Military vehicles once vital on the battlefield have now become obsolete due to advancements in technology and changing warfare needs. These vehicles, though once indispensable, are no longer in demand. Here are some military vehicles that have fallen out of favor.
Contents
M60 Patton Tank
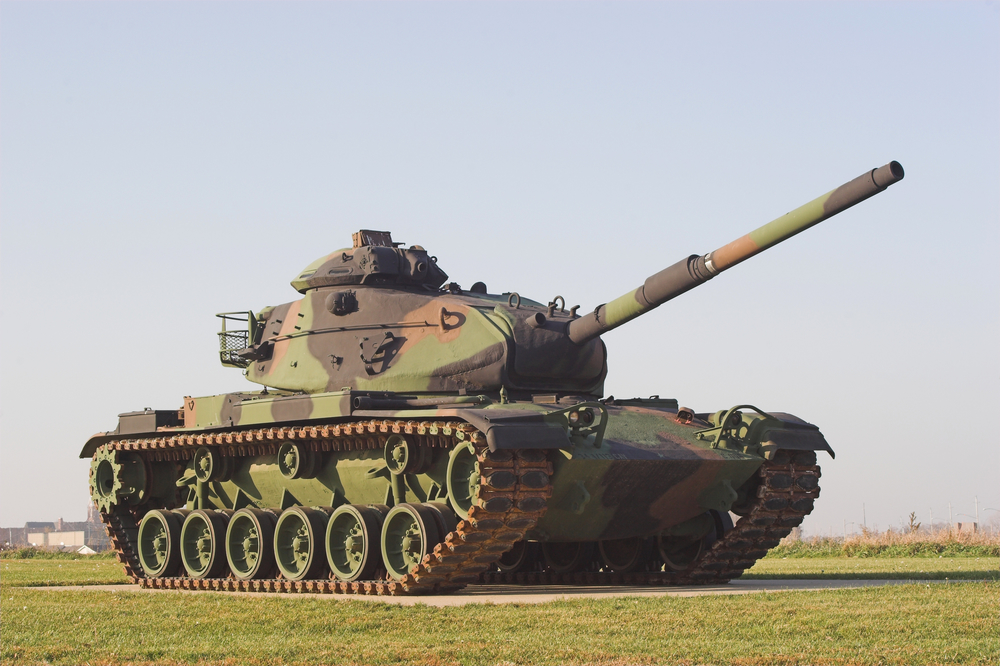

The M60 Patton tank, produced from 1960 to 1987, was a main battle tank used extensively by the U.S. and its allies during the Cold War. It featured a 105mm M68 gun, a Continental AVDS-1790-2 V12 diesel engine, and advanced fire control systems for its time. Despite its reliability and effectiveness, the M60 has been replaced by more modern tanks like the M1 Abrams. Its older design, lack of advanced armor, and outdated technology have made it obsolete in modern military operations.
F-4 Phantom II
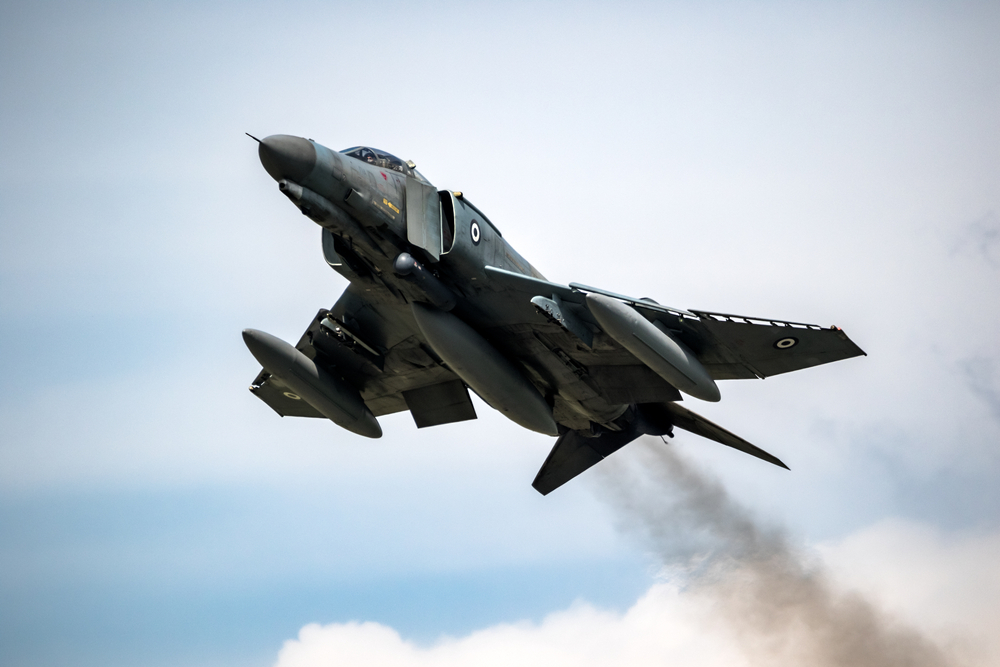

The McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II, produced from 1958 to 1981, was a versatile fighter-bomber used by the U.S. Air Force, Navy, and Marine Corps. It was equipped with twin J79-GE-17 engines and capable of carrying a wide range of armaments. The F-4 was highly effective during the Vietnam War but has since been phased out due to advancements in aviation technology. Modern fighter jets like the F-22 Raptor and F-35 Lightning II offer superior stealth, avionics, and multi-role capabilities, rendering the F-4 obsolete.
M113 Armored Personnel Carrier
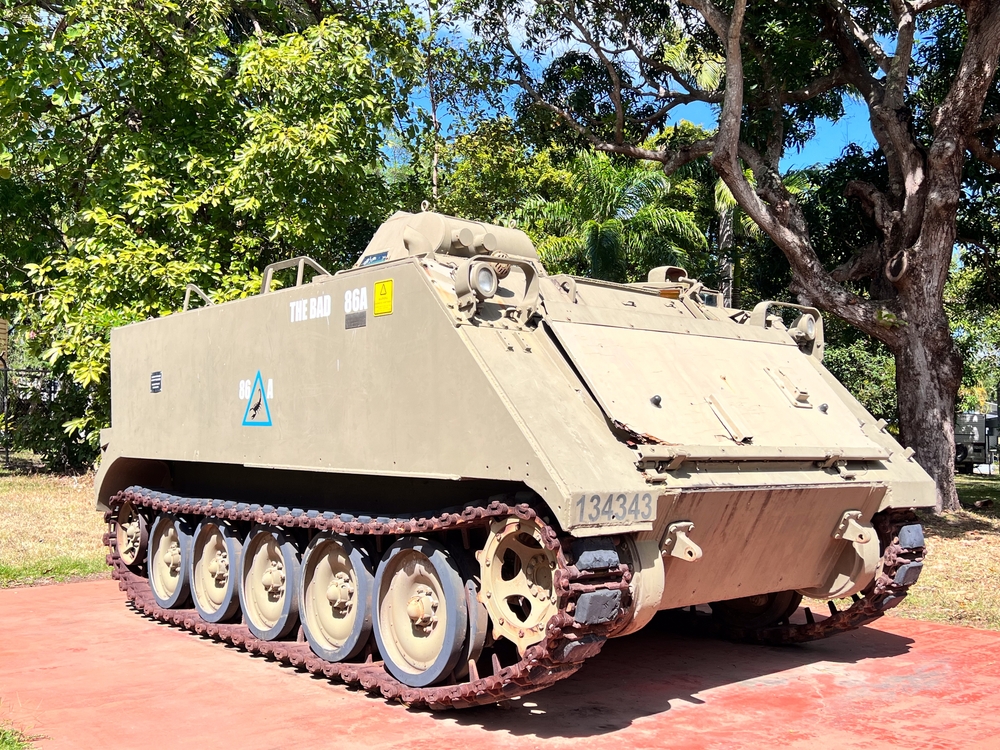

