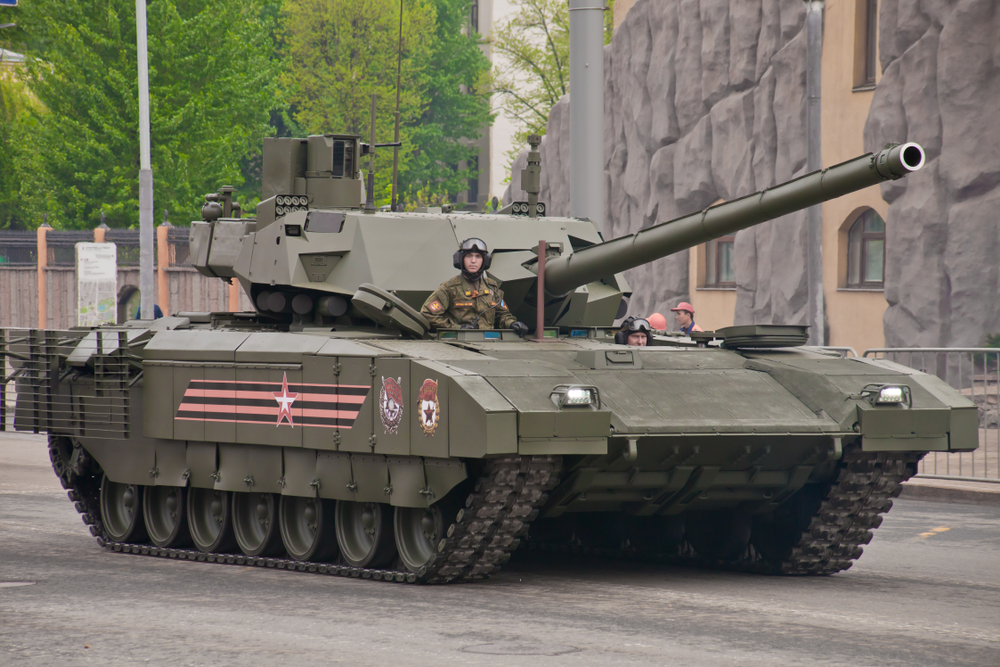

The Russian Armata T-14, unveiled in 2015, features cutting-edge technology and a fully automated turret. Its advanced armor, active protection systems, and powerful 125mm smoothbore gun make it one of the most advanced tanks in the world. The T-14’s modular design allows for future upgrades and adaptations. Its introduction highlights ongoing advancements in tank technology.
This article originally appeared on MyCarMakesNoise.
More from MyCarMakesNoise
20 Must-See Roadside Attractions for Your Next Adventure

Planning your next road trip? Don’t just focus on the destination—there’s a world of wonder waiting for you along the way. Read More.
Top 20 Lamborghini Supercars Dominating the Super Trofeo
When it comes to speed, power, and prestige, Lamborghini has consistently set the bar high in the world of motorsports. The Super Trofeo series is where these raging bulls truly shine, showcasing the brand’s most thrilling supercars in intense competition. Read More.
15 Common Misconceptions About Electric Car Efficiency

Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming increasingly popular as people look for more sustainable transportation options. However, there are still many misconceptions about their efficiency that can create confusion. Read More.














