The intake manifold is a component of any vehicle with an internal combustion engine that sits on top of the car’s engine and plays a critical role in the combustion process.
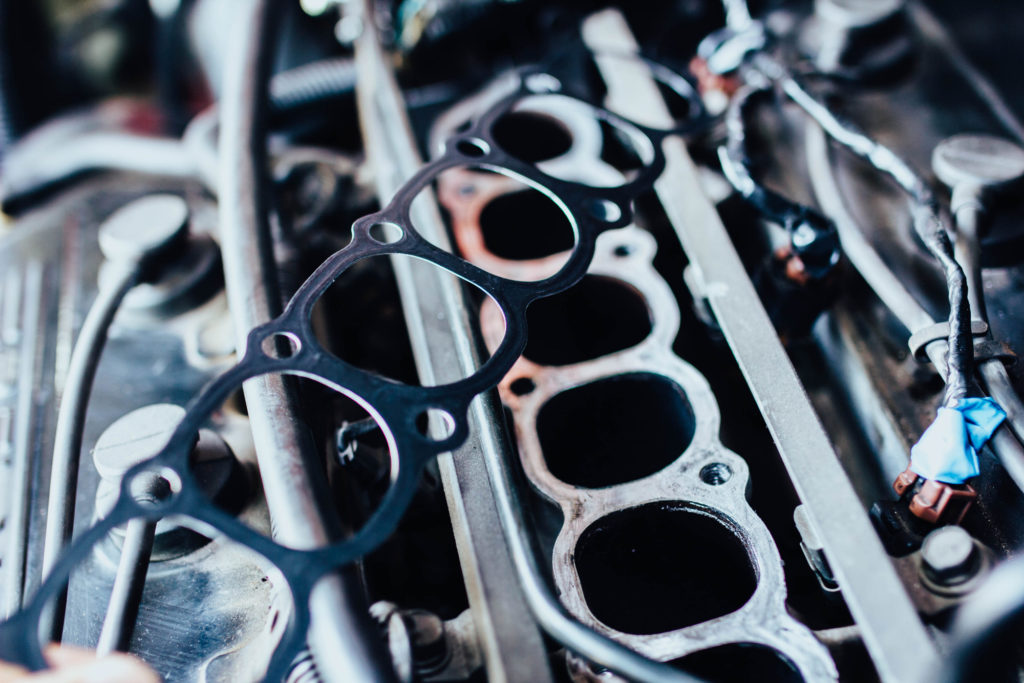

While the intake manifold usually is pretty durable, the intake manifold gasket seals connecting the manifold to the cylinder heads are prone to failure.
However, how can you determine whether you have an intake manifold gasket leak? More so, how much will the repair cost?
Contents
What is an intake manifold gasket?
The intake manifold gasket completely seals the space between the manifold and the engine, preventing air, coolant, and oil leakages. In combination with the throttle body, air intake, and fuel delivery system, it aids in delivering the appropriate air-fuel mix to the engine’s combustion chamber.
Its primary function is to prevent air from seeping out, which may lower the car’s efficiency. The intake manifold gasket is subjected to significant wear and tear over time, and it may eventually break or distort in ways that allow for leakage.
Where is the intake manifold gasket located?
The intake manifold gasket is positioned between the bottom of the intake manifold and the top of the engine block, providing a leak- and vibration-proof, flexible way of joining the two different metallic surfaces. Numerous manufacturers construct multi-piece intake manifolds by including extra gaskets between the plenum and runners or between the upper and lower portions.
Upper intake manifold gasket
The upper intake manifold gaskets are essential for sealing the manifold and preventing the system from receiving excessive air. When the gasket fails to perform its function, the cylinders will get an incorrect quantity of air, disrupting the fuel-air ratio.
Lower intake manifold gasket
The Lower Intake Manifold is positioned under the Upper Intake Manifold, between and above the two cylinder heads. It houses the fuel rail and has apertures that enable injected gas to reach the combustion chamber through the cylinder heads. Additionally, it serves as a mount for the top timing belt idler pulley and stud.
What causes the intake manifold gasket to go bad?
Excessive heat
A faulty intake manifold gasket is often caused by excessive heat. When the engine in your car overheats, the cylinder head expands, pressing the gasket, which no longer provides a strong seal as the metal expands.
Check the engine oil to ensure that coolant is not leaking into the engine oil if your vehicle has had significant and persistent overheating issues, your coolant levels continue to plummet, and you cannot identify the leak.
Age
Intake manifold gaskets are not made to last forever. For example, in an older vehicle, the intake manifold gasket may well have deteriorated due to age and exposure to the engine fluids.
With poorly designed and bad quality original manufactured gaskets, some engines are more likely to fail. Plastic intake manifold gaskets are especially prone to failure over time.
Vacuum Leak
Simple vacuum leaks caused by a defective intake manifold gasket happen less frequently than coolant leaks than you’d expect. However, the intake manifold gasket might be cracked, resulting in either too much or too little air entering the intake manifold gasket and blending with the gas. As a result, your car will perform badly.
Symptoms of bad intake manifold gasket
The most common symptoms are as follows:
Coolant leaks
If a gasket or manifold is compromised, coolant will ultimately leak underneath the car. This will typically be different and more noticeable than the condensation beneath the vehicle during the summer when the air conditioner is operating. You should treat coolant leaks immediately to avoid becoming a more significant problem.
Overheating engine
Overheating the engine is a symptom of the coolant leak. If a bad intake manifold gasket results in a coolant leak from inside, the coolant will enter the intake manifold. Because of this, your engine will eventually overheat.
While a defective intake manifold gasket will provide immediate symptoms, there are times when a leak is challenging to notice. However, if your engine overheats, you will be notified through your dashboard.