The M113, produced from 1960 onwards, is a tracked armored personnel carrier used by many countries worldwide. It features an aluminum hull, a 6V53 Detroit Diesel engine, and a .50 caliber M2 machine gun. Although it was versatile and widely used, the M113 lacks the protection, mobility, and firepower of modern armored vehicles. Newer APCs and IFVs like the Stryker and Bradley have replaced the M113 in frontline roles, making it less relevant in contemporary military operations.
A-10 Thunderbolt II
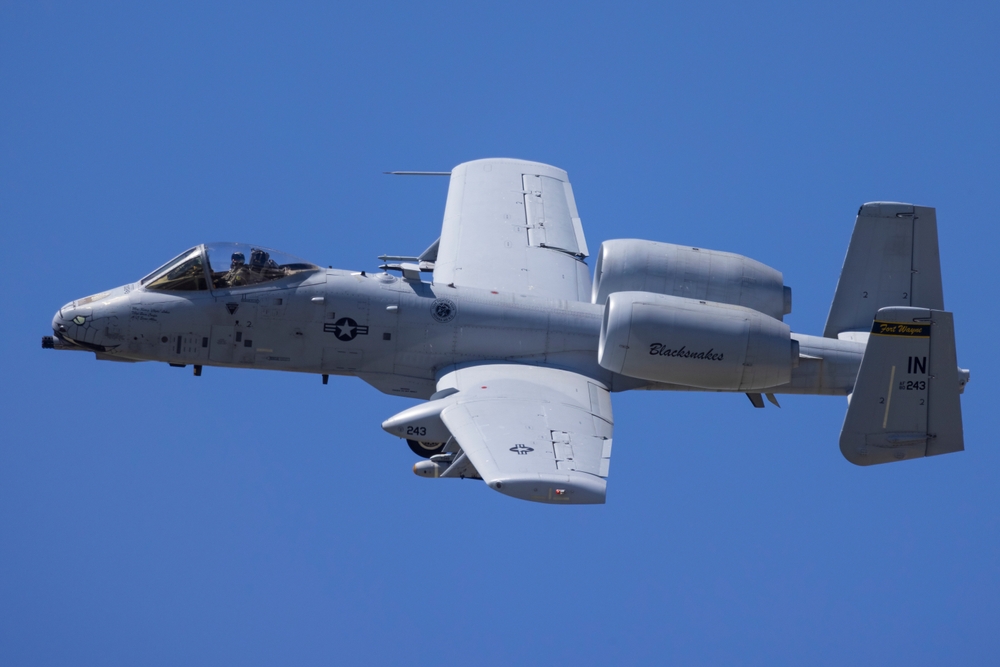

The Fairchild Republic A-10 Thunderbolt II, known as the “Warthog,” was introduced in 1977 and designed for close air support with its GAU-8 Avenger 30mm cannon and rugged design. Despite its effectiveness in anti-armor roles, the A-10 has faced retirement due to budget constraints and the shift towards multi-role aircraft like the F-35. Advances in precision-guided munitions and drone technology have also diminished the need for dedicated ground-attack aircraft.
M551 Sheridan
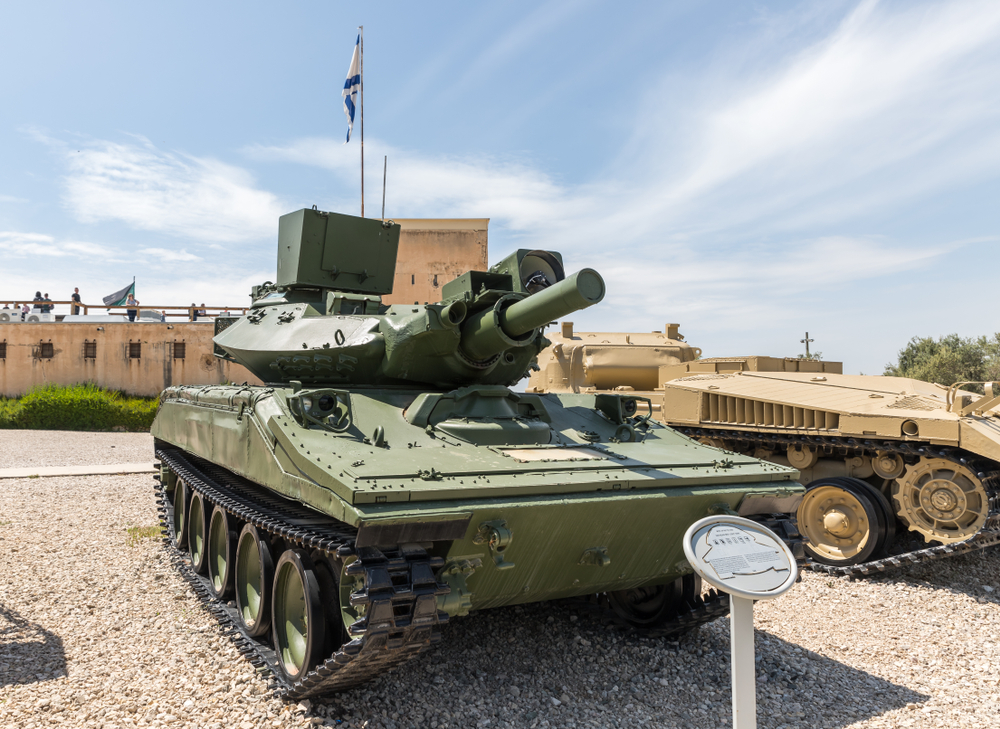

The M551 Sheridan, produced from 1967 to 1970, was a light airborne reconnaissance vehicle and tank equipped with a 152mm gun/launcher capable of firing anti-tank missiles. Its lightweight aluminum armor and powerful armament made it suitable for airborne and amphibious operations. However, its complex maintenance requirements, limited protection, and mechanical issues led to its retirement. The M1 Abrams and other more reliable armored vehicles have taken over its roles.
UH-1 Huey
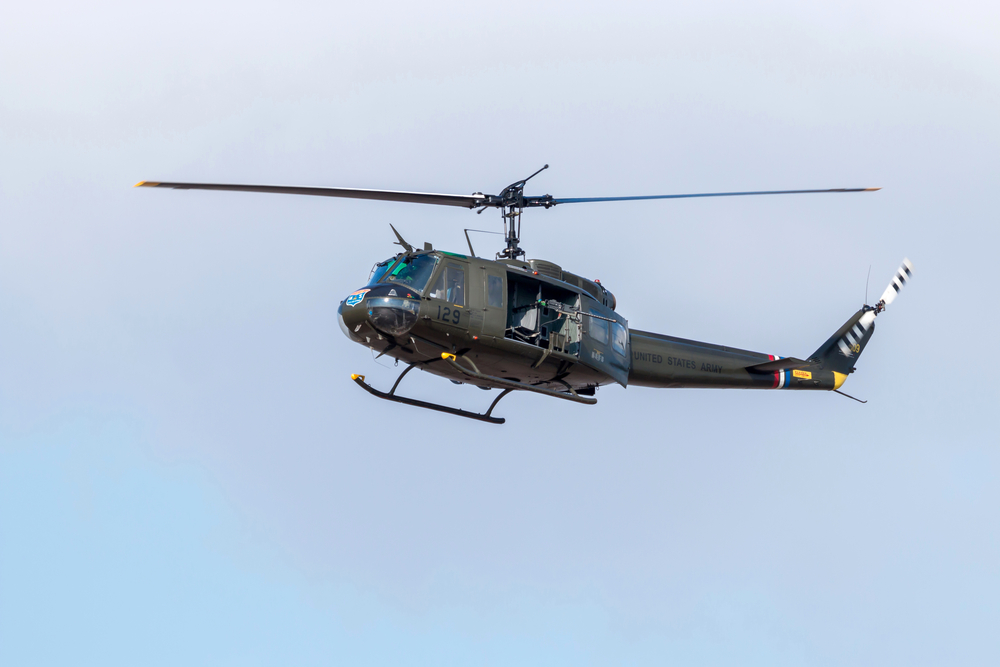

The Bell UH-1 Iroquois, commonly known as the “Huey,” was a utility helicopter introduced in the 1950s. It played a significant role in the Vietnam War, featuring a Lycoming T53-L-13 engine and capable of various missions from troop transport to medevac. Advances in helicopter technology have led to its replacement by more capable aircraft like the UH-60 Black Hawk. The Huey’s slower speed, lower payload capacity, and older avionics make it less suitable for modern military needs.
F-14 Tomcat
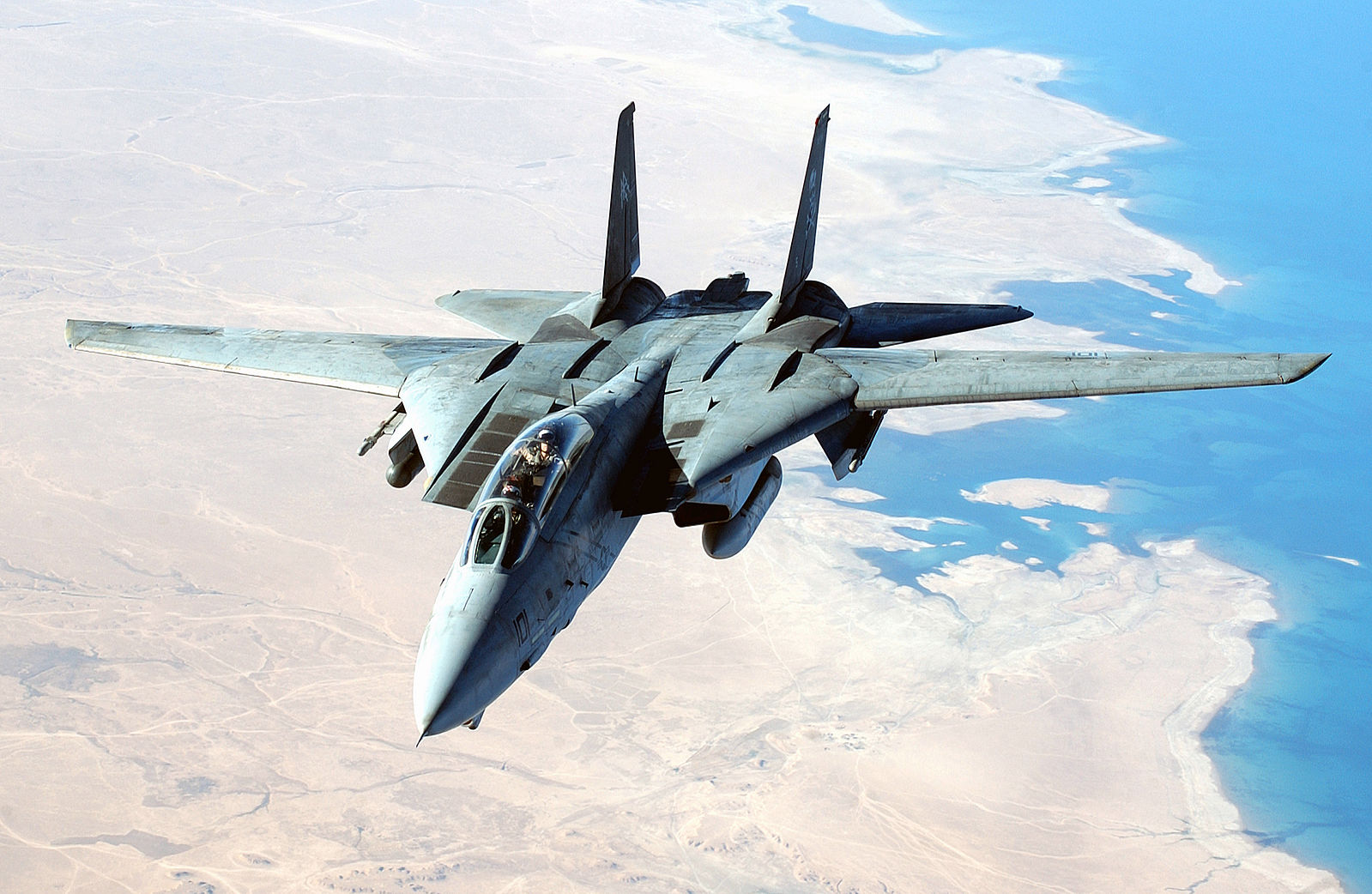

The Grumman F-14 Tomcat, introduced in 1974, was a carrier-based supersonic fighter aircraft equipped with twin Pratt & Whitney TF30 engines and the advanced AN/AWG-9 radar. It gained fame for its variable-sweep wings and air superiority capabilities. Despite its impressive performance, the F-14 was retired in 2006 due to high maintenance costs and the availability of more modern fighters like the F/A-18E/F Super Hornet and F-35. Its complex maintenance requirements and aging technology rendered it less practical for contemporary naval operations.
M47 Patton Tank
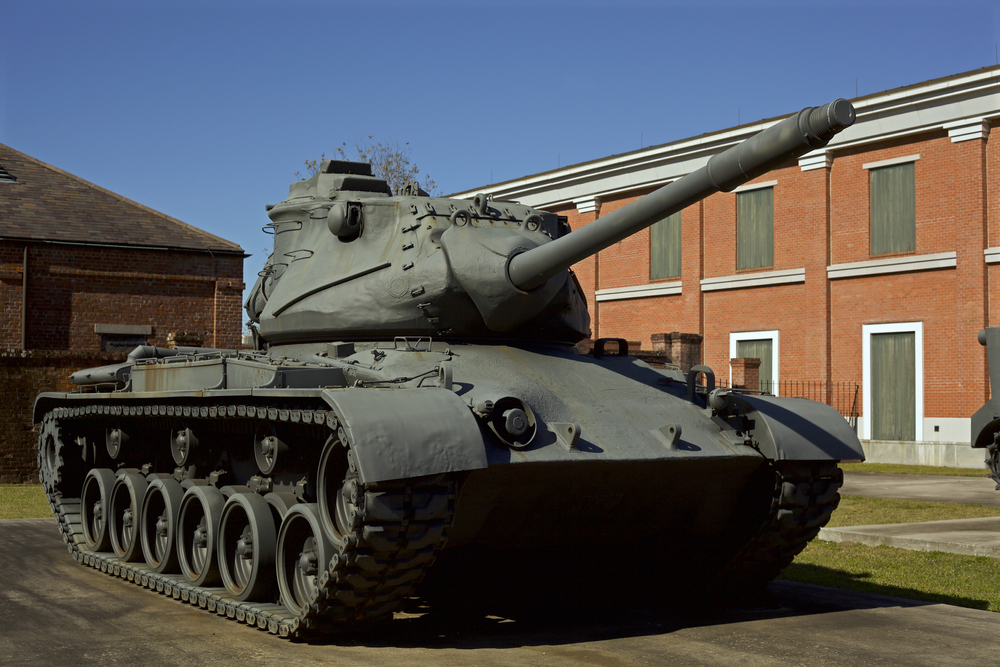