Reduction in fuel economy
Due to an air leak, the car’s computer may attempt to balance the equation by supplying more gasoline. This implies the engine consumes more fuel to do the same task. You’ll spend more money on fuel if you drive the same amount as you regularly do. As a consequence, your vehicle’s fuel efficiency will be significantly reduced.
Engine misfires, and power and acceleration drop
Engine performance troubles are one of the most prevalent signs of an intake manifold gasket issue. The intake manifold gaskets can wear out and leak as the car accumulates miles. This may significantly affect performance since the intake manifold gaskets seal the engine’s vacuum and pressure.
An exhaust leak produced by a faulty intake manifold gasket may skew the engine’s air-fuel ratio and result in engine performance problems such as misfires, decreased power and acceleration, and even stalling.
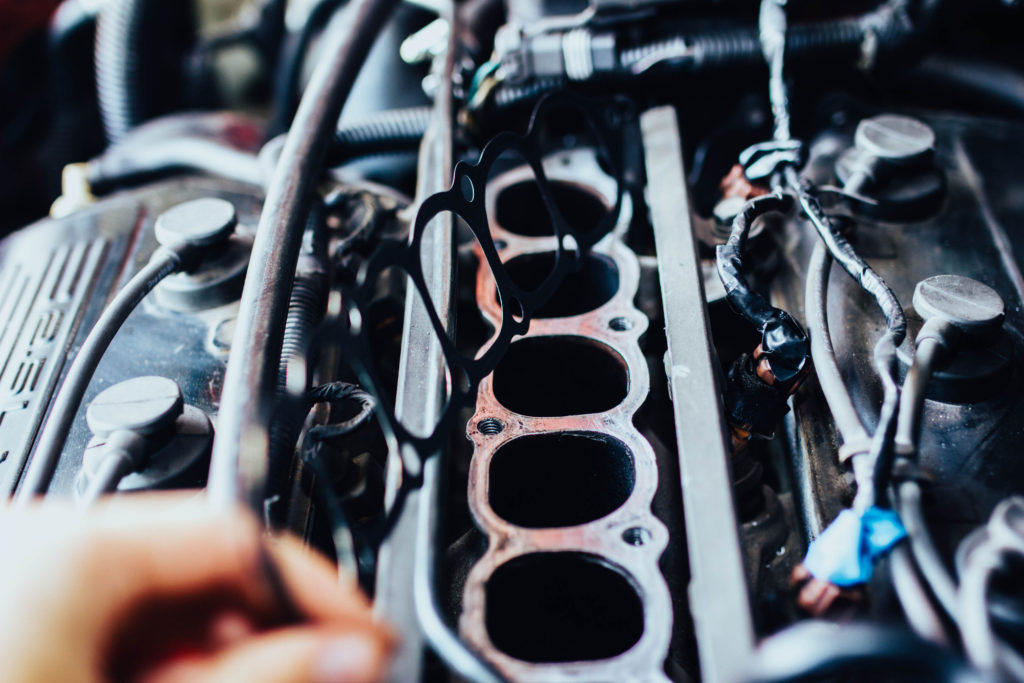
How to check the intake manifold gasket
Checking for a failing gasket that draws in the air or expels coolant outside the intake manifold might be more straightforward than identifying an interior leak. Take the following steps to diagnose an internal leak:
- Visually check the intake manifold where it connects to the cylinder heads and throttle body.
- Reach around blind spots you can’t see clearly, then inspect with your hand, feeling for moist patches. If required, use a telescopic mirror. Keep an ear out for hissing noises.
- Trace the space between the intake manifold and the cylinder head and where it attaches to the throttle body with a length of rubber tubing. Place one end of the hose on your ear and sketch the sealing areas with the other.
- A pronounced hissing sound emanating from the gasket parts indicates a leaking gasket.
- Spray starter fluid around the gasket region. A shift in idle speed, or a transition from a rough to a smooth idle, indicates the presence of a leaky area.
How to replace a leaking intake manifold gasket
Replacing an intake manifold gasket should be done by a certified mechanic. It is quite an intricate process that takes place when replacing the part.
Draining the coolant
The engine cover is removed while the engine is still cool, and if the intake manifold has internal cooling system channels, the coolant is drained to a level below those passageways.
- When the engine is cool, the cover is removed, and if the intake manifold has internal cooling system channels, the coolant is drained to a level below those passageways.
- Both the accelerator cable assembly and cruise control cable are removed before the electrical connections, exhaust and vacuum lines, are disconnected.
- The ignition parts, such as the coil, are removed as required.
- If the vehicle has an upper plenum, it is removed and stored separately.
- When the fuel rail is secured to the intake manifold, the supply and return lines of the fuel rail are separated.
- Once everything has been disconnected from the manifold, the next step is to unbolt and remove the manifold from the engine.
- Manifolds made from aluminum and plastic are flattened to ensure they meet the original equipment manufacturer’s specifications. If the manifold surface is not entirely smooth, the new gasket will not seal properly. On plastic manifolds, cracks, heat damage, and warpage are examined.
- Your mechanic will determine if the manifold can be reused or in need of repair or replacement.
- The new gasket is placed, the manifold is positioned, and the mounting bolts are torqued and calibrated. In some instances, RTV sealant must be applied to difficult-to-seal portions or corners of the mounting surface, as specified in the service manual.
- After removing all components, they are reinstalled in the reverse sequence of the previous phases.
- The final step is to get the car started and check if the leaks have stopped.
Intake gasket replacement cost
A new intake manifold gasket costs between $190 and $540. Labor will cost between $170 and $420. The gasket itself is rather affordable, costing between $20 to $120.