The M47 Patton, produced from 1951 to 1953, was an interim main battle tank during the early Cold War period. It featured a 90mm gun, a Continental AV-1790-5B engine, and an improved fire control system. Despite its improvements over earlier tanks, the M47 quickly became outdated with the introduction of the M48 Patton and later the M60 Patton. Its limited armor and firepower compared to modern tanks led to its phased retirement from active service.
CH-46 Sea Knight
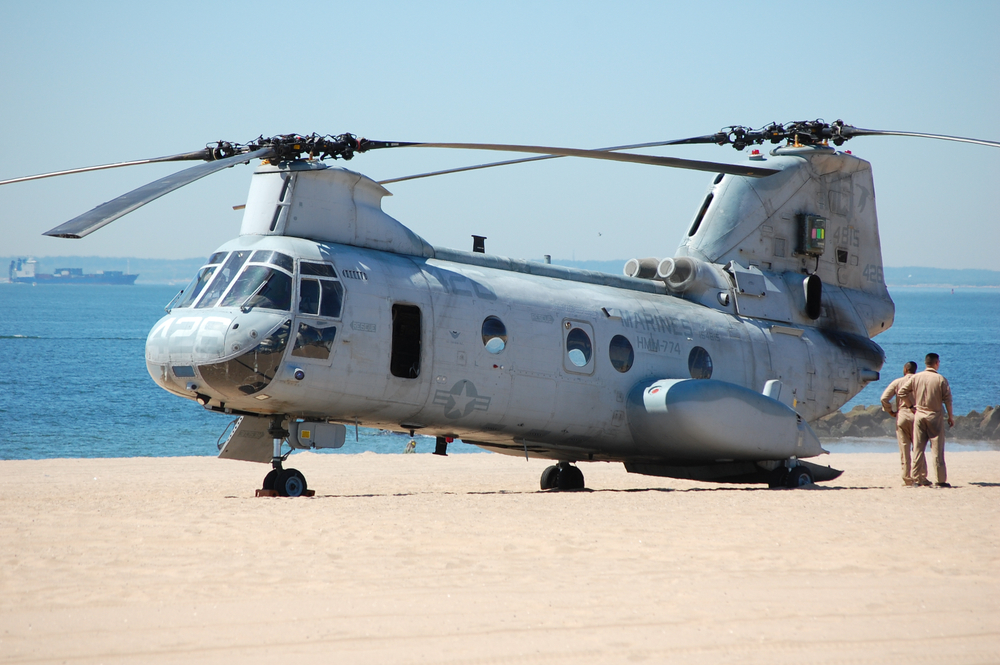

The Boeing Vertol CH-46 Sea Knight, introduced in 1964, was a medium-lift tandem-rotor transport helicopter used by the U.S. Marine Corps and Navy. Powered by twin T58-GE-16 engines, it was capable of carrying troops, cargo, and performing search and rescue missions. The CH-46 was replaced by the more advanced MV-22 Osprey, which offers greater speed, range, and versatility. The Sea Knight’s older design and maintenance challenges made it less viable for modern military operations.
M60A2 “Starship”
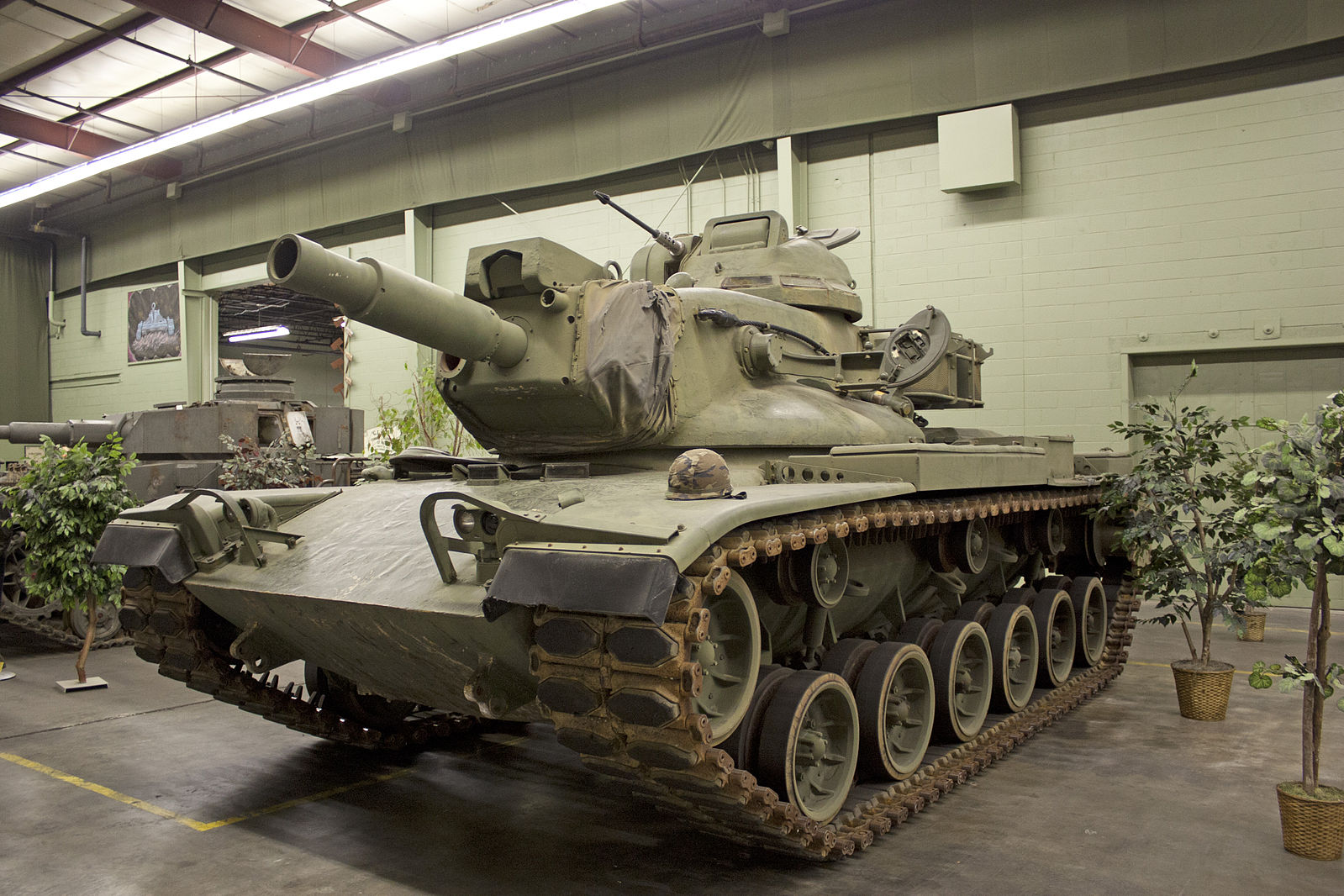

The M60A2 “Starship,” produced in the early 1970s, was an attempt to modernize the M60 Patton tank with a new turret and the 152mm M162 gun/launcher capable of firing Shillelagh missiles. Despite its advanced armament, the M60A2 faced numerous technical issues, including reliability problems with its missile system and complex maintenance requirements. The tank was phased out in favor of the more reliable M60A3 and later the M1 Abrams.
LAV-25
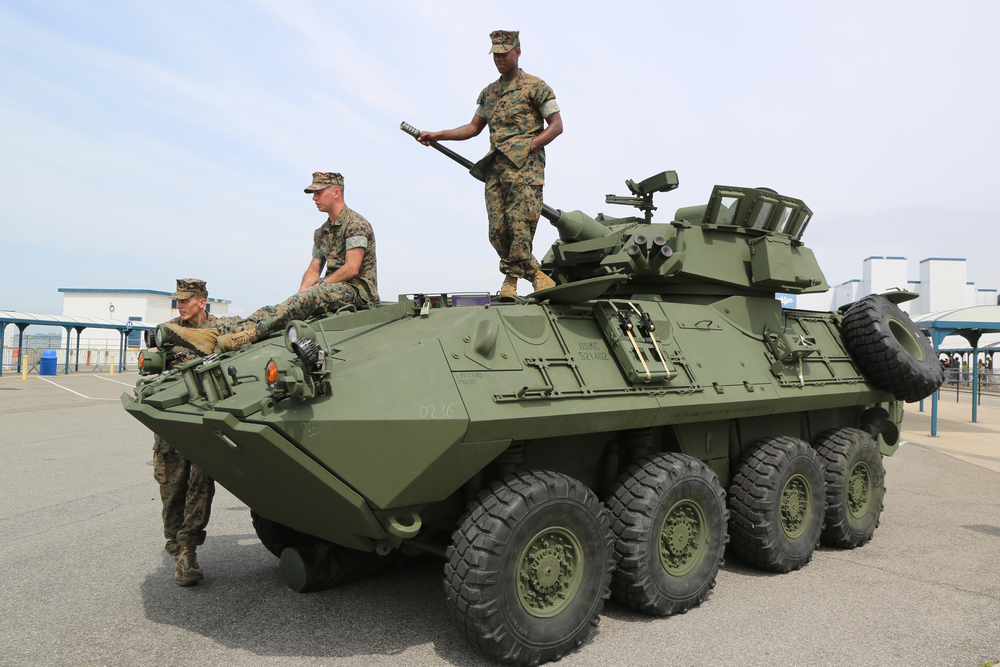

The Light Armored Vehicle (LAV-25), introduced in the 1980s, is a wheeled armored vehicle used by the U.S. Marine Corps. It features an M242 Bushmaster 25mm chain gun and a General Motors 6V53T diesel engine. While versatile and mobile, the LAV-25 has been gradually replaced by more advanced vehicles like the Amphibious Combat Vehicle (ACV) that offer better protection, firepower, and amphibious capabilities. The LAV-25’s lighter armor and aging design make it less suitable for modern combat scenarios.
M48 Patton Tank
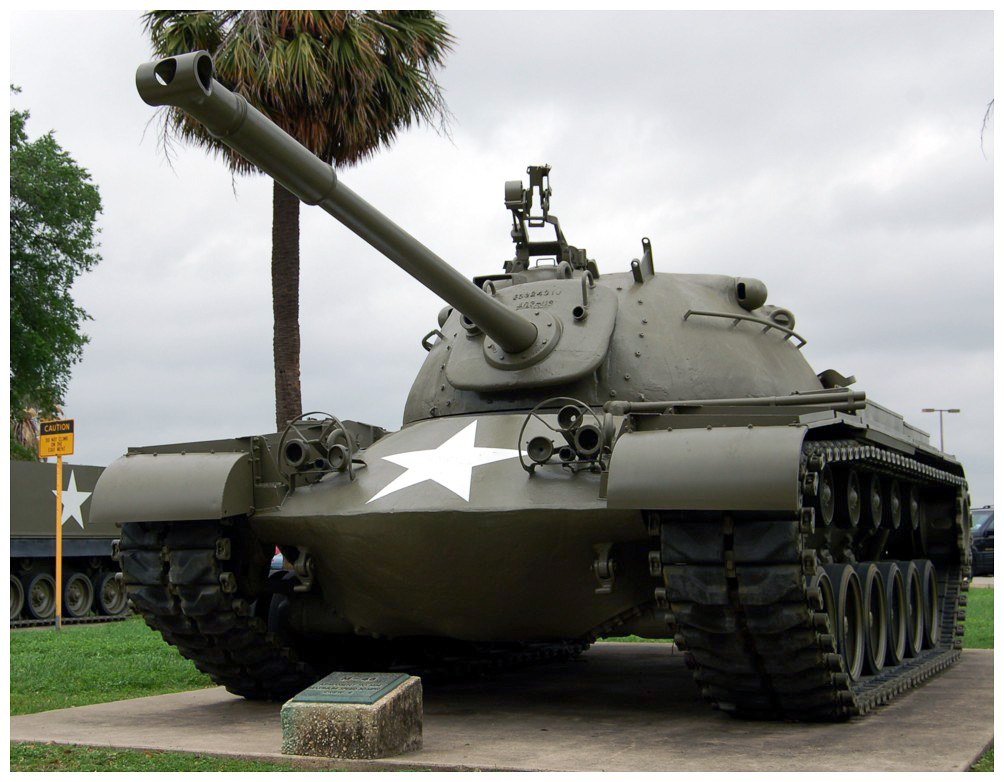

The M48 Patton, produced from 1952 to 1959, was a main battle tank equipped with a 90mm gun and a Continental AVDS-1790-2 V12 diesel engine. While it served effectively during the early Cold War, it was eventually superseded by the more advanced M60 Patton. The M48’s armor and firepower became inadequate against newer threats, and its phased retirement was inevitable as more modern tanks were developed.
SEPECAT Jaguar
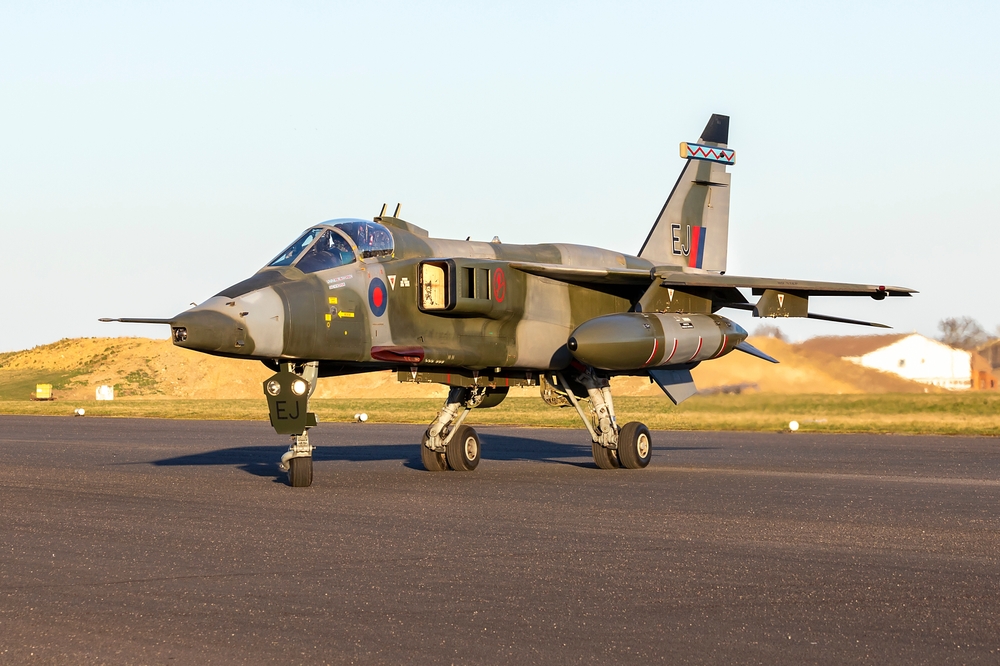

The SEPECAT Jaguar, introduced in the 1970s, was an Anglo-French ground-attack aircraft powered by twin Rolls-Royce Turbomeca Adour engines. It was known for its robust design and ability to operate from rough airstrips. However, advancements in aircraft technology and the need for multi-role capabilities led to its retirement in favor of more modern aircraft like the Eurofighter Typhoon and Dassault Rafale. The Jaguar’s aging avionics and airframe couldn’t compete with newer generations of fighters.
M114 Armored Fighting Vehicle
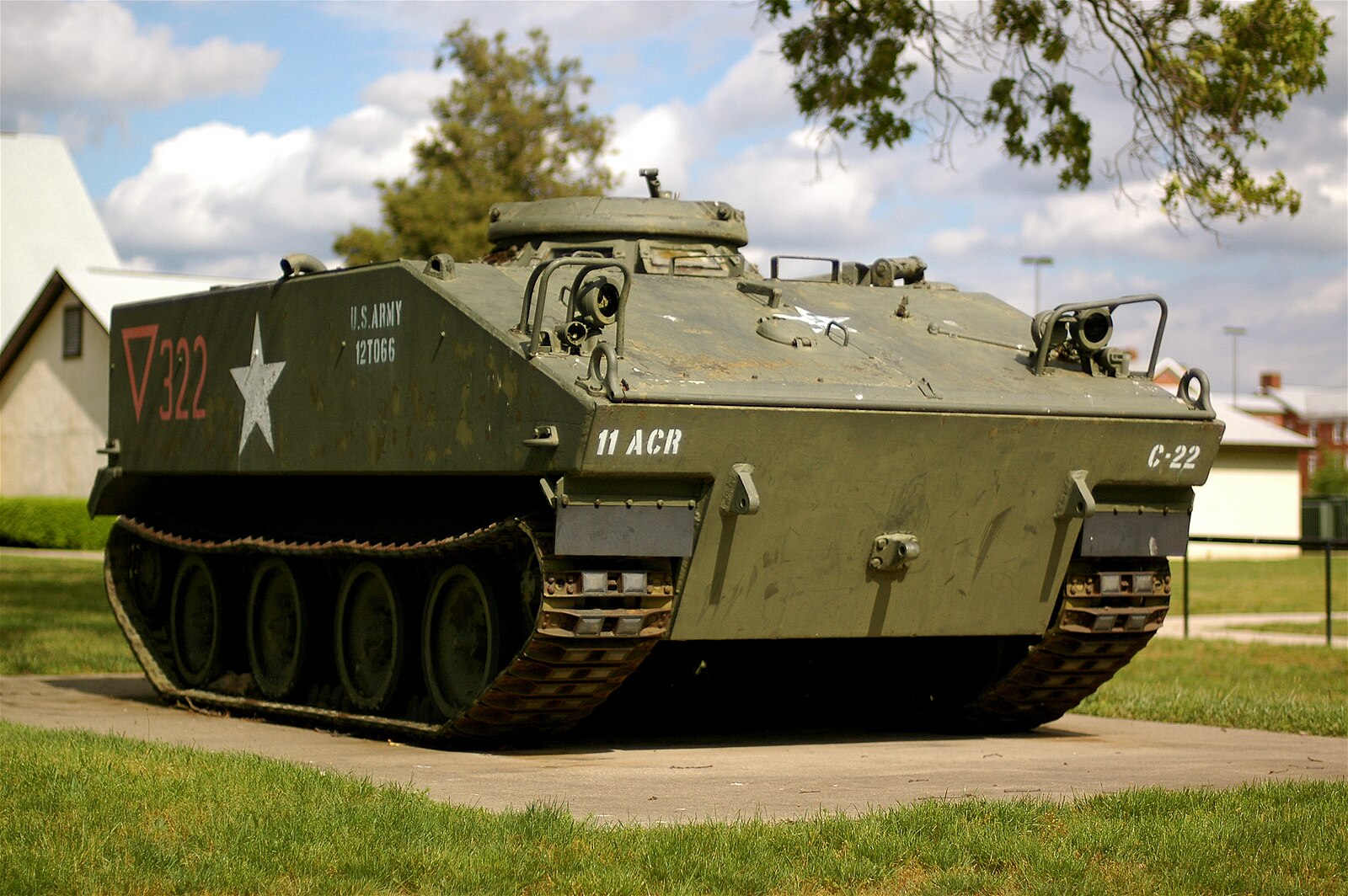

The M114, produced in the 1960s, was a light armored reconnaissance vehicle intended to complement the M113. It featured an aluminum hull and a Chevrolet 283 V8 gasoline engine. The M114 faced numerous reliability and performance issues, including poor cross-country mobility and vulnerability to small arms fire. It was eventually phased out in favor of more capable vehicles like the M3 Bradley.
F-111 Aardvark
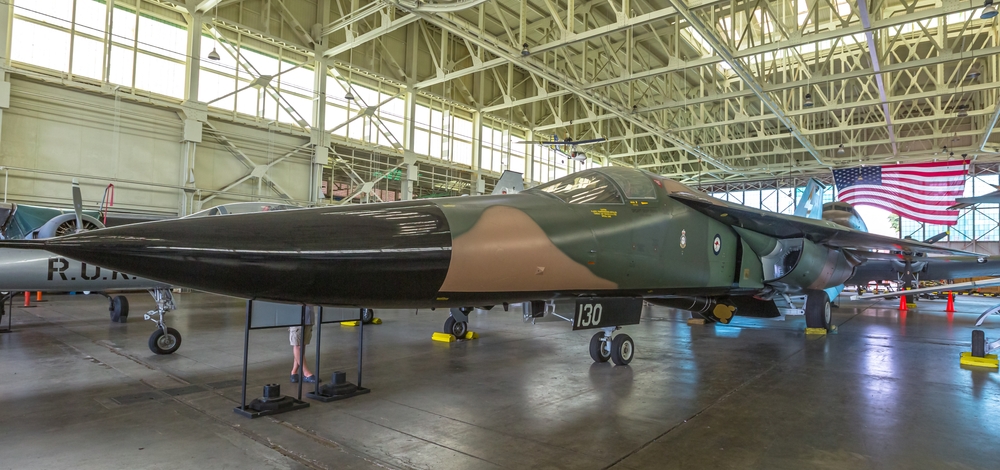

The General Dynamics F-111 Aardvark, introduced in the 1960s, was a multipurpose tactical fighter-bomber equipped with variable-sweep wings and advanced avionics. Despite its innovative design and capabilities, the F-111 faced numerous technical challenges and high maintenance costs. It was retired in favor of more versatile and cost-effective aircraft like the F-15E Strike Eagle and F/A-18 Hornet, which offered better performance and reliability.
M247 Sergeant York
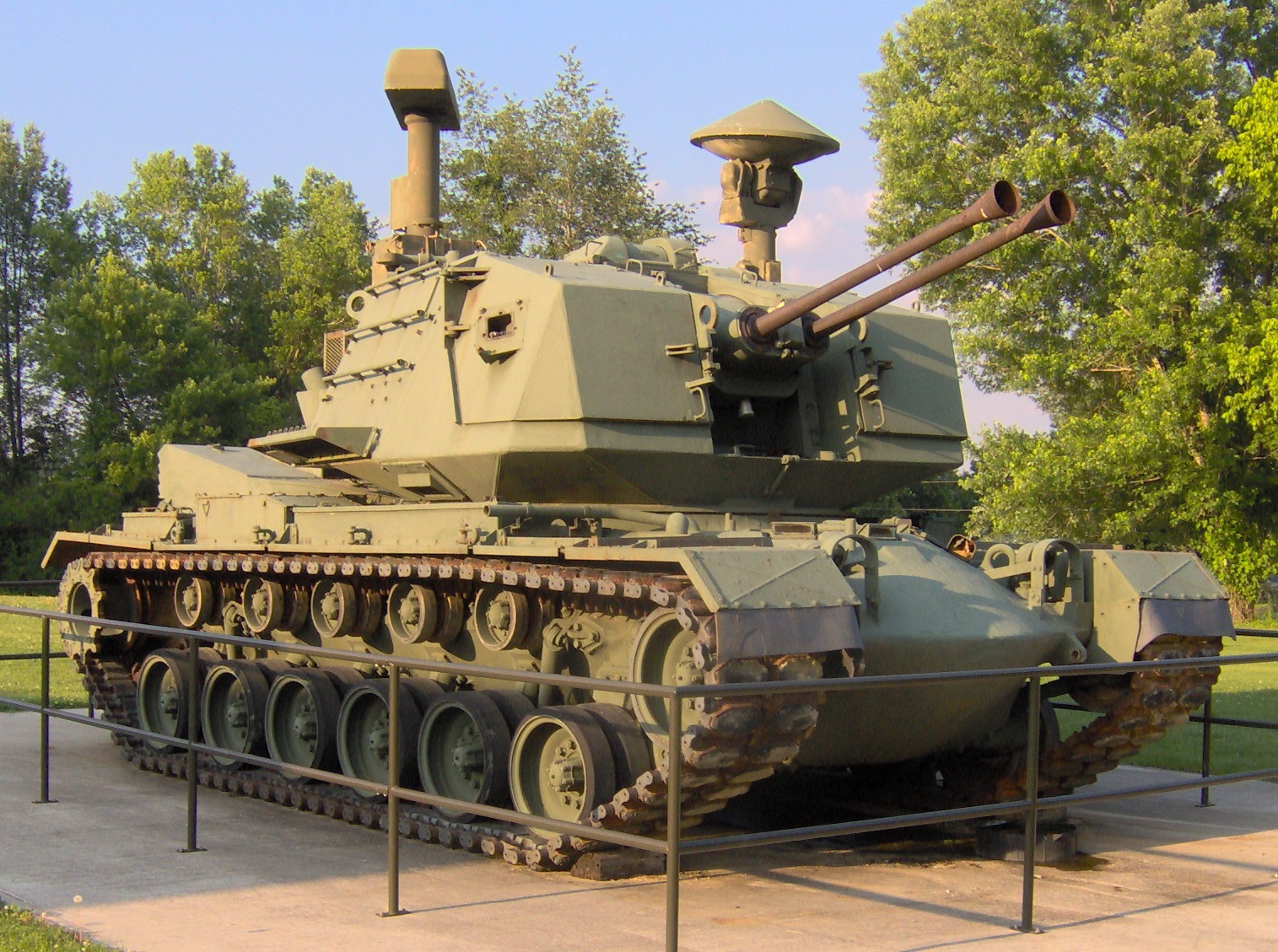

The M247 Sergeant York, developed in the late 1970s and early 1980s, was an anti-aircraft tank based on the M48 Patton chassis. It featured twin 40mm Bofors cannons and advanced radar systems. However, the M247 faced significant performance issues during testing, including difficulties in targeting low-flying aircraft. The project was eventually canceled, and the M247 never entered full production, as it couldn’t meet the operational requirements of the U.S. Army.
M1 240mm Howitzer
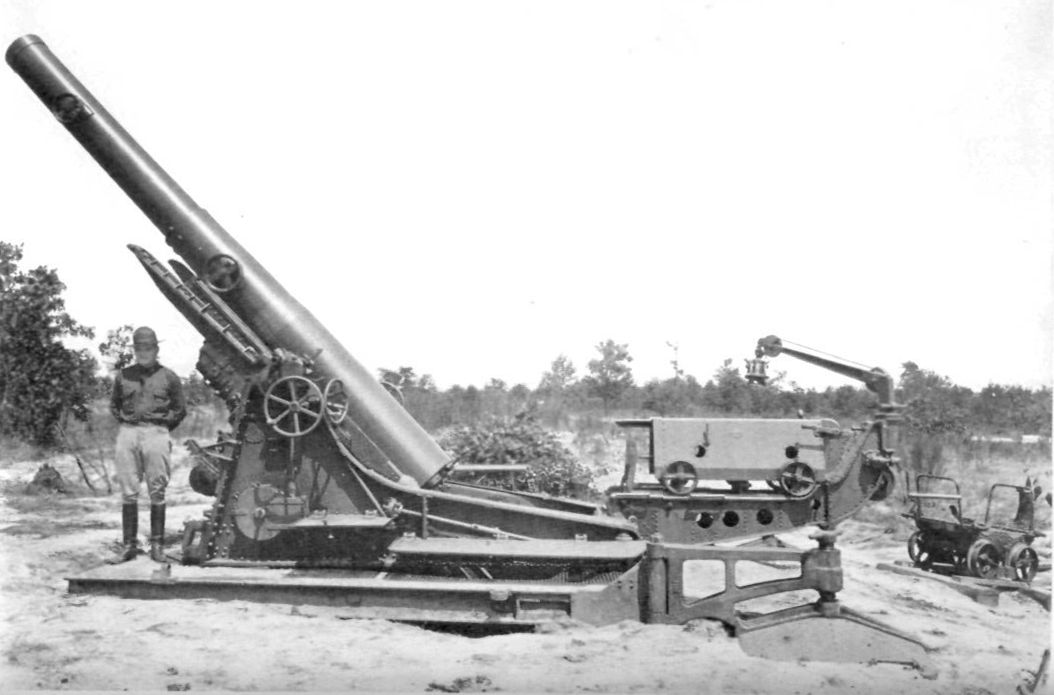

The M1 240mm Howitzer, introduced during World War II, was a powerful artillery piece capable of delivering massive firepower. Despite its effectiveness, the howitzer was extremely heavy and difficult to transport and deploy. Advances in artillery technology and the development of more mobile and versatile systems led to the M1’s retirement. Modern artillery systems offer better range, accuracy, and ease of use.
Lockheed C-141 Starlifter
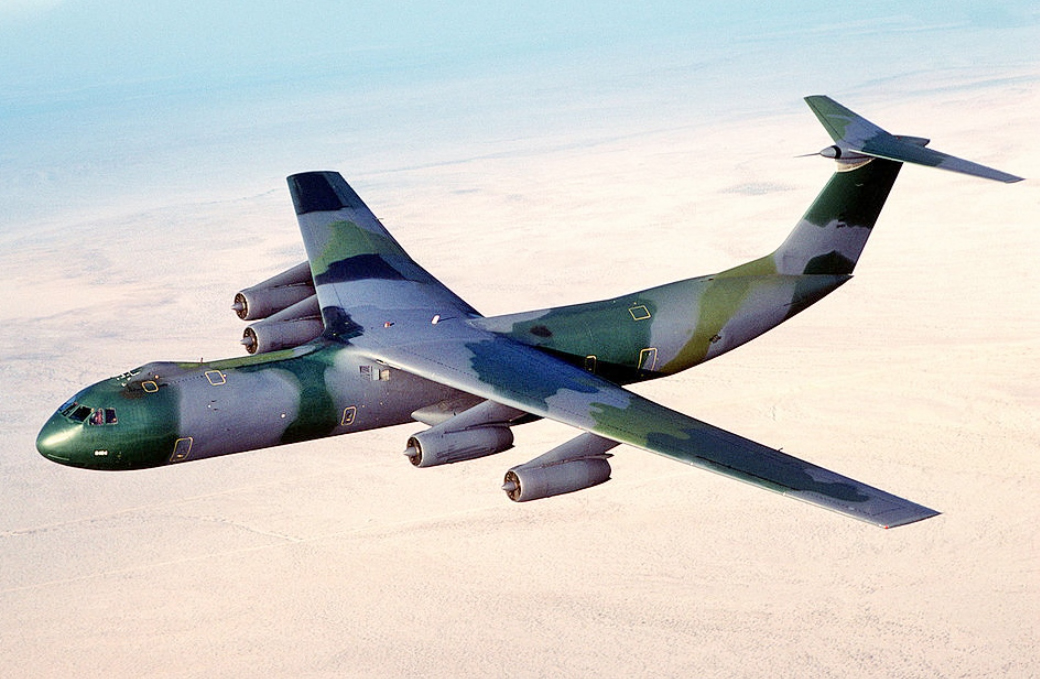

The Lockheed C-141 Starlifter, introduced in the 1960s, was a strategic airlift aircraft used by the U.S. Air Force. It featured four TF33 turbofan engines and could carry a wide range of cargo and troops. The C-141 was eventually replaced by the more advanced C-17 Globemaster III, which offered greater payload capacity, range, and modern avionics. The Starlifter’s aging airframe and limitations in cargo capacity led to its retirement.
M101 Howitzer
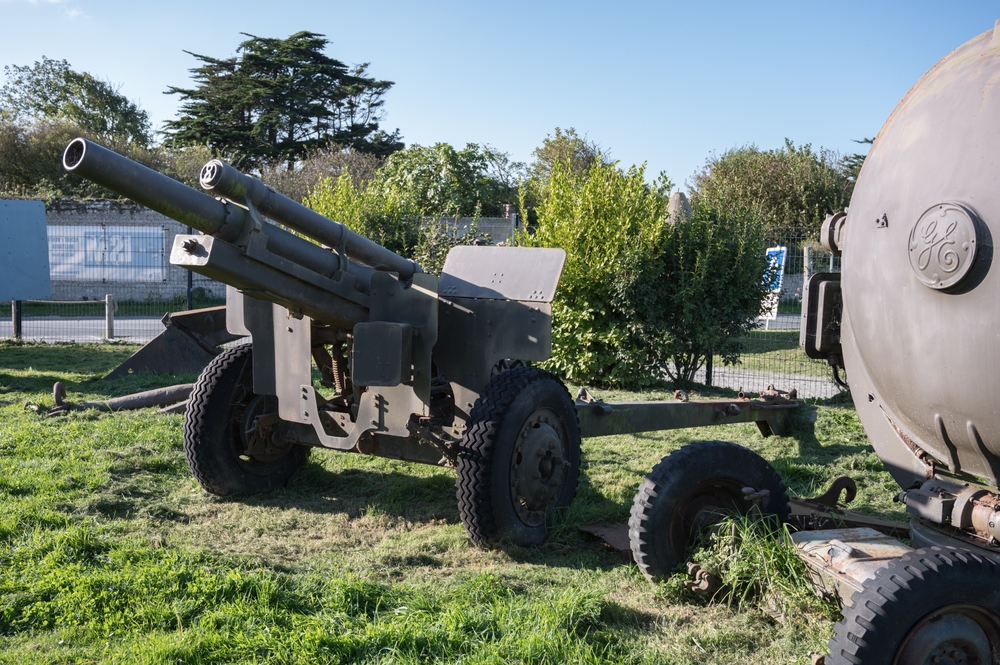

The M101 105mm Howitzer, introduced during World War II, was a highly effective and versatile artillery piece used by the U.S. military and allied forces. Despite its reliability and effectiveness, the M101 was eventually replaced by more modern artillery systems like the M119 and M777 howitzers, which offer greater range, accuracy, and mobility. The M101’s older design and limitations in range made it less suitable for modern warfare.
Lockheed P-3 Orion
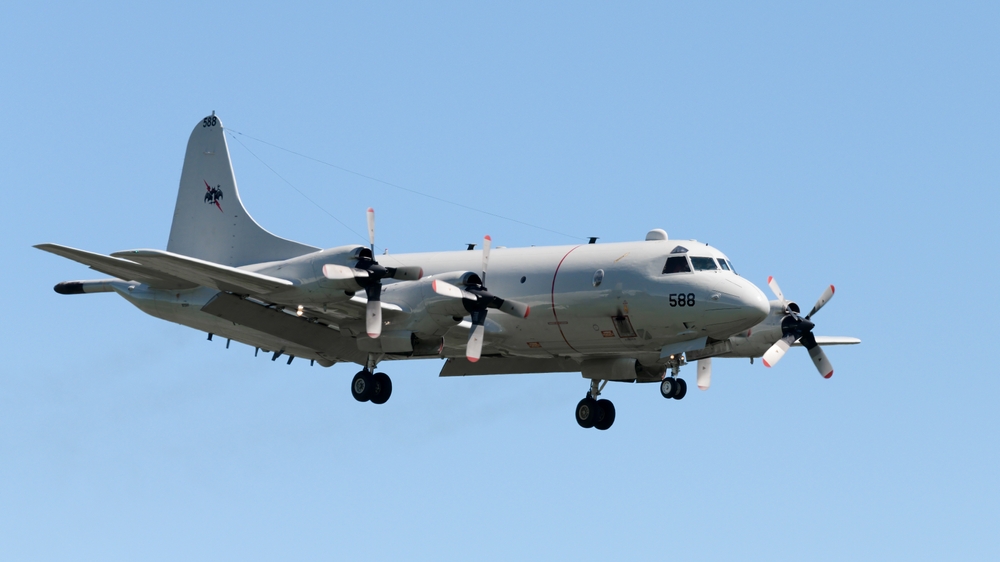

The Lockheed P-3 Orion, introduced in the 1960s, was a long-range maritime patrol aircraft used by the U.S. Navy and other countries. It featured four Allison T56 turboprop engines and advanced anti-submarine warfare (ASW) capabilities. The P-3 Orion has been gradually replaced by the more advanced Boeing P-8 Poseidon, which offers superior range, speed, and modern avionics. The P-3’s aging airframe and limited capabilities compared to the P-8 led to its decline in demand.
This article originally appeared on MyCarMakesNoise.
More from MyCarMakesNoise
18 Underrated Motorcycles with Surprising Performance

When it comes to motorcycles, some of the best rides often fly under the radar. In this list, we’re highlighting 18 underrated motorcycles with surprising performance that deserve more recognition. Read More.
15 Compelling Reasons to Postpone Your Electric Car Purchase

Thinking about making the switch to an electric car? While the idea is exciting, there are a few important factors to consider before making the leap. In this article, we’ll explore 15 compelling reasons why you might want to hold off on purchasing an electric vehicle just yet. Read More.
20 Elusive Muscle Cars You’ll Only See in Your Dreams

Muscle cars are the epitome of American automotive power and style, capturing the hearts of enthusiasts and collectors alike. In this article, we explore the rarest and most coveted muscle cars ever made. Read More.